Database Search Engine
In comparison with document search engines, database search engines are much easier to build because they do not need crawlers to crawl the Web to build the index database. Instead, traditional database systems such as Oracle or SQL-server are usually used by database search engines to store and manage data.
The stored data are often compiled and entered by human users. Unlike Web pages that have little structure, the data in database search engines are generally well structured. For example, the database of an online Web bookstore contains various books, and every book has attributes such as title, author, ISBN, publication date, and so on.
To make the data in a database search engine Web- accessible, an HTML form-based Web search interface like Fig. 2 is created on top of the underlying database system. The Web search interface often has multiple fields for users to specify queries that are more complex than the keywords queries for document Web search engines.
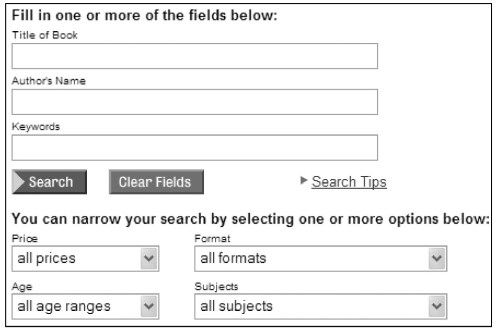
Figure 2. The book search interface of bn.com.engine
For example, the search interface of bn.com (Fig. 2) contains fields like title, author, price, format, and so on. A user query submitted through the Web search interface of a database search engine is usually converted to a database query (e.g., SQL) that can be processed by the underlying database system; after the results that satisfy the query conditions are returned by the database system, they are wrapped by appropriate HTML tags and presented to the user on the dynamically generated Web page.
Database search engines are often used by organizations or companies that want to publish their compiled data on the Web for information sharing or business benefits. For example, a real estate company may employ a database search engine to post housing information, and an airline may use a database search engine to allow travelers to search and purchase airplane tickets.
It should be noted that structured data that are stored in database systems and are accessible via database search engines constitute a major portion of the Deep Web. A recent survey estimated that, by April 2004, among the 450,000 search engines for the Deep Web, 348,000 were database search engines.
Date added: 2024-07-23; views: 456;
