Calculations: Space for Furniture. Calculations: Archive Space
A wide range of office furniture is available. The suitability of furniture for any office is influenced by its flexibility, adjustability, durability, IT compatibility, storage space, ergonomics, aesthetics and cable handling.
The space required while seated and standing is used to calculate the minimum clearance between individual desks or tables (preferably a minimum of 1 m), depending on whether they are placed against walls or other tables, or in front of filing cabinets.
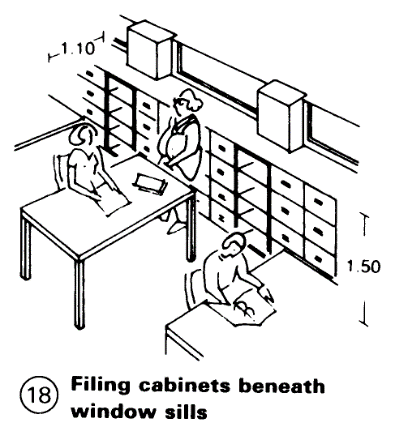
Windows placed high in the wall provide satisfactory illumination deep into the room, which allows efficient use of space and access to the window ledge – (18).
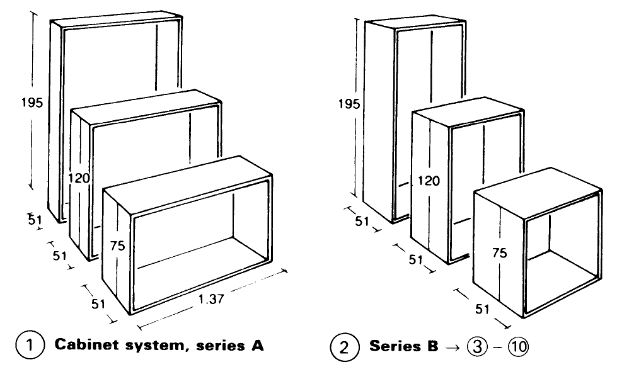
Many furniture systems in contemporary offices are still designed according to standards in use since 1980. In addition, furniture units such as simple work tables and desks that incorporate filing systems are still used. Because of the increasing use of VDUs and keyboards, European standards for workstations specify a surface height of 72cm high. A new desk measuring 140cm x 70cm x 74cm - (2) has been introduced, together with the standard desk whose dimensions are 156cm x 78cm x 78cm. The requirements include adjustable workstation height, protection against vibrations, a sound-absorbent surface and foot rests with ergonomically correct height, preferably adjustable.
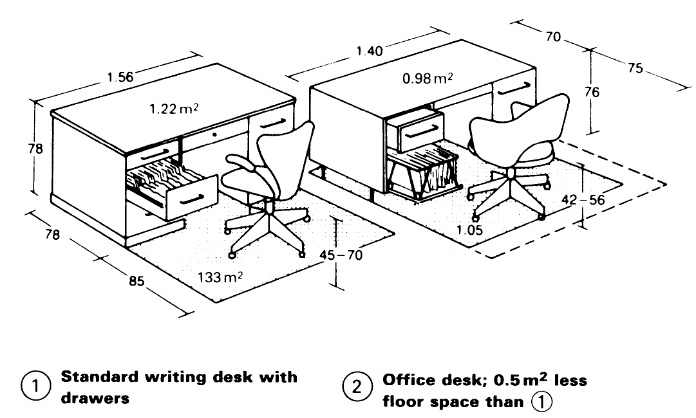
Chairs should be adjustable, with castors and upholstered seats and backs. Properly contoured back support for the lumbar curve is essential in an office chair. It should also provide firm support for the lower part of the back and the upper thighs. Many combinations of typewriter stand and desk are available, ranging from space-saving units to built-in systems.
Filing, archives and card indexes may use cabinets without sides, usually in steel units of standard dimensions.
Counters for transactions with a person standing on the other side are generally long, and should be 62cm wide and approx. 90cm high - (6). If a counter is only 30cm wide, its height should be approx. 100cm (7). In public areas of a building where high security is required, this makes it difficult for any person in front of the counter to reach anything behind it - (7). Clearance to stand and deal with members of the public should be provided behind the counter (2) - (6). Individual counters are easier to reorganise since the floor space is more flexible - (8).
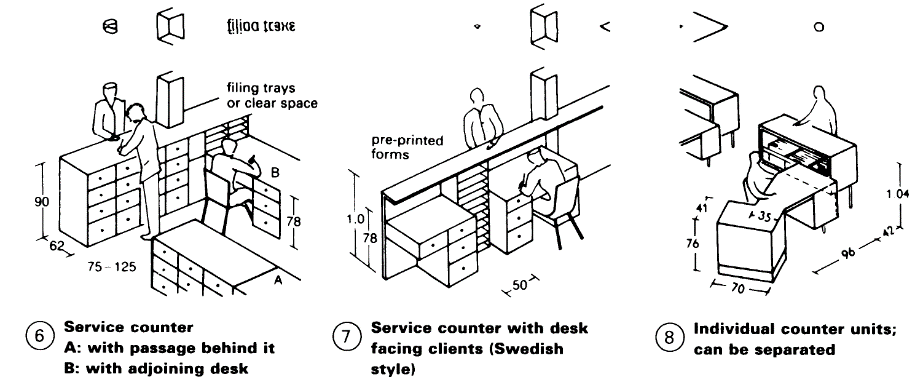
Some counters and switchboards, e.g. in reception areas, hold VDU terminals and probably keyboards. Their design should take account of this.
Calculations: Archive Space. In spite of new office technologies, the use of paper as the main storage medium for information has increased. Paper consumption doubled every 4 years until 1980. Computer memory has now become a more common way of storing information in office communication systems, but the need for what is known as uncoded information (printed letters, texts, periodicals etc.) means that paper will continue to be used.
It is necessary to arrange stored documents in a clearly labelled system, with short circulation routes and efficient use of space. Space should also be available for archives - (1). As cabinet widths increase, the aisle between cabinets should also get wider.
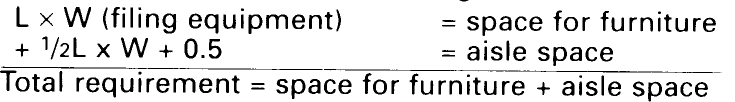
Total requirement = space for furniture + aisle space Deep filing cabinets are more economical. The diagram in - (11) shows the relationship between furniture floor area and aisle space required for a vertical filing system using large archival shelves (Velox system) or a flat filing system. The floor area needed for a vertical filing system is 5.2m2, and the aisle space should be 4.6m2 (100:90). For flat filing systems, the floor area is 3.2m2 and the aisle space 3.6m2 (90:100, ratio reversed).
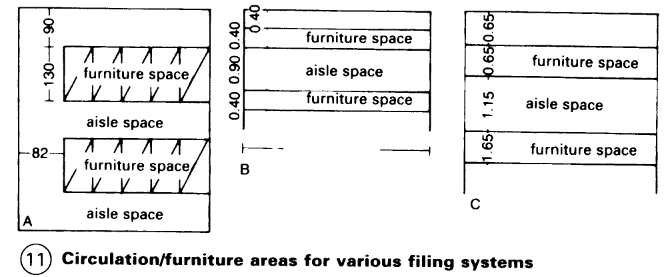
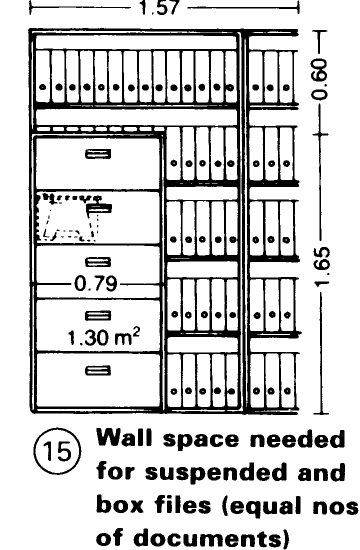
Flat filing systems cannot hold as much as vertical ones, and high shelf units are hard to organise. Vertical files may reduce staffing levels in the filing section by 40%. Hanging files use wall space 87% better than box files - (15). An efficient way to move files is by paternoster elevator. Workstations should include shelves for sorting, a small table and a chair on castors.
The filing room should be centrally located, and the best window grid module is between 2.25m and 2.50m. Since a clear height of only 2.10m is required, three storeys of filing could be fitted into a space which would only take two storeys in normal offices. Dry storage rooms are essential, and therefore attics and basements are unsuitable.
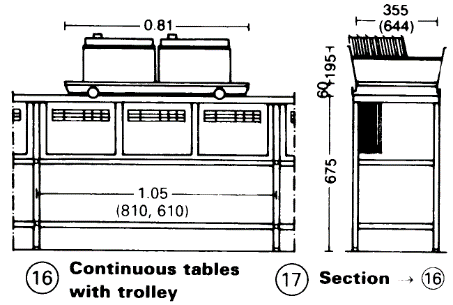
Narrow shelves – (16) and (17) with hanging files and a writing surface can provide a functional connection between workstations. Trolleys can be used either as writing surfaces or for card-index boxes. Movable filing systems give substantial space saving (100-120%) by eliminating intermediate passages – (18) B.
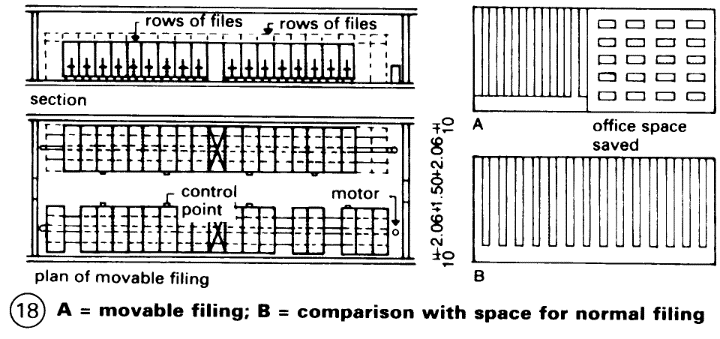
There are no fixed standards for filing systems. They are usually adapted to suit individual requirements, such as registries, archives, libraries and storage areas. The increase in load for each square metre of floor space must be taken into account. File shelving may be moved by hand or by mechanical means. In some designs, the entire filing system, or only parts of it, can be locked by one handle.
Date added: 2023-01-05; views: 875;
