Data Security. Introduction
The term data security refers to the protection of information against possible violations that can compromise its secrecy (or confidentiality), integrity, or availability. Secrecy is compromised if information is disclosed to users not authorized to access it. Integrity is compromised if information is improperly modified, deleted, or tampered. Availability is compromised if users are prevented from accessing data for which they have the necessary permissions. This last problem is also known as denial-of-service.
The problem of protecting information has existed since information has been managed. However, as technology advances and information management systems become more and more powerful, the problem ofenforcing information security also becomes more critical.
The increasing development of information technology in the past few years, which has led to the widespread use of computer systems to store and manipulate information and greatly increased the availability and the processing and storage power of information systems, has also posed new serious security threats and increased the potential damage that violations may cause.
Organizations more than ever today depend on the information they manage. A violation to the security of the information may jeopardize the whole system working and cause serious damages. Hospitals, banks, public administrations, and private organizations, all of them depend on the accuracy, availability, and confidentiality of the information they manage.
Just imagine what could happen, for instance, if a patient’s data were improperly modified, were not available to the doctors because of a violation blocking access to the resources, or were disclosed to the public domain.
Many are the threats to security to which information is exposed. Threats can be nonfraudulent or fraudulent. The first category comprises all threats resulting in nonintentional violations, such as natural disasters, errors or bugs in hardware or software, and human errors. The second category comprises all threats causing intentional violations.
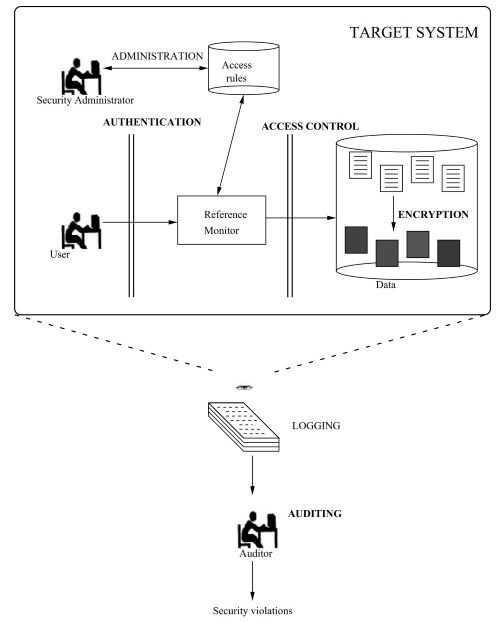
Figure 1. Authentication, access control, audit, and encryption
Such threats can be represented by authorized users (insiders), who can misuse their privileges and authority, or external users (intruders), who can improperly get access to the system and its resources. Ensuring protection against these threats requires the application of different protection measures. This article focuses, in particular, on the protection of information against possible violations by users, insiders, or intruders. The following services are crucial to the protection of data within this context (1):
1. Identification and Authentication. It provides the system with the ability of identifying its users and confirming their identity.
2. Access Control. It evaluates access requests to the resources by the authenticated users, and based on some access rules, it determines whether they must be granted or denied.
3. Audit. It provides a post facto evaluation of the requests and the accesses occurred to determine whether violations have occurred or have been attempted.
4. Encryption. It ensures that any data stored in the system or is sent over the network can be deciphered only by the intended recipient. In network communication, it can also be used to ensure the authenticity of the information transmitted and of the parties involved in the communication.
Figure 1 illustrates the position of these services within the system working. Their treatment is the focus of this article.
Date added: 2024-07-23; views: 447;
