Language and Culture. The Major Languages of the World
We noted in Chapter 2 that culture is the set of shared behaviors, values, and institutions common to a group of individuals. Language structures the process of communication, which in turn is essential to the development and preservation of culture.
A language is a collection of sounds and symbols whose meanings are commonly understood by its speakers. In order to communicate, speakers and listeners must understand the same language. In other words, both the speaker and the listener must recognize and accept common relationships between sounds and symbols and their meanings.
Language provides a means by which members of a culture can develop shared identity. The ability to speak in a particular language provides a person access to the histories and traditions associated with its culture. Throughout the world, people are concerned that their language and cultural traditions be taught to their children so that their cultural heritage will be passed on to succeeding generations. Political conflict often results when members of a particular culture are prohibited from using their language or providing education in that language to their offspring.
The Major Languages of the World.Several thousand languages are spoken throughout thecontemporary world. Some are spoken by only a smallnumber of individuals and restricted to very small areas.Others are spoken by large numbers of people spreadacross wide areas.
Twelve languages are spoken by at least 100 million people (table 4-1). Some of these twelve major languages are spoken in many different countries. English is the major language of the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom. Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, and many other countries. Spanish is spoken not only in Spain, but throughout much of Latin America. Arabic is prevalent throughout Southwest Asia and North Africa. Other languages, such as Hindi and Bengali, are confined primarily to a single country.
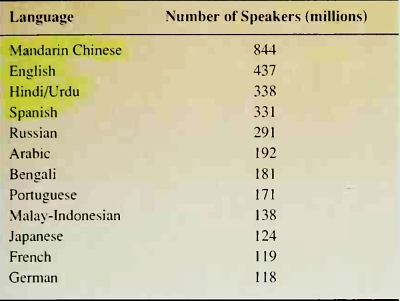
Table 4-1. Major Languages of the World
Six of the twelve major languages—English, French, Spanish. Russian, Mandarin Chinese and Arabic—are the official languages of the United Nations (figure 4-1). All official U.N. business must be conducted in one of these languages. Why were these particular languages chosen as the official languages of the United Nations? As World War II drew to a close, the victorious Allied powers began to lay the groundwork for the formation of an international peace-keeping organization.

The United Nations Headquarters. Six official languages and dozens of other national languages are spoken by delegates to the United Nations. The activities of the United Nations illustrate the importance of language in international communication
The United Nations Charter specified that five Allies—the United States, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, France, and China—would serve as permanent members of the Security Council. Thus, English, Russian, French, and Mandarin Chinese became official languages of the United Nations. Spanish, meanwhile, was the language of the independent Latin American countries (excluding Brazil) that were charter members of the United Nations. Arabic was added to the list of official languages later, in recognition of its importance in a large number of countries from Morocco to Iraq and Saudi Arabia.
Date added: 2023-01-14; views: 794;
