Roof Slopes and Flat Roofs. Essential Detail Points
Cold roof - p. 81: constructed with ventilation under roof covering; critical in respect of through flow of air if the slope is less than 10%, therefore, now only used with vapour barrier. Warm roof in conventional form - (4): (construction including a vapour barrier) from beneath is roof structure - vapour barrier - insulation - weatherproofing - protective layer.
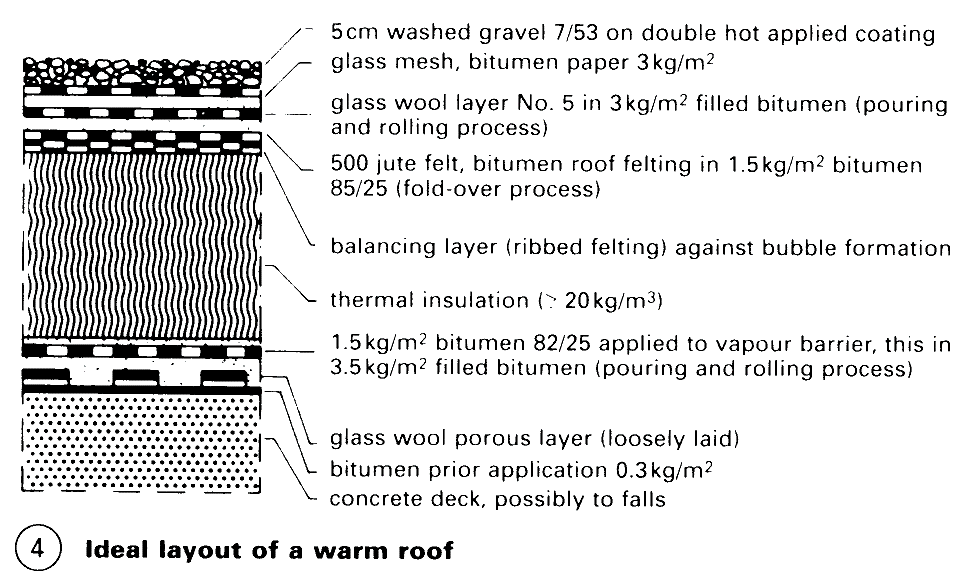
Warm roof in upside-down format - p. 81: construction from beneath is roof structure - weatherproofing - insulation using proven material - protective layer as applied load. Warm roof with concrete weatherproofing - p. 81: built from underneath: insulation - concrete panels as roof structure and waterproofing (risky).
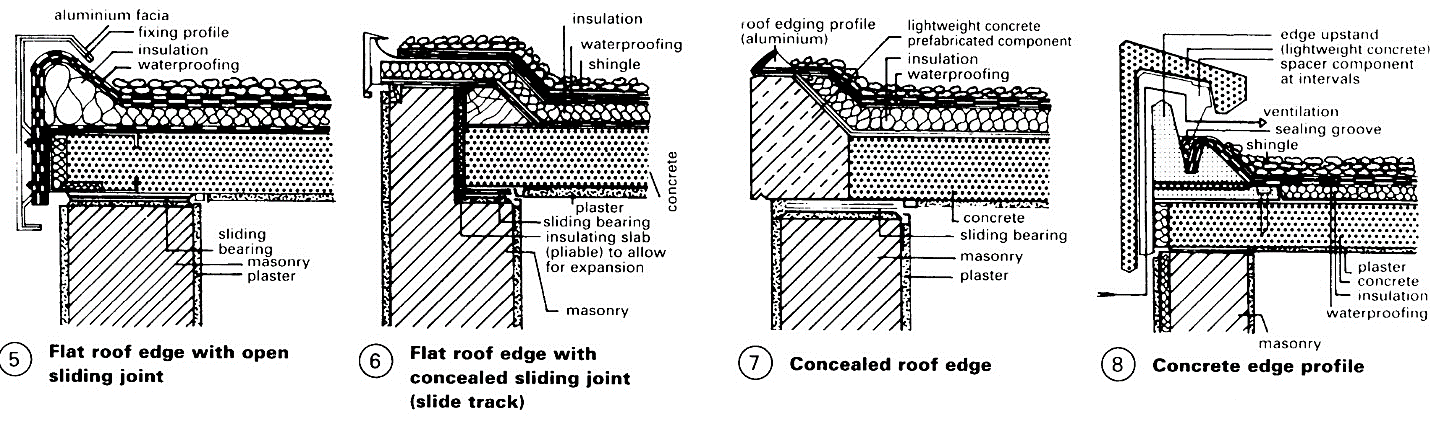
Solid slab structure - must be arranged to provide room for expansion due to heat; consequently, flexible joints arrangement over supporting walls - p. 80 (5)-(8) and separation of internal walls and roof slab (Styrofoam strips are first attached by adhesive to the underside of the slab). Prerequisites for correct functioning: built-in slope > 1.5%, and preferably 3% (or a build-up of surface water can result).
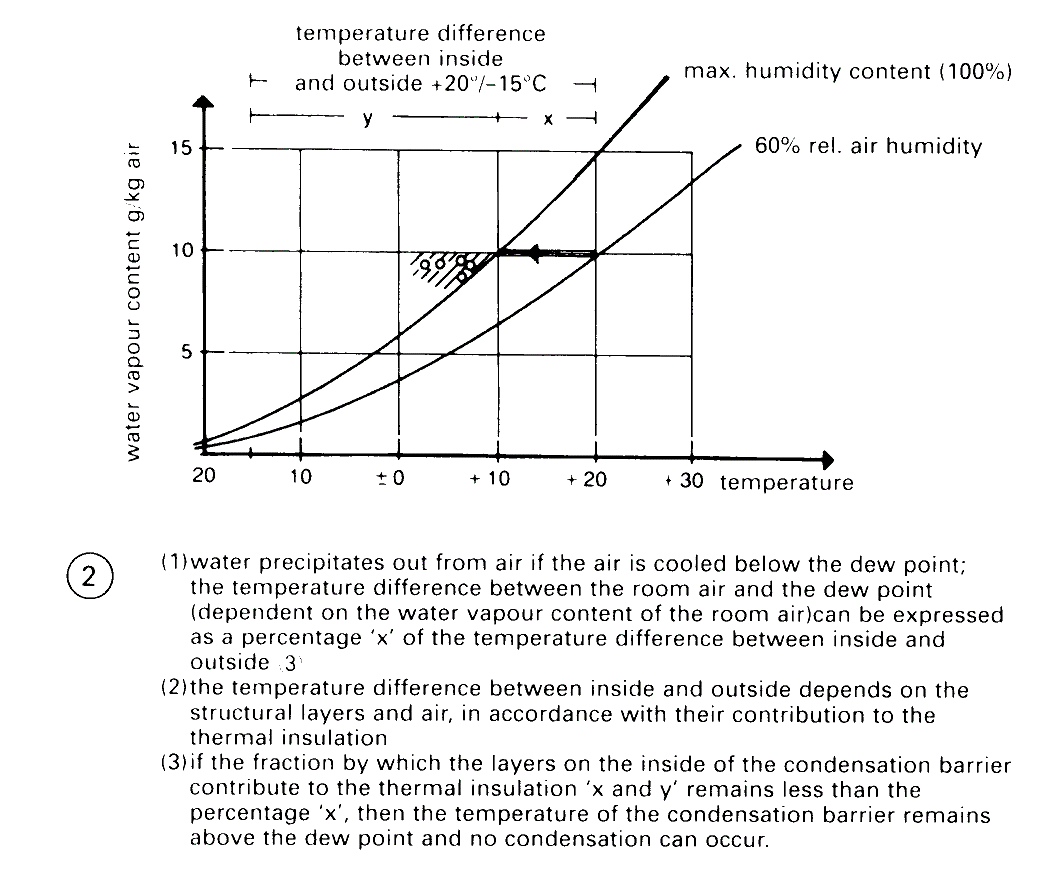
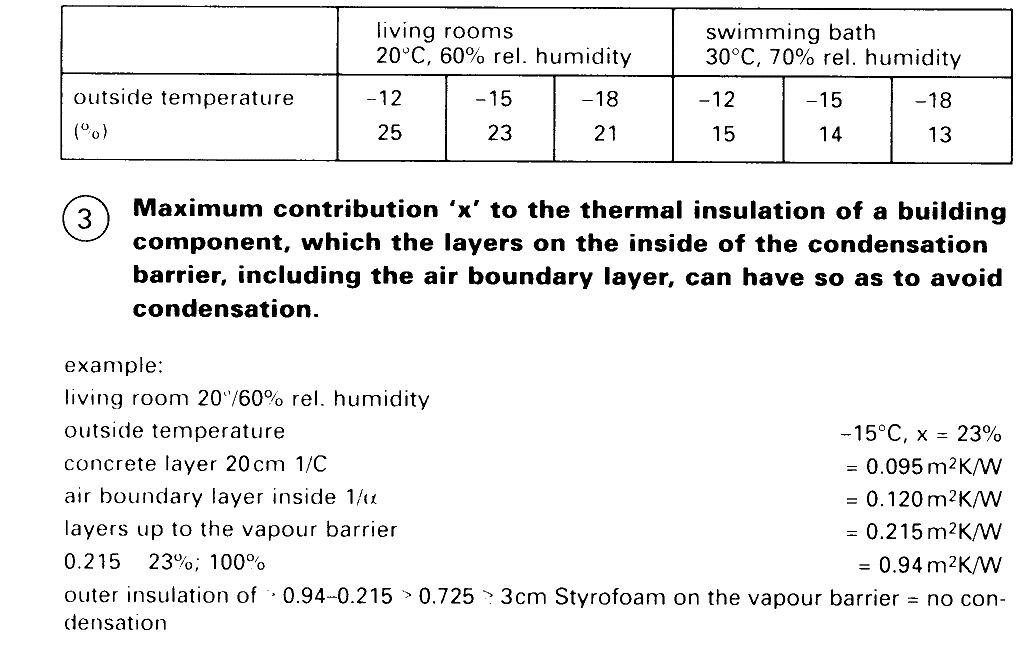
Vapour barrier: if possible, as a 2 mm roof felt incorporating aluminium foil on a loosely laid slip layer of perforated glass fibre mat on top of the concrete roof slab, treated with an application of bitumen solution as a dust seal. The vapour barrier is laid as far beneath the roof buildup as required to exclude condensation (2) + (3).
Insulation of non-rotting material (foam); see dimensions in (4); two-layer arrangement or single layer with rebated joints: ideally, interlocking rebates all round.
Roof membrane on vapour permeable membrane (corrugated felting or insulating layer to combat bubble formation), triple layer using the pouring and rolling technique with two layers of glass fibre based roofing felt with a layer of glass fibre mat in between, or two layers of felt using the welding method with thick bitumen course (d > 5mm). A single layer of sheeting is permissible, but due to risk of mechanical damage caused by the thinness of the layer and possible faulty seams, two layers offer additional safety.
Protective layer should consist, if possible, of a 50mm ballast layer with 15-30mm grain size on a doubled hot brush applied layer on a separating membrane; prevents bubble formation, temperature shocks, mechanical stresses, and damage from UV radiation. Additional protection with 8-mm layer of rubber shred sheeting under the ballast layer. The joints should be hot sealed (a basic prerequisite for terraces and roof gardens).
Essential detail points. Outlets p. 80 – (1) - (4) always thermally insulated, two draining levels, with connection also at the vapour barrier, to form an outlet then sealed against the drain pipe. For thermally insulated discharge pipe with condensation layer - p. 80 (4) for prevention of damage due to condensation. The surface slope to the intakes should exceed 3%. A Ventilator' for the expansion layer is not required. The flexible joint should be continued to the edge of the roof - p. 80 (5) - (8). The edge details must be flexible, using aluminium or concrete profiles - p. 80 (5) - (8); zinc connections are contrary to technical regulations (cracking of roof covering).
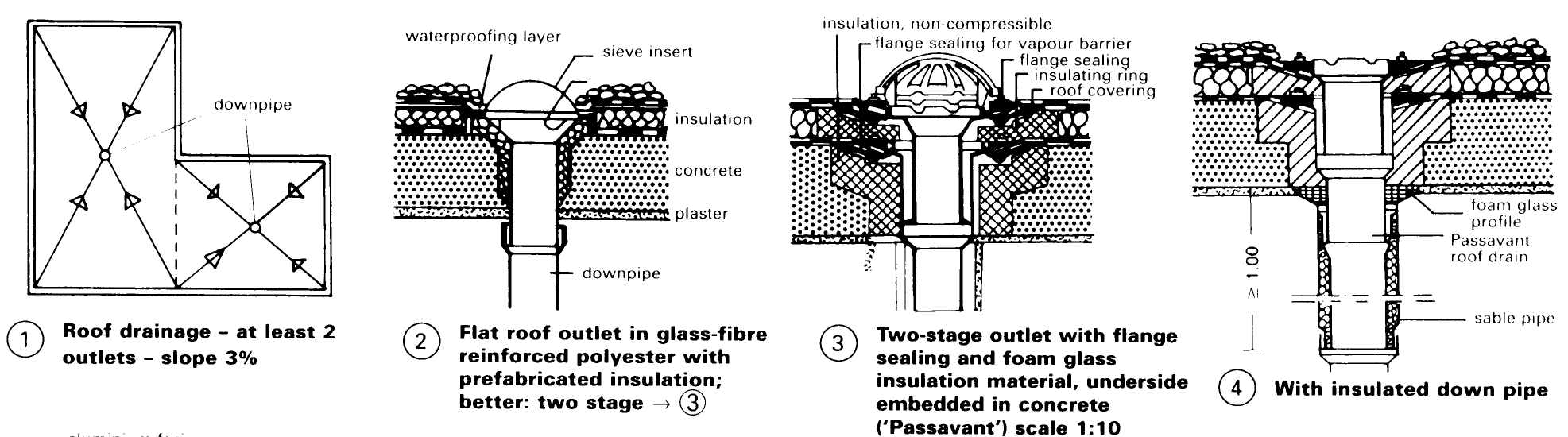
Wall connection should be > 150mm above the drainage level and fixed mechanically, not by adhesive only. If steel roof decking is used as a load-bearing surface, the roof skin may crack due to vibration; precautions are required to increase the stiffness by using a thicker sheet or a covering of 15mm woodwool building board (mechanically fixed), to reduce the vibrations (gravel ballast layer) and crack resistant roof sheeting! The vapour barrier on the decking should always be hot fused (due to thermal conduction).
Date added: 2023-01-01; views: 791;
