The Geographical Position of the State of Bangladesh. Government of the Country
Bangladesh, is a South Asian nation that once formed part of Pakistan. Bangladesh gained independence in 1971 after a nine-month civil war between East Pakistan and West Pakistan. From 1947 to 1971, the region that is now Bangladesh was East Pakistan. More than half the people of Pakistan lived there.
The northeast part of India borders Bangladesh on three sides. Bangladesh shares many cultural and geographical features with nearby West Bengal, which is a state of India. Bangladesh and West Bengal form a region that is known as Bengal. Bangladesh is sometimes called East Bengal. The name Bangladesh means Bengal nation.
Bangladesh is one of the world's most densely populated countries. The nation's rapid population growth has led to serious overcrowding. The people of Bangladesh are called Bangladeshis. Dhaka, formerly spelled Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh.
Widespread poverty has long characterized the region. Most Bangladeshis are poor farmers who struggle to make a living on small plots of land. Many laborers in the cities work for about a dollar a day. Most of Bangladesh's adults cannot read or write. About 85 percent of the country's people are Muslims, and most of the rest are Hindus.
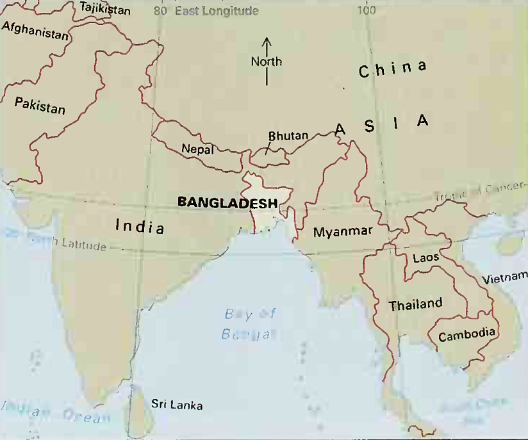
Bangladesh lies in southern Asia, north of the Bay of Bengal. It is bordered by India and Myanmar
Plant life thrives in the warm, humid climate of Bangladesh. Most of the country's land consists of a flat, fertile flood plain, and is crisscrossed by innumerable rivers and streams. The rivers deposit fertile soil along their banks during periodic floods. However, many of the floods also cause widespread destruction in Bangladesh's rural villages.
The region that now makes up Bangladesh has been governed by Hindu, Muslim, and Buddhist rulers at various times in its history. The British East India company became the leading power in the area in 1757. The region became part of the British Empire when Britain took control of India in 1858.
Bloody conflicts that occurred between Hindus and Muslims led to the division of India into two nations in 1947, when India gained independence. Pakistan—consisting of East Pakistan and West Pakistan—was created out of the northeastern and northwestern parts of India. The majority of the people living in both areas were Muslims.
Numerous differences, both cultural and economic, divided the peoples of East Pakistan and West Pakistan. In 1971, civil war led to the establishment of East Pakistan as an independent country—Bangladesh. For more detailed information on the events leading up to the creation of Bangladesh, see the History section of this article.

The Bangladesh flag was officially adopted in 1972. The red stands for the sun and the green for scenic beauty

National emblem. A water lily, the national flower of Bangladesh, appears in the center of the emblem
Government. National government. Bangladesh has a parliamentary system of government. A prime minister is the head of government and is chosen from the political party that wins the most seats in Parliament. Cabinet members are appointed by the prime minister to head departments that carry out the functions of the government. A president serves as head of state. The position of president is mainly ceremonial. The president is elected by Parliament to a five-year term.
The Parliament makes the country's laws. It has 330 members. The people elect 300 of the members to five year terms. The 30 other seats in Parliament are reserved for women, who are chosen by the elected members of Parliament for five-year terms.

The National Parliament Building in Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh, was completed in the early 1980's. It is part of a complex of government buildings
Local government. Villages are the smallest units of local government in Bangladesh. Villages are grouped together to form unions. These unions, in turn, form administrative units that are called thanas. A group of thanas forms a zilla (district), the largest unit of local government in Bangladesh. Governing councils at each level of local government consist of officials who are elected by the people.
Political parties. Bangladesh has many political parties. The three most important parties are the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP), the Jatiya Dal (National Party), and the Awami League. The Awami League gained control of Parliament after elections in June 1996. The BNP had held a majority of seats in Parliament before the June 1996 elections.
The Awami League led the fight for independence in Bangladesh. The league supports many socialist economic policies. The BNP and the Jatiya Dal parties have similar platforms. Both of them favor a free enterprise economic system.
Armed forces. During the civil war of 1971 , a guerrilla resistance army called the Mukti Bahini (Freedom Force) was formed in what was then East Pakistan. After the war, members of the Mukti Bahini became part of the regular army, navy, and air force of Bangladesh. The country also has a militia.
Date added: 2022-12-12; views: 941;
