Calculations: Building Technology. Calculations: Division of Space
The gross volume of space needed and the total construction cost mean that fully air- conditioned buildings are 1.3-1.5 times more expensive than nonair-conditioned buildings, i.e. those which are naturally ventilated – (1).
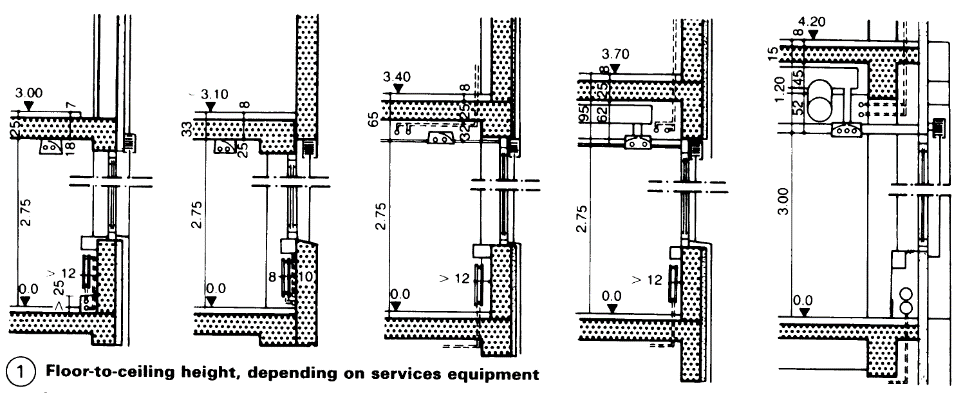
A ceiling height of 3.0-3.10m is suitable for buildings with little service equipment, no suspended ceilings and heating pipes on an exterior wall. Electric power should be supplied through ducts in window sills or floors, and the power supply for ceiling lights through conduits or partitions. Corridor areas should also be used for ducts and pipes.
A ceiling height of 3.4m is suitable for a building with some service equipment, but without ventilation equipment. Ducts under the floor in corridor areas (h = 32cm) should be used for heat, electricity and water.
A ceiling height of 3.70m is suitable for office buildings using ventilation equipment. A duct height of at least 50cm is needed for air-conditioned offices, with long ducts in the corridor area.
Open-plan offices need a clear ceiling height of only 3.00 m. However, the ceiling height should be 4.20m if ventilation ducts are to be installed. All height-related building components affect the cost of the building in relation to its usable office floor area.
Air-conditioning systems with capillary tube mats use water and the principle of localised cooling – (2) – (3). The air intake is equivalent to the minimum airchange rate. Comfortable cooling is achieved by radiant protection and displacement ventilation without turbulence (expanding- air ventilation). This creates a flow of fresh air (with outlets near the floor and at the base of furniture), a cushion of warm air at the ceiling, and an air flow through the room (5) caused by the temperature gradient (main surfaces 32°C at the ceiling, 20°C at each wall).
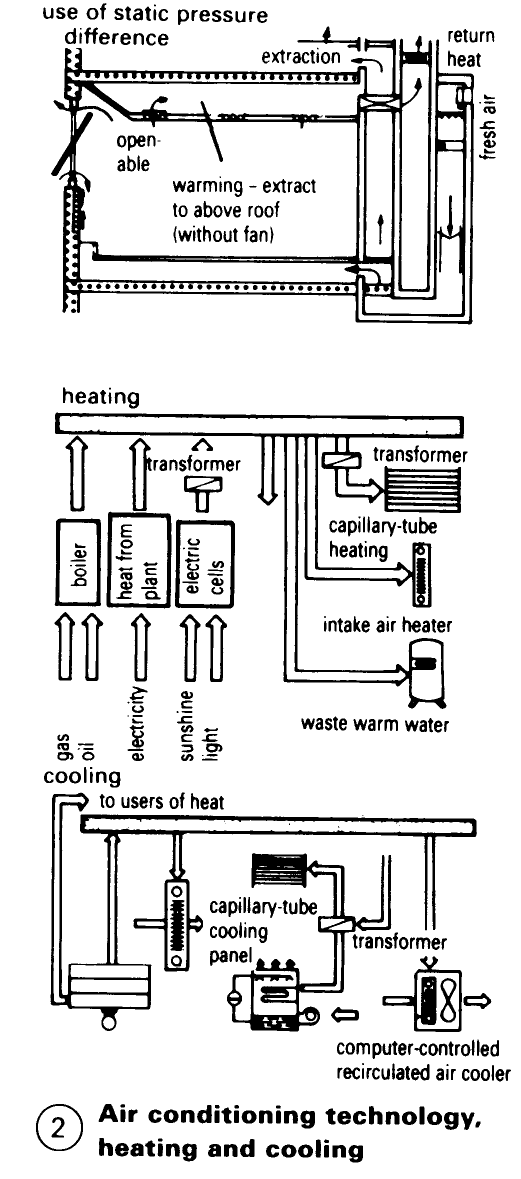
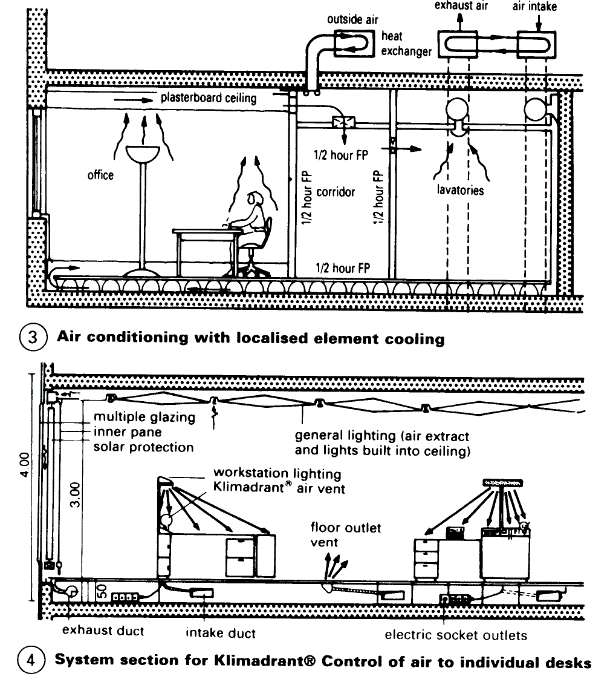
Radiant heating from panels in combination with an air intake system may be sufficient for heating -> (6). Such a system uses less equipment and thus increases the usable floor area. The cost of air conditioning with localised cooling compares favourably with the cost of conventional air conditioning. The advantages include no draughts, quiet, lower investment and operating costs (the volume of water that has to be conveyed is 1000 times less than the volume of air for a closed system with the same output and heat recovery), a reduction of the space required for services (water instead of air) and a smaller energy plant. Raised floors are required to achieve the necessary room ventilation and for installing services to areas with a large amount of equipment. There is an increased demand for space for services (cables, office automation), and a need to guarantee flexibility when functional processes change (7) + (8).
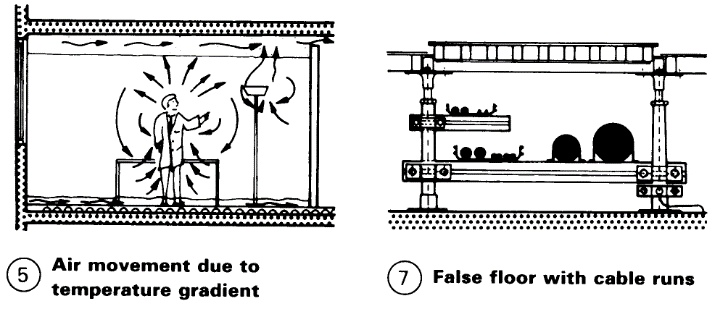
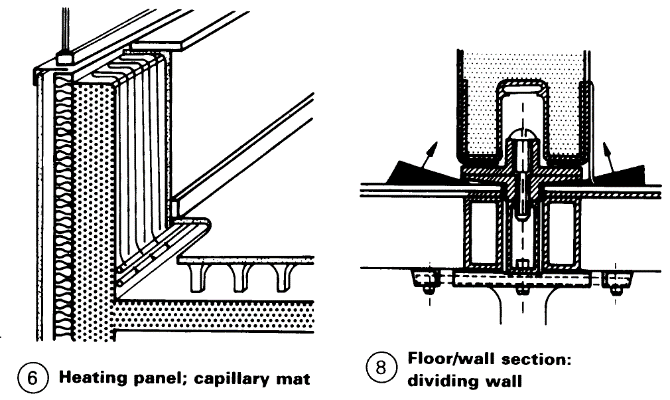
The selection of a heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) system is usually based on performance characteristics, system capacity and the availability of space to accommodate the equipment.
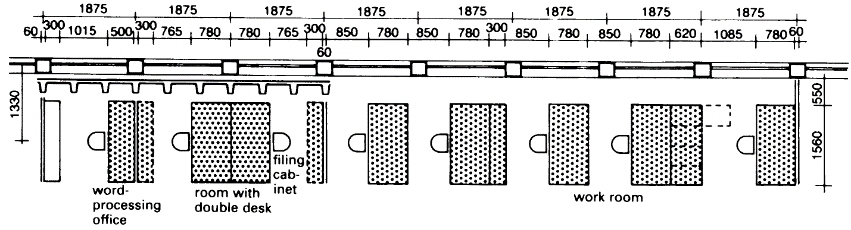
Calculations: Division of Space. With standard desks (size 0.78 x 1.56 m), a division of 187.5 is suitable for a ribbed/slab-and-beam floor 4 having a 62.5 grid module (Koenen floor) with normal formwork. Better for movable partitions.
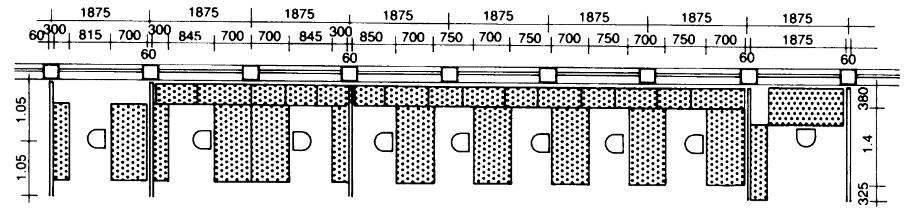
Modular desks (size 0.70 x 1.40 m, Velox system). By combining modular desks with Velox continuous table with filing units below windows instead of filing cabinets ( - (1)), one grid module in every five was saved. Desk clearance of 75 cm is possible only when swivel chairs on casters are used.
Date added: 2023-01-05; views: 864;
