Old Peoples Accommodation
Depending on the degree of support required, there are three main types of accommodation and care for the elderly: (1) old people's housing, (2) old people's homes and (3) nursing homes.
In the United Kingdom, depending, inter alia, on type of dwelling and facilities provided, housing for elderly people can be classified into: category one housing, category two housing, sheltered housing, very sheltered housing, retirement housing, extra-care housing, residential care homes, nursing care homes, and dual registration homes. In the United States, although similar building types have been developed, the terminology differs. The building types that house elderly people in the United States can be described as independent retirement housing units, congregate housing, personal care housing, skilled nursing home, and life care communities.
Old people's housing - (3) – (8) consists of self-contained flats or apartments which cater for the needs of the elderly so that they can avoid moving into an old people's home for as long as possible. Such housing is usually scattered around residential areas, with a density of 2-10%. Flats for one person are 25-35m2; for two people 45-55m2. Sheltered balconies >3m2.
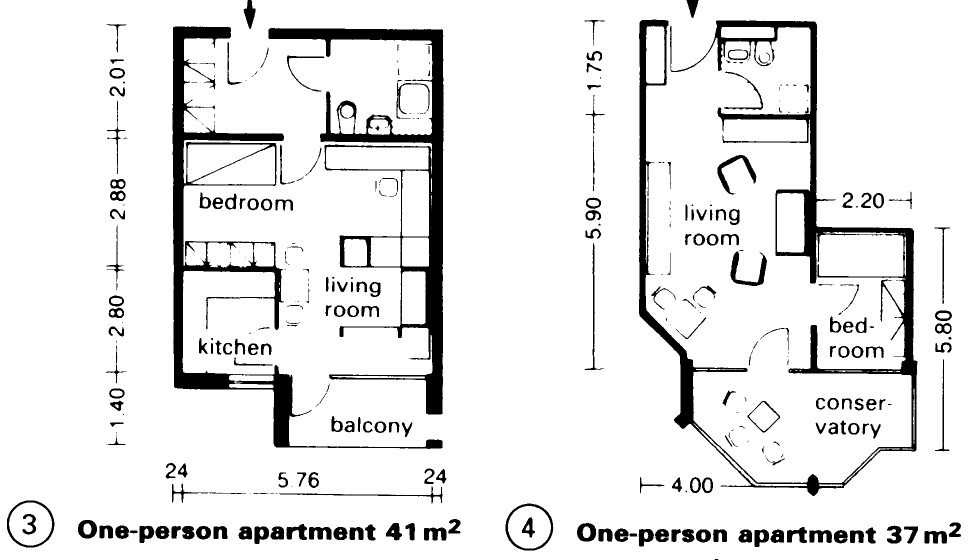
Sheltered housing is generally a group of flats (each >20m2) in one building, with common rooms and a tea kitchen. A good solution is to build these facilities close to a nursing home for the elderly which offers meals, leisure, recreation and various therapies. Provide one car parking space per 5-8 residents. Note that heating costs will be 2% higher than normal.
Old people's homes offer residential care facilities and must conform to regulations on planning, licensing. The large amount of ancillary space required means the most economic size is about 120 places. Meals, entertainment and therapies are provided and an integrated nursing section for short-term care. General design features: stairs 16/30cm without open riser; edges of steps defined with a colour; handrails on both sides of stairs and in corridors; where necessary, lifts for moving patients on stretchers or in folding chairs. The buildings should all be adapted for the disabled and have open spaces with benches.
Homes should be sited close to the infrastructure of a town or village and to public transport. The inclusion of a daycare centre should be considered to provide opportunities for people living independently to make contact and receive nonresidential care (approximately one daycare centre is needed per 1600 elderly people).
Nursing homes for the elderly provide care for people who are chronically ill and in need of medical attention. The residential area consists of a 50:50 split of single and double rooms – (1) – (4). It must be clearly separated from the administration and office areas - (6). Residents are frequently split into groups consisting of 8-10 people, with a shared lounge and possibly a tea kitchen where meals may also be eaten - (5). Provide one treatment room per two groups.
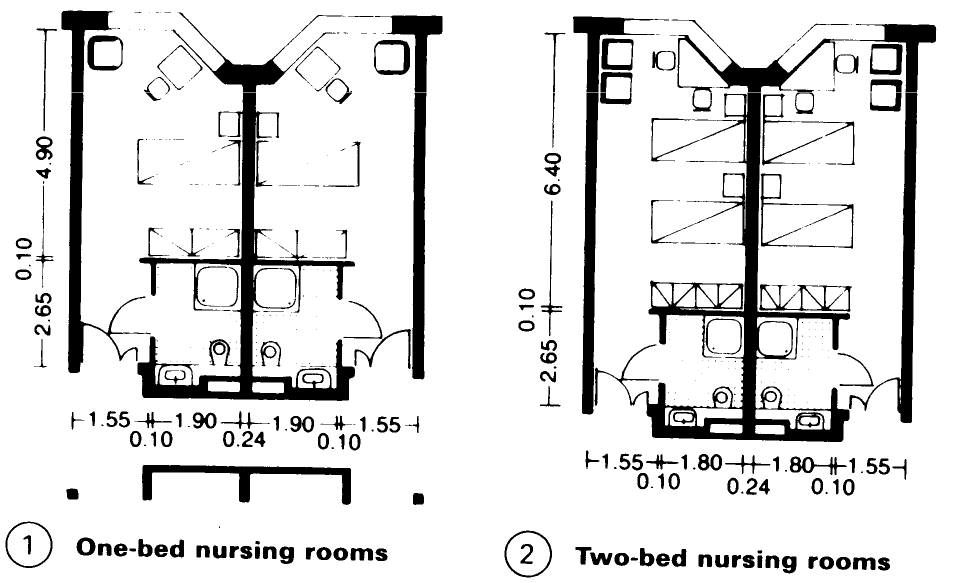
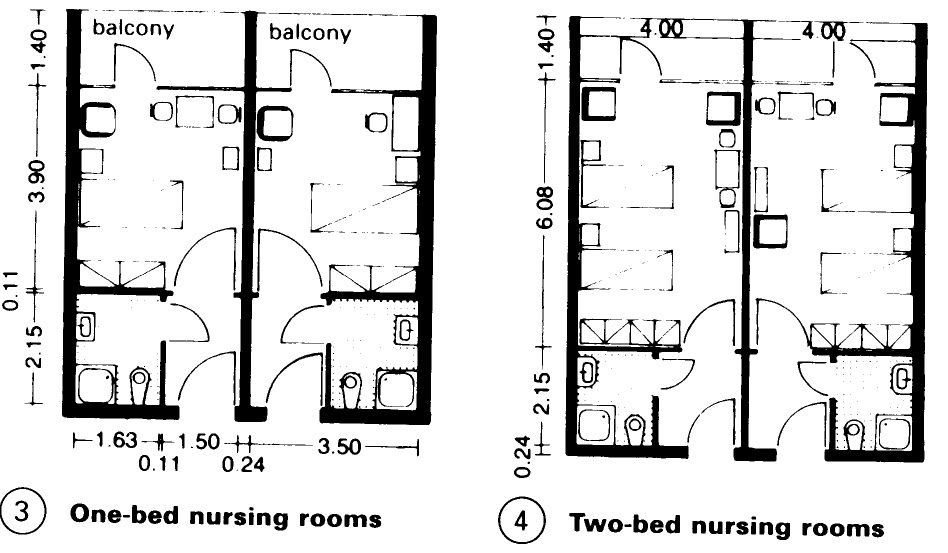
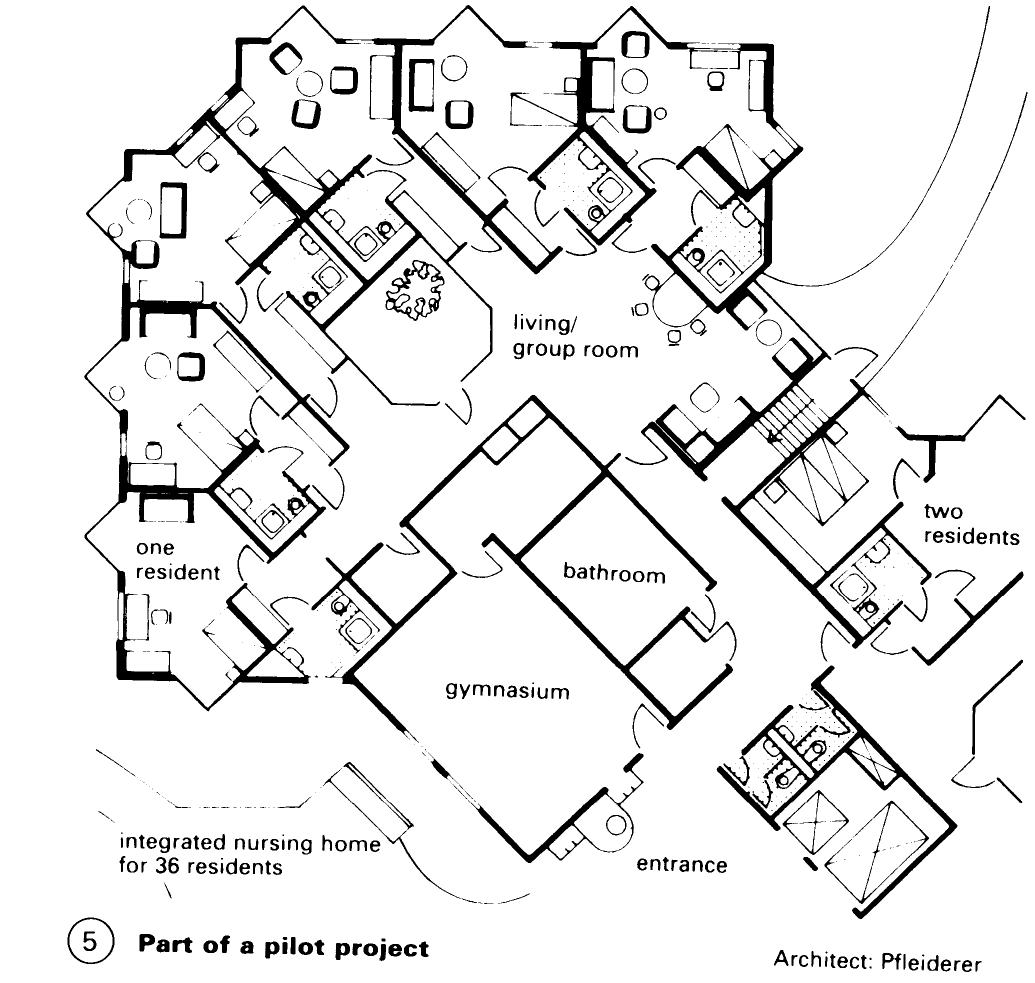
Central facilities are best grouped together on ground floor. Rooms are required for administration, consultation, occupational therapy, physiotherapy, chiropody. In addition, rooms for entertainment, common rooms, cafeteria and hairdressing should be provided.
Date added: 2023-01-05; views: 497;
