The human fertilization
Ovum and sperm have a limited life span and that why a limited ability for fertilization. A liberated from follicle human ovum preserves fertilization ability during 24 hours, whereas spermatozoa are still active during 4 days if placed in female sexual ways. However, they are able to fertilize ovum only in first 2 days. The speed of sperm movement varies between 1.5-3 mm/min.
There are 350 millions of spermatozoa in an average human ejaculate. Only part of them reaches the oviduct to take part in fertilization. If a number of spermatozoa in men’s ejaculate is less than 150 millions (or 60 millions per 1 ml), the probability of fertilization is very small. Generally, “useless” excess of sperm numberplays an important role in fertilization.
During human ovulation, an ovum is liberated from ovarium. It is surrounded by layer of follicular cells, which is bounded to each other by proteoglycans. In such complicated dressing ovum is unavailable for sperm penetration. It should be liberated from “corona radiata”. One sperm cannot dissolve such coat. They need to work all together to dissolve it. From a great number of spermatozoa attacking ovum only one can enter it. Ovum membrane bulges out making an acception hill toward sperm, permitting a sperm nucleus to enter the cytoplasm of the egg. Only this nucleus will fuse with ovum nucleus. If any other sperm would enter the ovum cytoplasm, it will be destroyed in cytoplasm.
When sperm has touched ovum, it perform acrosome reaction. It is liberation of enclosed in acrosome enzymes, such as hyaluronidase, protease, and enzyme dissolving follicular cells attachments. During this reaction, a sperm plasmolemm and external acrosome membrane touch each other in many sites. Then, they produce holes in these sites. The enzymes are liberated through these holes. Apparently, sperm pass zona pellucida with help of proteolytic enzyme. Then, it touches ovum plasmolemm by head side and ovum membrane incorporates sperm membrane.
Mammalian spermatozoa, which just have entered female sexual ways, are unable to perform acrosome reaction. To receive these properties they need to be subject to capacitation in oviducts. During capacitation sperm become activated under influence of female sexual ways mucosa. It takes different time in different species. In rats, it lasts for 3 hours, in rabbits for 5 hour, in humans for 7 hours. In contrast to maj ority of animals, the human sperm head keeps it primary orientation in ooplasm and moves to female nucleus without turning. Gradually, sperm nucleus changes to male pronucleus. Its chromatin becomes more dispersed.
The human spermatozoa penetrate ovicell, which is in maturation period. 10 hours after penetration oocyte eliminate primary polar body and 24 hours later secondary polar body (pic 5.5). Right after sperm penetration, the ovicell performs cortical reaction. It helps to make impermeable coat for other sperms. At the same time, the other sperms surrounding ovum loose their directed activity, although keeping their mobility. After that the ovum changes its metabolic activity, such as increasing membrane permeability, increasing of warm producing, accelerating of oxidation-reduction reactions rate in more than 70 times, activation of protein synthesis, activation of lipid and carbohydrate exchange.
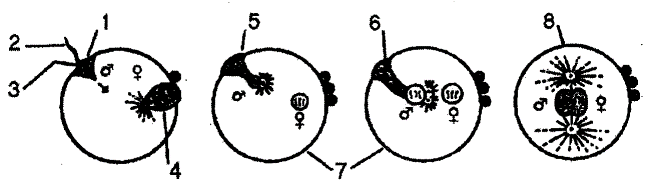
Pic. 5.5. The scheme of following stages of sperm and ovicell fusing in human during fertilization: 1 - sperm head, 2 - sperm tail, 3 - accepting hill, 4 - second meiosis division, 5 - entering way, 6 - nucleuses getting closer to each other, 7 - formation of polar bodies, 8 -nucleuses fusing (by K. Villy, V.Detier, 1971)
Humans have similar rhythms of reproductive activity as animals do. Such rhythms were formed according to environmental factors influences. It is known that menstrual cycles have a same length as moon cycles, although a direct connection between them is lost. Today around 10% of menstrual cycles of healthy women are without ovulation. The interchange of ovulatory and anovulatory cycles depends on activity of neuroendocrine system.
Thus, a birth rate statistics in Western Europe, Australia and USA showed that birth rate curve have a following structure. It has a wide peak during winter, spring recession, slight summer raise and significant decrease during autumn. Hence, human copulation, similar to other mammalian, occurs more often during spring and autumn months.
Strong social and cultural factor invasion to human biology has led to sexual intercourse act estrangement from reproductive purposes. It serves as a source of getting pleasure. It leads to disynchronisation ovulation and fertilization, to overmaturation of female and male gametes. The influence of this factor is proved by higher rate of chromosome defects in human embryo on early stage of development and by wide spectrum and higher rate of “spontaneous” development defects in humans than in animals.
Date added: 2022-12-30; views: 793;
