Lifts for Offices, Banks, Hotels etc. and Hospital Bed Lift. Hydraulic Lifts
The building and its function dictate the basic type of lifts which need to be provided. They serve as a means of vertical transport for passengers and patients.
Lifts are mechanical installations which are required to have a long service life (anything from 25 to 40 years). They should therefore be planned in such a way that even after 10 years they are still capable of meeting the increased demand. Alterations to installations that have been badly or too-cheaply planned can be expensive or even completely impossible. During the planning stage the likely usage should be closely examined. Lift sets normally form part of the main stairwell.
Analysis of use: types and definitions. Turn-round time is a calculated value indicating the time which a lift requires to complete a cycle with a given type of traffic.
Average waiting time is the time between the button being pressed and the arrival of the lift car:
average waiting time (s) = cycle time (s) number of lifts/set
Transportation capacity is the maximum achievable carrying capacity (in passengers) within a five minute (300s) period:
transportation capacity = 300(s) x car load (passengers) cycle time (s) x no. of lifts
Transportation capacity expressed in percent:
transportation capacity (%) = 100 x transportation capacity number of occupants of building.
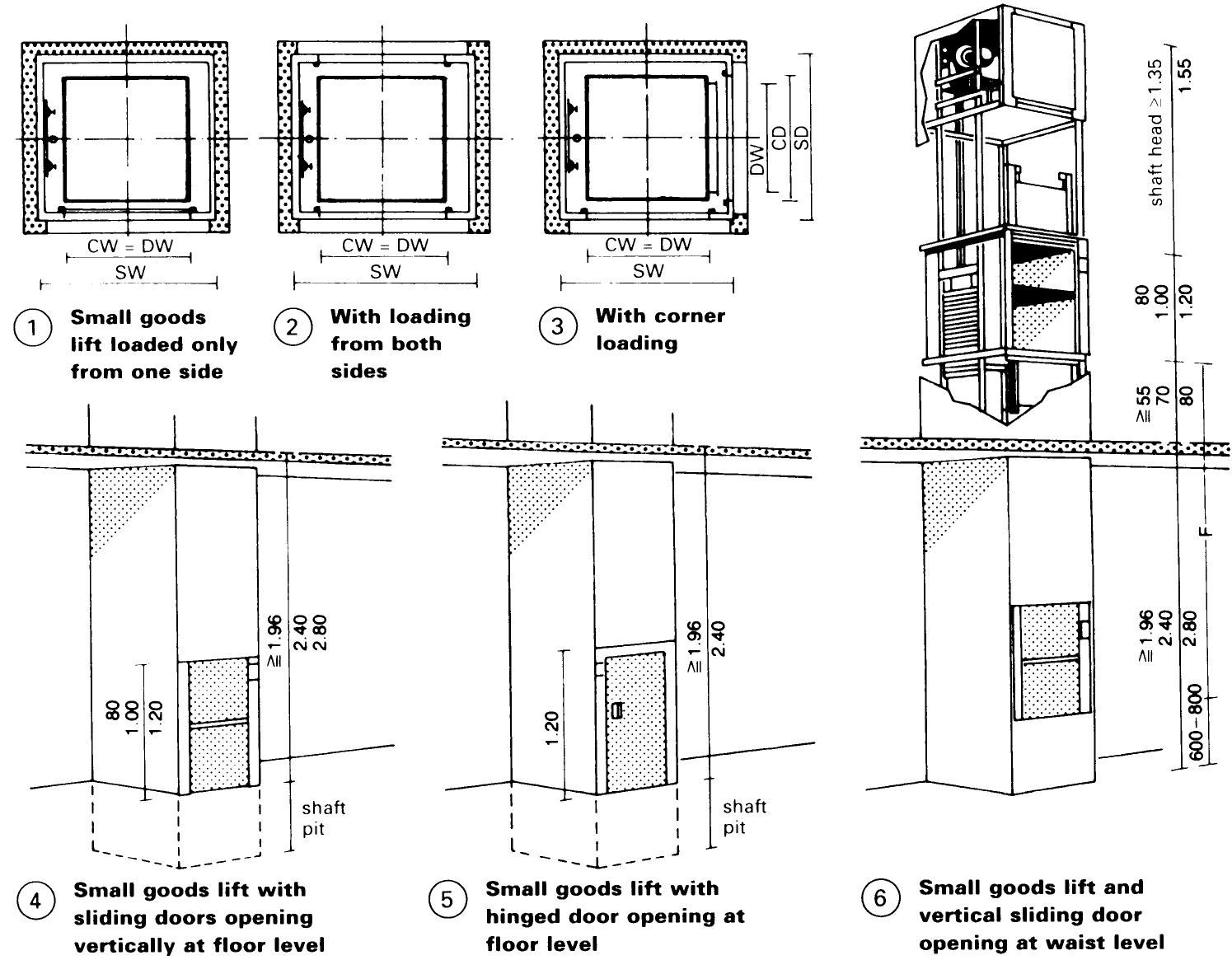
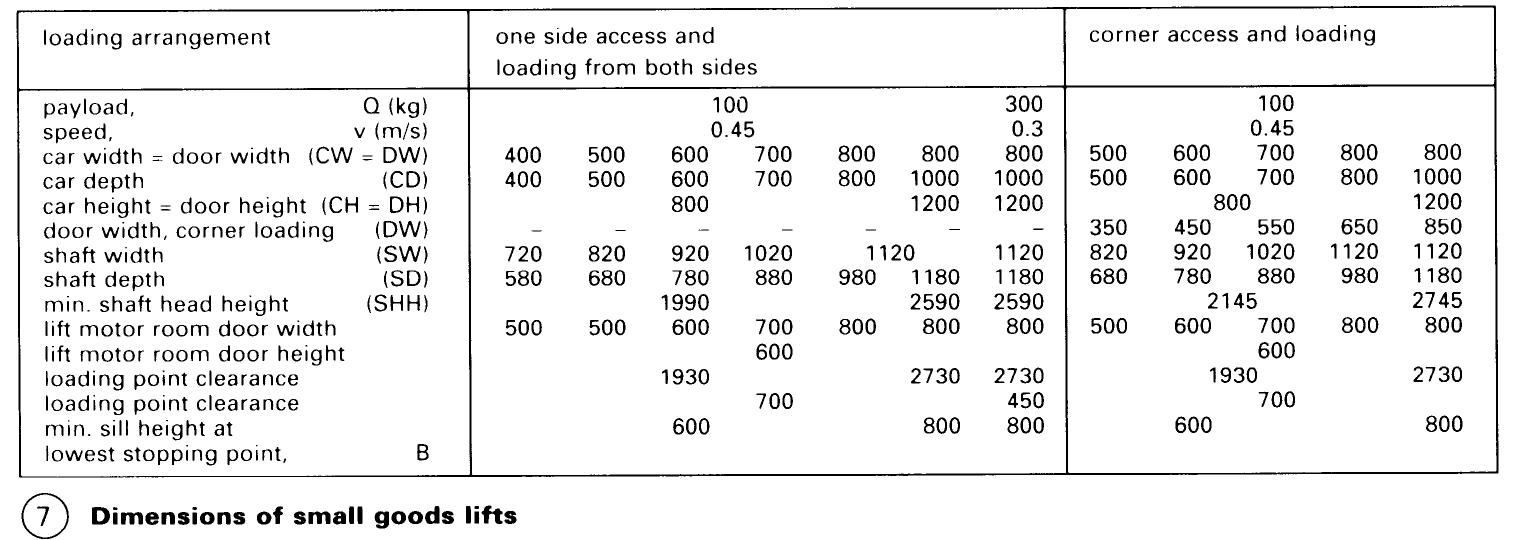
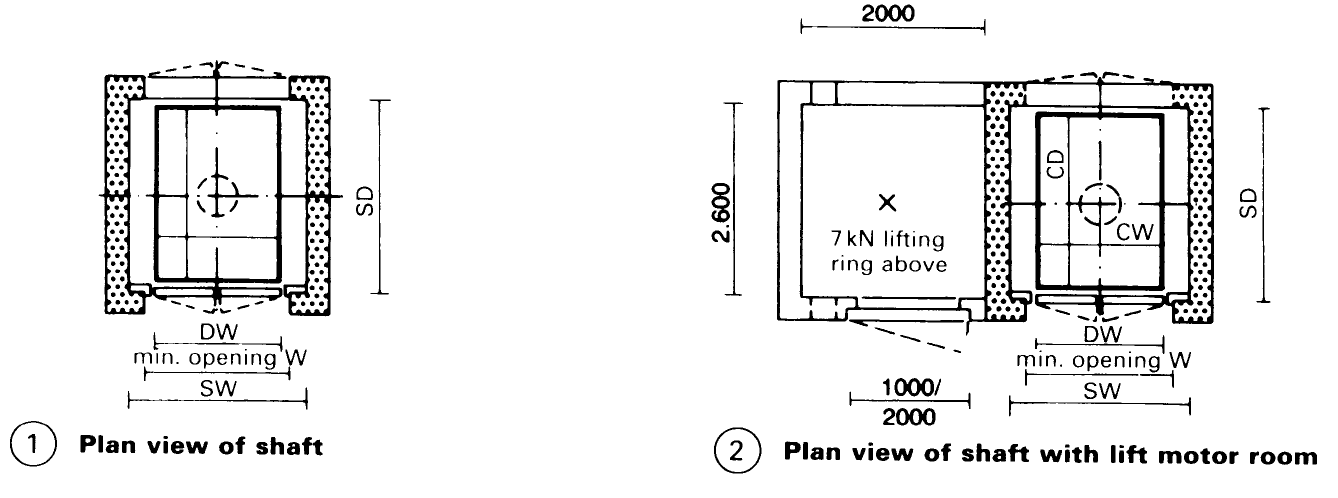
Small Goods Lifts. Small goods lifts: payload >300kg; car floor area <0.8m2; for transporting small goods, documents, food etc.; not for use by passengers. The shaft framework is normally made of steel sections set in the shaft pit or on the floor, and clad on all sides by nonflammable building materials. - (1) - (6) Dimensions and load-carrying capacity - (7).
The following formula is used to estimate the time, in seconds, of one transport cycle:

With single doors t2 = 6s; with double doors, 10s; with vertical sliding doors for small goods lifts, about 3s.
The maximum transportation capacity in kg/min can be found from the time for one transport cycle, Z, and the maximum load the lift can carry:
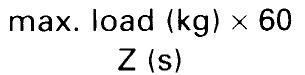
Under building regulations, the lift motor room must be lockable, have sufficient illumination and be of a size such that maintenance can be carried out safely. The height of the area for the lift motor must be >1.8m.
For food lifts in hospitals, the lift shafts must have washable smooth internal walls.
An external push-button control must be provided for calling and despatching the lift to/from each stopping point.
Larger goods lifts may be designed to convey goods and carry passengers employed by the operator of the installation.
Accuracy of stopping: for goods lifts without deceleration = ±20-40mm; for passenger and goods lifts with deceleration = ±10-30 mm
Speeds: 0.25, 0.4, 0.63 and 1.0 m/s.
Hydraulic Lifts. These meet the demand for transporting heavy loads economically up and down shorter lift heights and are best used for up to 12 m lift height. The lift motor room can be located remotely from the shaft itself.
Standard direct-acting piston lifts can be used to lift payloads of as much as 20t up to a maximum height of 17 m – (1) - (3), while standard indirect acting piston lifts can lift 7t up to 34m. The operating speed of hydraulic lifts is 0.2-0.8m/s. A roof mounted lift motor room is not required. Several variations in hydraulics can be found – (6) – (9). The most commonly used is the centrally mounted ram – (1) - (3).
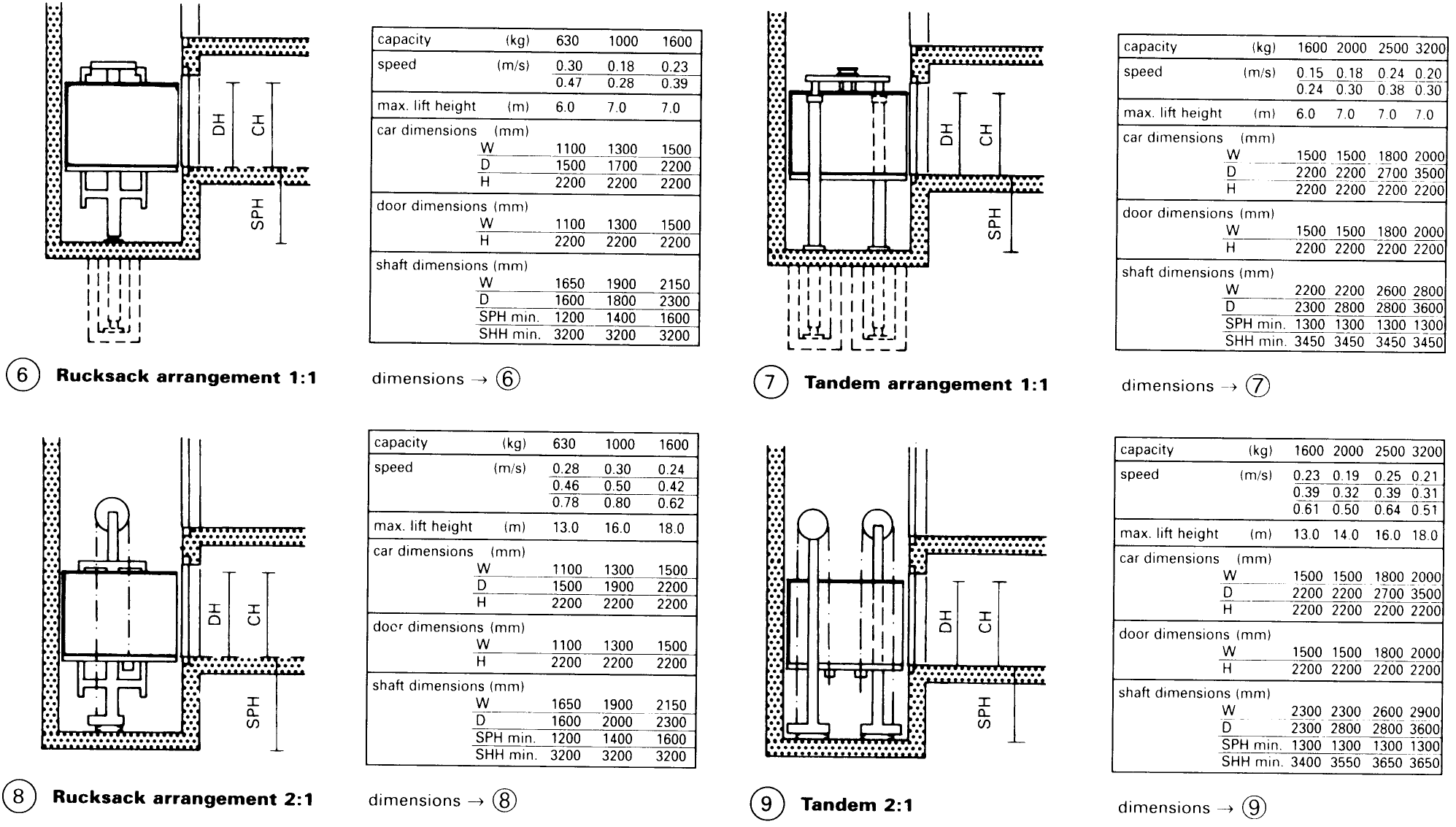
The ram retraction control tolerance, regardless of load, has to be kept within ±3mm, so that a completely level entry into the lift car is obtained. Height clearance of the lift doors should be 50-100mm. greater than other doors. Double swing doors or hinged sliding doors can be fitted - either hand-operated or fully automatic, with a central or side opening.
Date added: 2023-01-01; views: 702;
