Transfer RNA. Ribosome RNA. Messenger or matrix RNA
Transfer RNA. The number of nucleotides in this RNA is no more than 7585. The molecular weight is 25 -28.000 Daltons. The tRNA presents 10% from the all cellular RNAs. These RNA are not bound to any particles. While realization of genetic information each of tRNA bind and transfer specific amino acid. The complementary bindings of pairs make a “clover leaf-like” structure (pic 2.4).
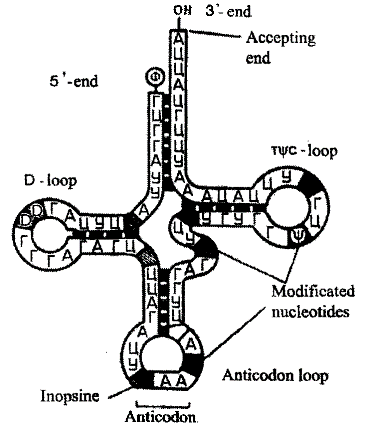
Pic 2.4. The Structure of transfer KNA molecule (R.W. Holley et al„ 1965 with changes)
In this structure, there are four parts, which carry out different functions. The first is accepting part, made by two complementary bounded terminal parts. It is consist of 7 base pairs. The 3' end of this part is a little bit longer. It form a single strand region which is ended by CCA fragment with free -OH group. To this end, amino acids are attached.
Three other parts are complementary bounded nucleotide sequences, which are ended by non-complementary loops. The middle part of the loop consist of 5 nucleotides and contain in it own structure anticodon (three nucleotides which are complementary to mRNA codon, which code the amino acids, transported by this tRNA).
The different types of tRNA are characterized by stable nucleotide sequence and more often consist of 76 nucleotides. Varying numbers of nucleotides are connected to changing that number in additional loop. The primary structure of tRNA as a sequence of nucleotides forms secondary structure of tRNA in a cloverleaf form.
The secondary structure form third structure, characterized by being two double helixes. It was determined existing of several tRNA types able to bind with same codon. As result of this, there are around 40 types of tRNA in the cytoplasm in spite 61 by codon number. This quantity is enough to provide transportation of 20 different amino acids to a place of protein construction in the ribosome.
Ribosome RNA. There are three types of rRNA. 5S-RNA consists of 120-121 nucleotides and has a molecular weight around 40000 Daltons. It is associated with the large subunit of the ribosome. The molecule contains 3-4 bounded spiral regions and probably has a secondary structure in form of cloverleaf. 5.8S-RNA consists of 1 ЗО-160 nucleotides and has a molecular weight around 55000 Daltons. It is bounded in the ribosome with rRNA. It contains many modified bases. rRNA presents 85% of all cell RNA. It may be light (rRNAl), including 1600- 2000 nucleotides and having a molecular weight around 700000 Daltons and heavy (rRN A2), including 3200- 5200 nucleotides and having a molecular weight around 1700000 Daltons. The light RNA is in the small ribosome subunit and heavy RNA is in the large ribosome subunit.
The ribosome RNAs are not only structural elements of ribosomes. They also provide binding of mRNA special sequence. By this is the start point of translation and reading frame states. In addition, rRNA provides interaction of tRNA and ribosome.
Messenger or matrix RNA. It presents 5% of total cell RNA. It consists of 300-3000 nucleotides and has a molecular weight until 10*7 Daltons. The size of molecule depends on required information. It is single stranded, but may have complementary bounded regions. The regions have information surrounded by non-informational regions. The leader sequence to start translation on a 5' end and terminal sequence on a 3' end to terminate it.
The synthesis of mRNA starts from recognizing of promoter site on DNA by RNA polymerase. The strands of DNA separate from each other and on a one of them, the RNA transcription starts. The linkage of nucleotides is performed according with its complementarity to DNA nucleotides. The RNA polymerase can make polynucleotide only in one direction from 5' to 3' end. That is why only one strand of DNA can serve as a matrix for RNA synthesis. This strand is called codogenic strand.
As the RNA polymerase moves along the strand into the gene, encountering each DNA nucleotide in turn, it adds the corresponding complementary RNA nucleotide to the growing RNA strand. When the enzyme arrives at the special stop signal at the far edge of the gene, which is called terminator, it disengages from RNA and releases the newly assembled RNA chain. The fragment of DNA molecule including promoter, transcribed sequence and terminator has a name – transcripton.
Date added: 2022-12-30; views: 743;
