Flat Roofs. Cold Roof Construction
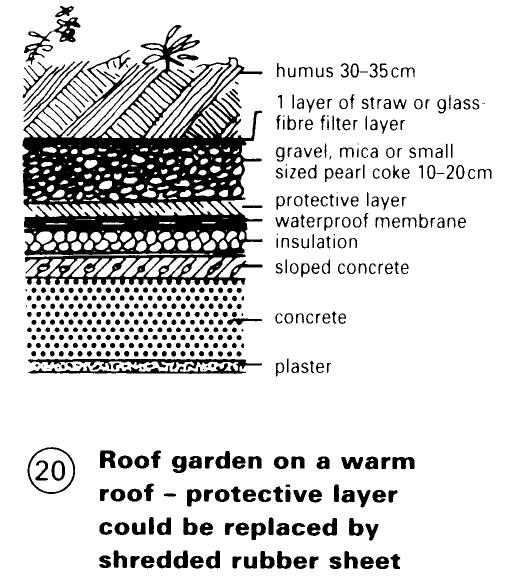
Roof terrace surfaces are loose laid in a bed of shingle or on block supports. Advantage: water level is below surface; no severe freezing. Roof garden has surface drainage through drainage layers, ballasting of shingle or similar, with a filter layer on top - p. 80 (20).
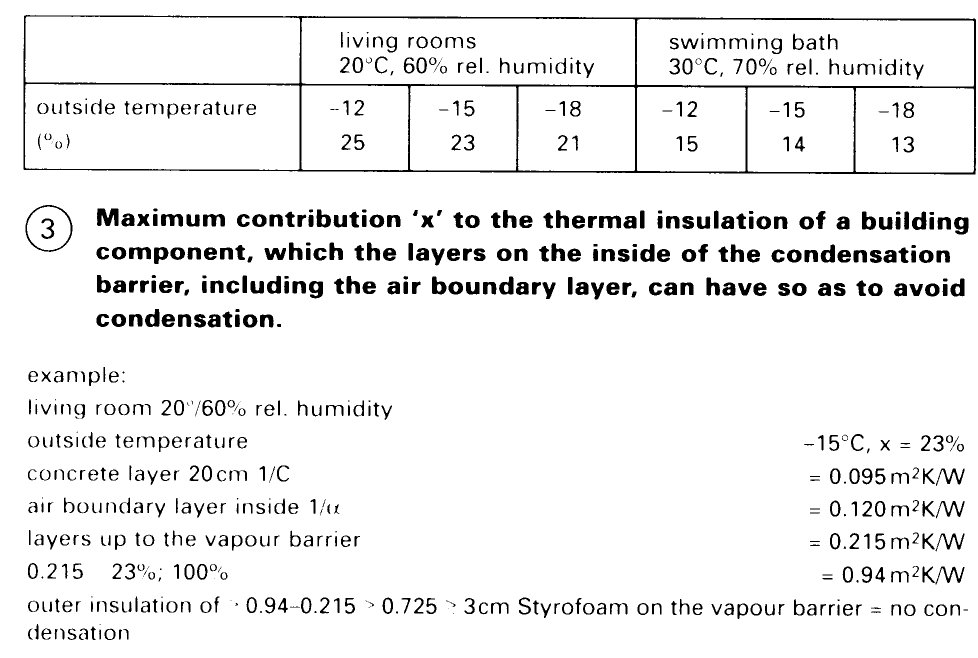
Roofs over swimming pools, etc. are suspended ceilings with ventilated or heated void; see Table (3) p. 79. Usually, the contribution of all layers up to the vapour barrier, including the air boundary layer, gives a max. 13.5% of the resistance to heat 1/k.
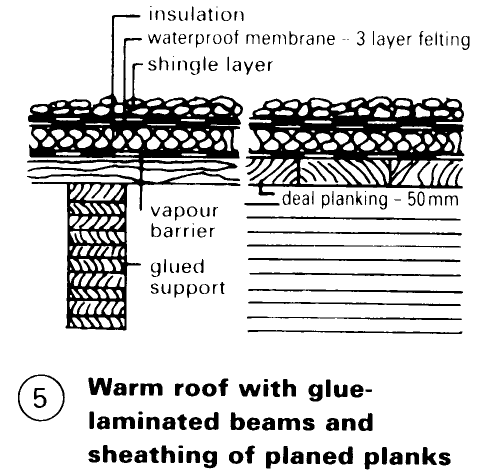
On wood - (5) is a simple solution, and good value for money. NB: insulation above the vapour barrier should be thicker than with a concrete roof, not only due to the low surface weight, but also because the contribution of the layers up to the vapour barrier (air boundary layer + wood thickness) would otherwise be too high.
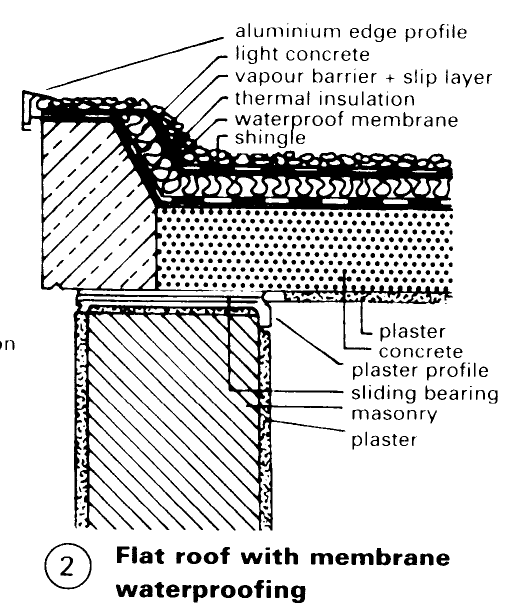
An inverted roof - (2) is an unusual solution with long-term durability (up to now, however, only achievable with various polystyrene foam materials). Shingle alone as the upper roof layering is insufficient in certain cases; it is better to have a paved surface. Advantage: quickly waterproof, examination for defects is easy, no limit to use. Insulation 10-20% thicker than for a normal warm roof.
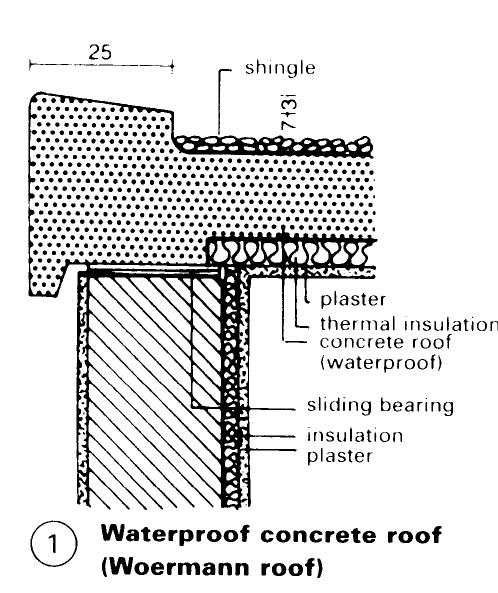
With a concrete roof - (1), due to the position of the insulation, condensation occurs in certain conditions, which always dry out in the summer; unsuitable for humid rooms. The risk is dependent on the care taken by the manufacturer to avoid cracks due to the geometry (shrinkage) and solving the problem of connections to, and penetrations of, the concrete.
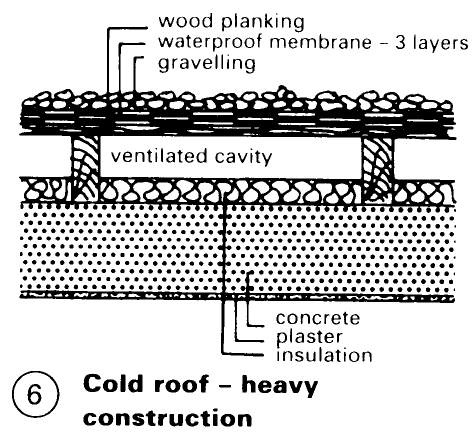
A completely flat cold roof - (6) - (8) is only allowable with vapour barrier: diffusion resistance - pp. 111-14 of the inner skin > 10m; the air layer here is only for vapour pressure balance, analogous to the warm roof, as it does not function properly as a ventilation system unless the slope is at least 10%. Layer sequence - (6) and (8) - NB: inner skin must be airtight; tongue and groove panelling is not. Insulation - p. 79. Waterproofing as for warm roof - p. 80. Slope > 1.5%, preferably 3% - important for drainage. Inlets should be insulated in the air cavity region; use insulated inlet pipes - (9). It is necessary for the vapour barrier to be unbroken (tight overlapping and wall connections, particularly for swimming pools; unavoidable through-nailing is permissible).
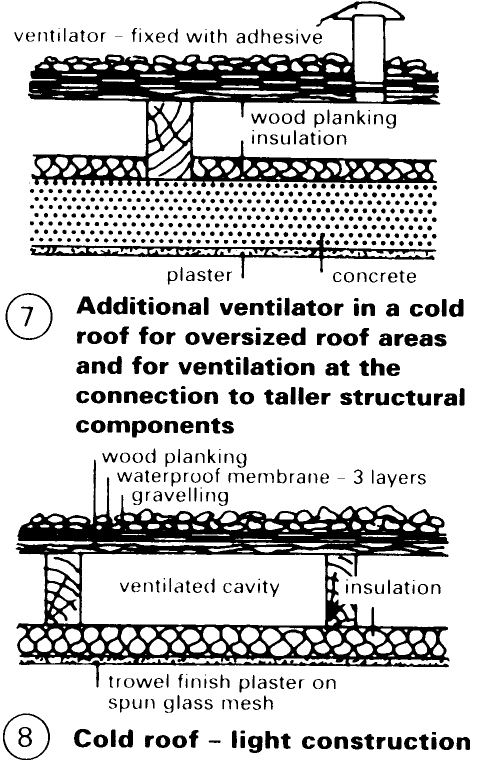

On light constructions, the internal temperature range should be improved by additional heavy layers (heat storage) under the insulation. Unfavourable internal temperature range: temperature fluctuations almost the same as those outside implies an internal climate similar to that of an unheated army hut; this cannot be improved by thermal insulation alone. A quick response heating system and/or additional thermal mass is required. For the artificial ventilation of rooms under cold roofs, always maintain a negative pressure; otherwise, room air will be forced into the roof cavity.
Date added: 2023-01-01; views: 686;
