Balconies. Access Corridors/decks
Balconies offer an effective means of improving the attractiveness of domestic accommodation units. They also give an extended work space as well as an easily supervised outdoor children's play area. Typical uses include relaxation, sunbathing, sleeping, reading, eating etc.
In addition to the required functional living space an area for plant boxes should be provided wherever possible (8) + (14).
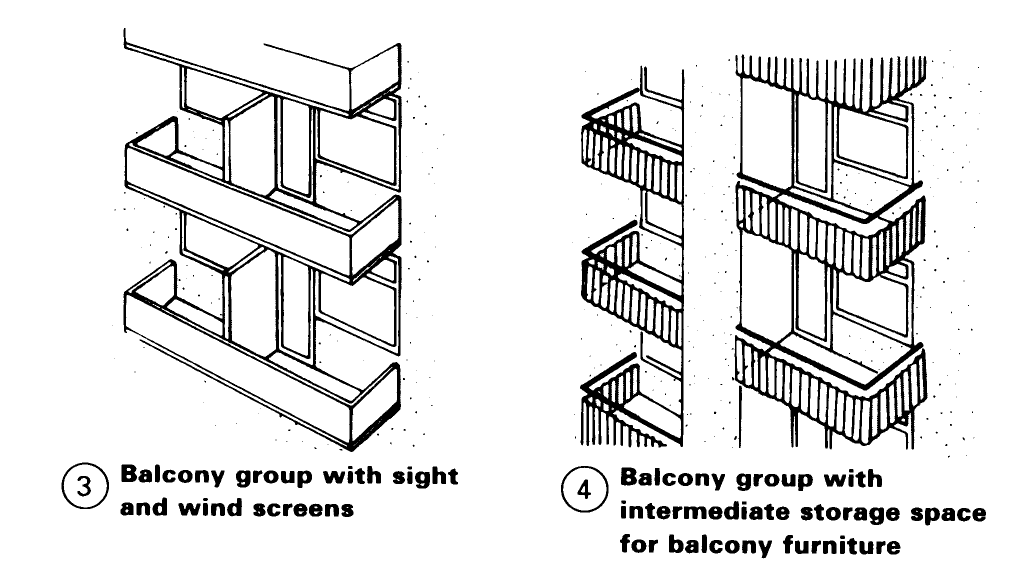
Corner balconies - (1) offer privacy and good shelter and are therefore preferable to open balconies. Open balconies require a protective screen on the side facing the prevailing wind (2).
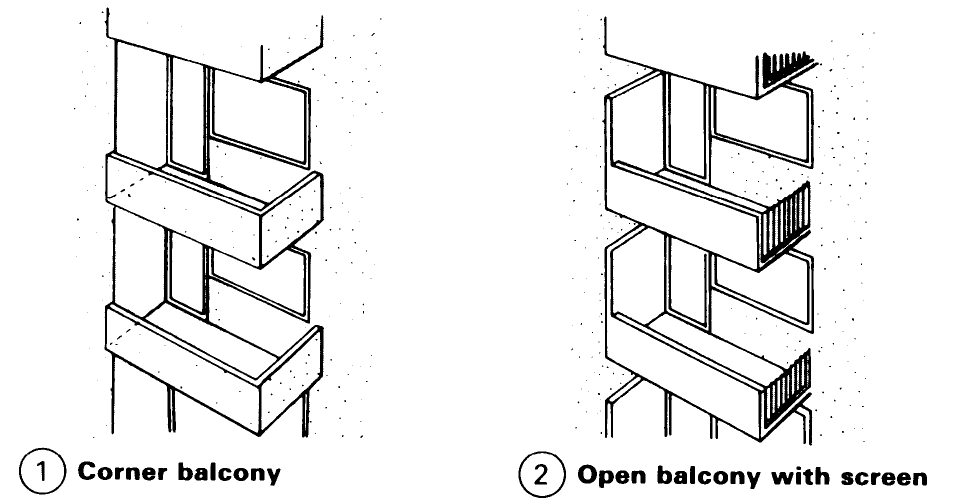
Where there are groups of balconies (as in blocks of flats), screens should be used to ensure privacy and give shelter from the wind - (3). Even better is to separate the balconies with part of the structure because this makes it possible to include some storage space (e.g. for balcony furniture, sunshade etc.) (4) + (12).
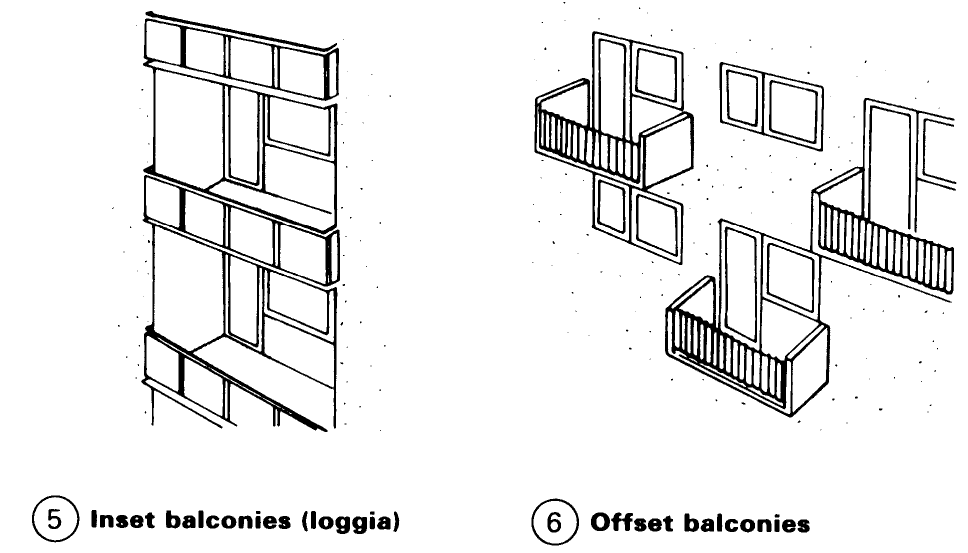
Loggias are justifiable in hot climates but are inappropriate in cooler countries. They only get the sunshine for a short time and cause an increase in the external wall areas of the adjacent rooms, which increases heat loss - (5). Balconies which are offset in their elevation can make fagades less severe but it is difficult to provide privacy and protection from the weather and sun - (6). Balconies which are offset in their plan layout on the other hand offer excellent privacy and shelter - (7).
During planning specify:
- good orientation in relation to the the path of the sun and the view;
- appropriate location with respect to neighbouring flats and houses;
- effective spatial location with respect to adjacent living rooms, studios or bedrooms;
- sufficient size, privacy, protection from noise and the weather (wind, rain and direct sunshine);
- suitable materials for parapets (e.g. opaque glass, plastic or wooden balusters within a frame).
The balcony frame is best made from light steel profiles or tubes with a good anchorage in the masonry. Balcony balusters made from vertical steel rods (note that horizontal rods can be climbed by children) can be considered but are not desirable because they do not offer shelter from the wind and lack privacy. Where they are used, they are often covered by the tenants themselves with all sorts of different materials.
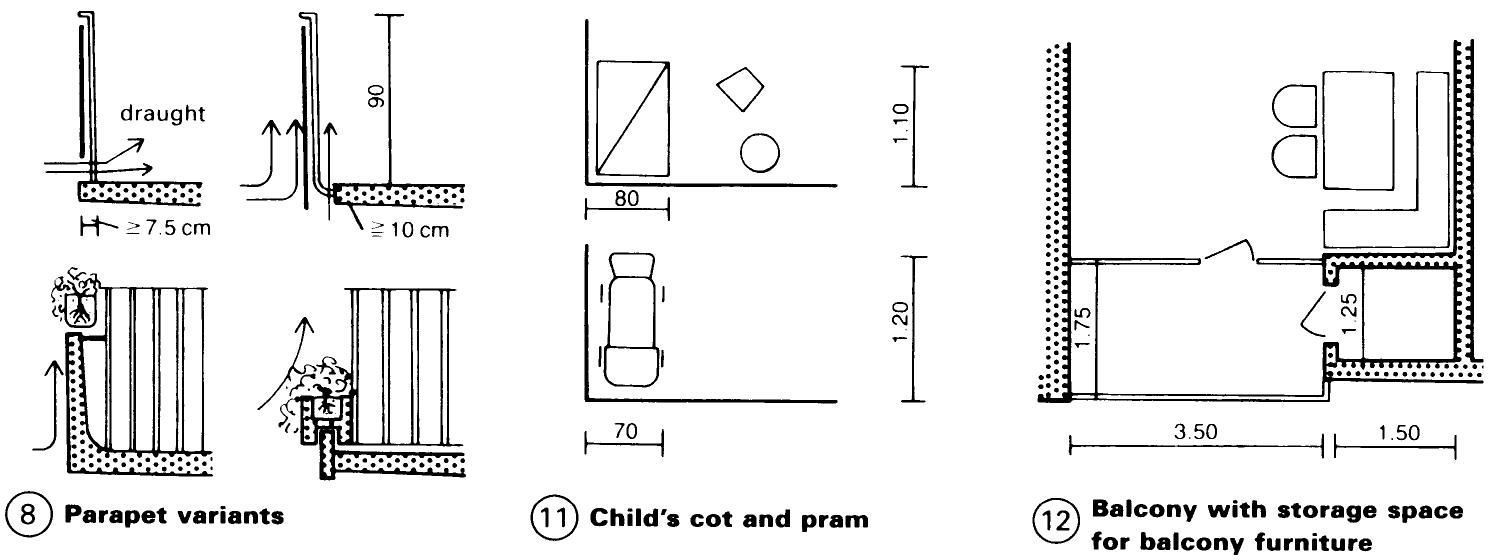
Draughts can occur in the intermediate spaces between parapets and the concrete slab - (8), so it is better to extend the parapet down in front of the balcony slab or to have a solid parapet. This must be kept low to avoid a trough-like character and there must be a steel rail above it at the regulation height (>900mm). Allow space for flower boxes if possible (8).
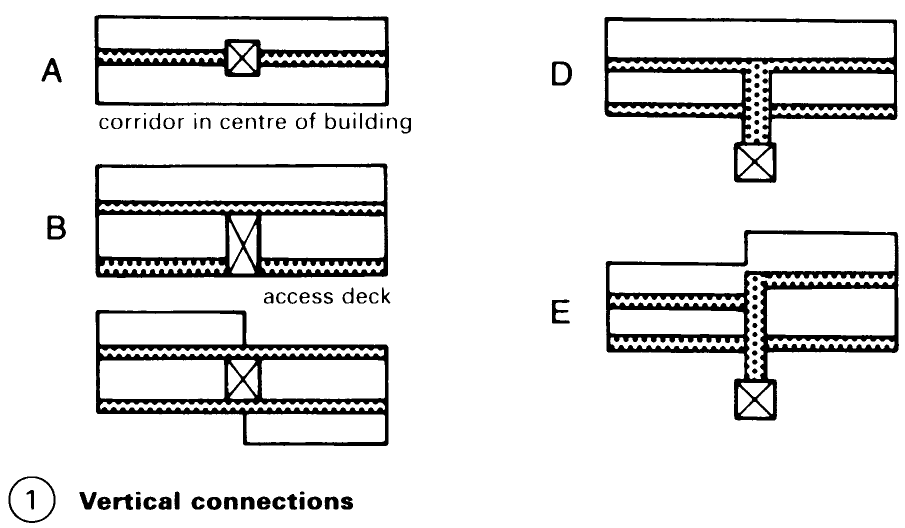
Access Corridors/decks. An alternative to the centralised layout (i.e. buildings with dwellings on each floor around a central staircase or lift) is to have the dwellings accessed from an internal corridor or a covered external walkway. This is more economical in large housing projects. Each level is served by one or more vertical connection points (lifts and/or stairs) which also lead to the main entrance to the building. In addition to stairways and lifts, vertical systems of service shafts are needed and there should be a clear differentiation of built- in, added and free-standing constructions (1).
Dwellings on either side of an interior corridor have a single orientation and this makes it desirable to employ a design that uses two or more levels - (3). A similar arrangement can be exploited in buildings with an access deck running along the exterior – (6) + (7). Note that open access decks can cause problems in harsh climates.
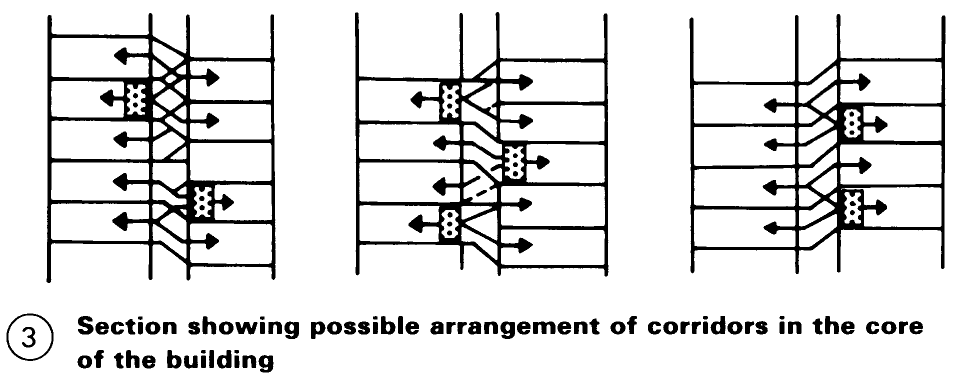
It is considerably better if the dwelling is on two or more levels because it allows the functional requirements to be met more satisfactorily and half-storey split levels, for example, can be stacked easily - (2). Dwellings on only one level are particularly suitable as studio flats - (5).
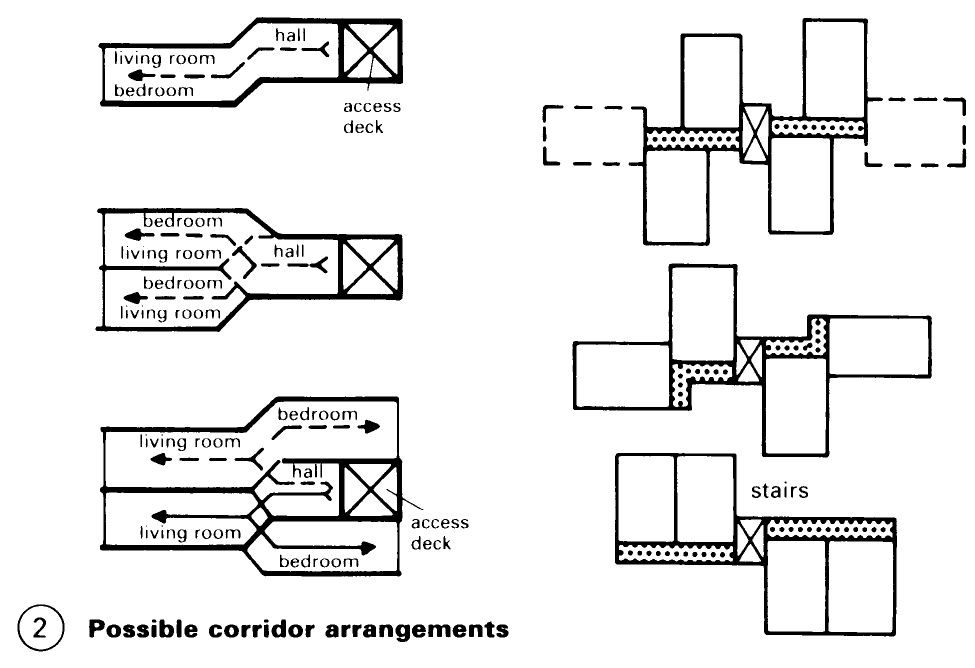
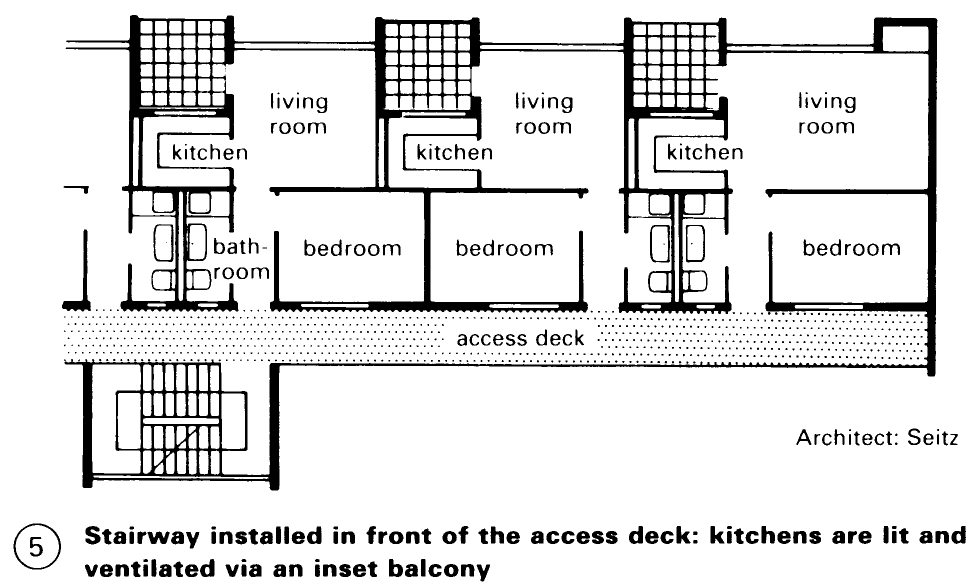
To improve the realtionship between circulation and dwelling areas the goal should be to minimise the length of horizontal access routes. Planning corridors on alternate floors provides the best arrangement for larger multi-level dwellings and good solutions can be attained by siting the deck access on alternate sides. The number of corridors can also be reduced with a mirrored staggering of maisonettes or a similar arrangement of split-level dwellings.
Date added: 2023-01-05; views: 577;
