Roof Gardens. History. Roof Construction
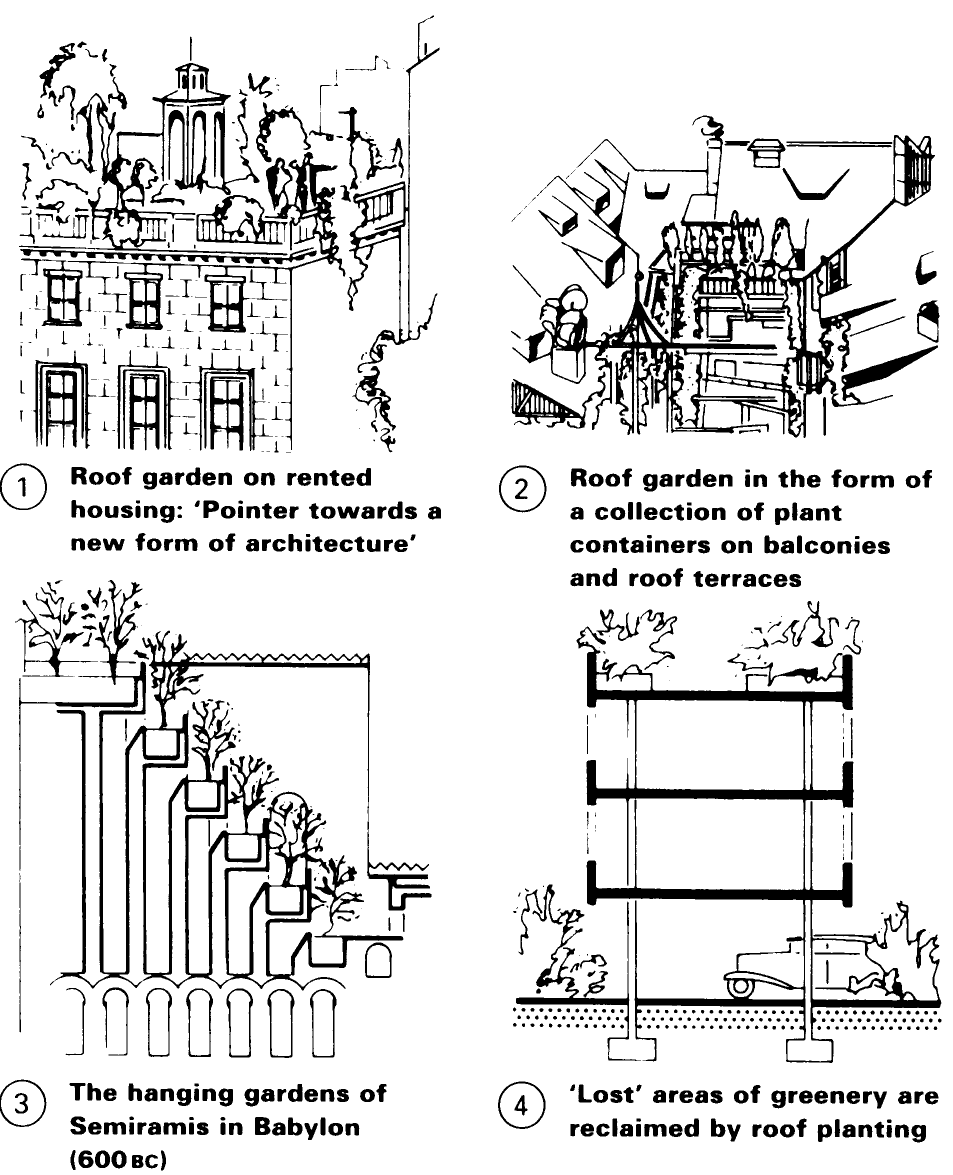
The concept of roof gardens and roof cultivation had already been exploited by the Babylonians in biblical times by 600вс. In Berlin, in 1890, farm house roofs were covered with a layer of soil as a means of fire protection, in which vegetation seeded itself. Le Corbusier was the first in our century to rediscover the almost forgotten green roof.
The characteristics of roof cultivation:
1. Insulation by virtue of the layer of air between blades of grass and through the layer of soil, with its root mass containing microbial life processes (process heat).
2. Sound insulation and heat storage potential.
3. Improvement of air quality in densely populated areas
4. Improvements in microclimate.
5. Improves town drainage and the water balance of the countryside.
6. Advantageous effects for building structures: UV radiation and strong temperature fluctuations are prevented due to the insulating grass and soil layers.
7. Binds dust.
8. Part of building design and improves quality of life.
9. Reclamation of green areas.
Roof slope. The slope of a double pitch roof should not be greater than 25°. Flat roofs should have a minimum slope of 2-3%.
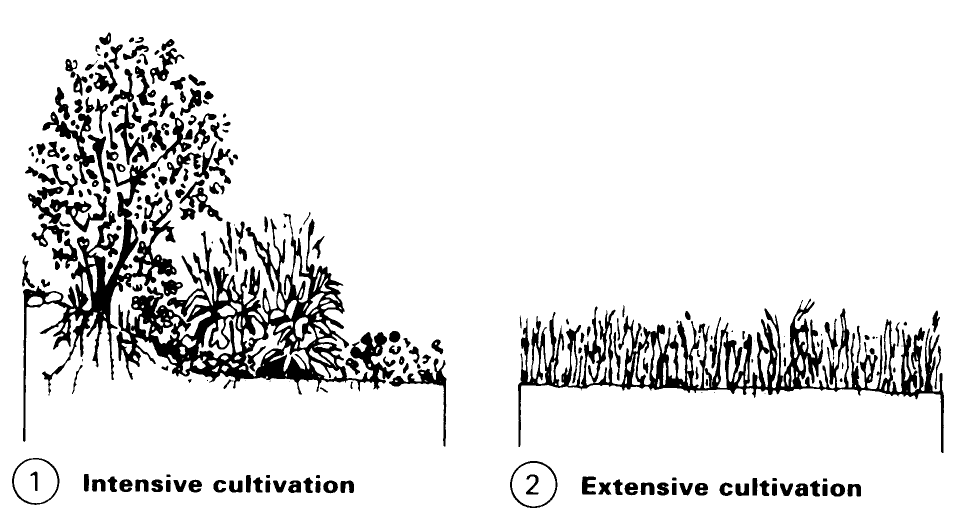
Types of roof cultivation. Intensive cultivation: the roof is fitted out as a domestic garden, with equipment such as pergolas and loggias; continual attention and upkeep are necessary; planting - grass, shrubs and trees. Extensive cultivation: the cultivation requires a thin layer of soil and requires a minimum of attention; planting - moss, grass, herbs, herbaceous plants and shrubs. Mobile cultivation: plants in tubs, and other plant containers serve for the cultivation of roof terraces, balustrades and balconies.
Watering. Natural watering by rain water: water is trapped in the drainage layer and in the vegetation layer. Accumulated water: rain water is trapped in the drainage layer and is mechanically replenished if natural watering is inadequate. Drip watering: a water drip pipe is placed in the vegetation or drainage layer to water the plants during dry periods. Sprinkling system: sprinkling system over the vegetation layer.
Fertiliser. Fertiliser can be spread on the vegetation layer or mixed with the water during artificial watering.
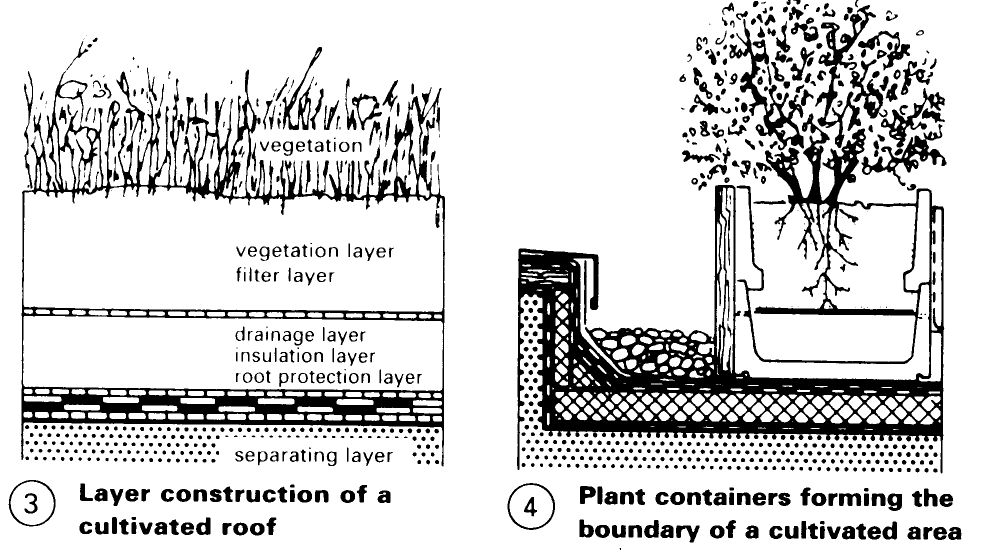
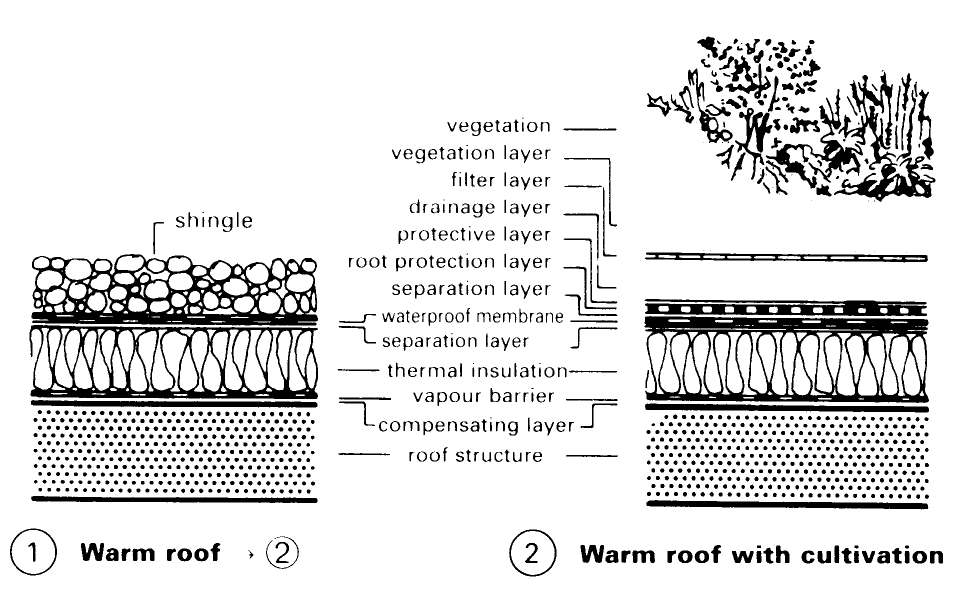
Roof Construction. For the vegetation layer, expanded clay and expanded slate are used, these materials offering structural stability, soil aeration, water storage potential and lending themselves to landscaping. Problems to be solved: storage of nutrients, soil reaction (pH value), through-ventilation, water storage. The filter layer, comprising filter material, prevents clogging of the drainage layer. The drainage layer prevents excessive watering of the plants and consists of: mesh fibre mats, foam drainage courses, plastic panels and protective structural materials.
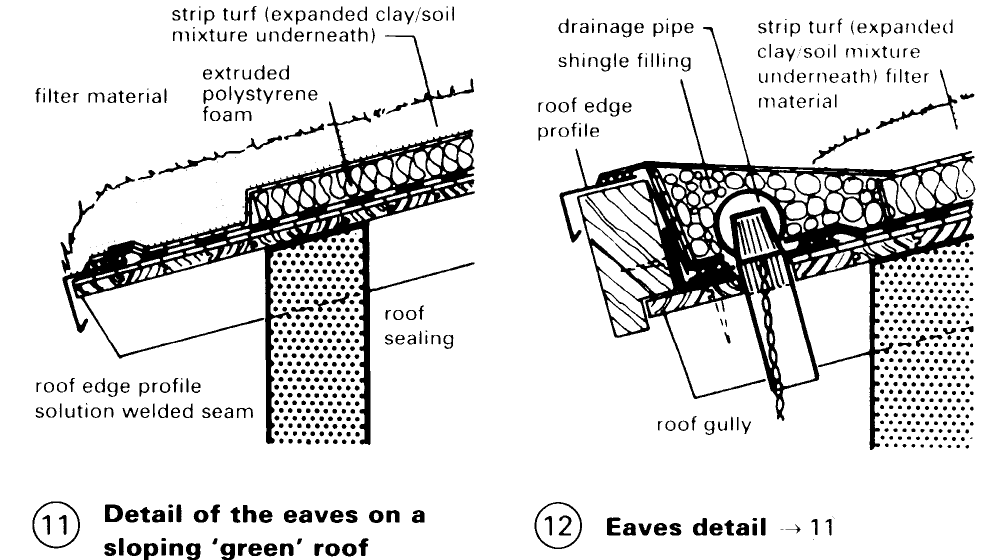
The protective layer provides protection during the construction phase and against point loading. The root protection layer of plants, etc., are retained by PVC/ECB and EPDM sheeting. The separating layer separates supporting structure from the roof cultivation. Examples (1) – (8) illustrate a range of customary flat roof structures and variations incorporating roof cultivation. Before roof cultivation is applied, the integrity of the roof and of the individual layers must be established.
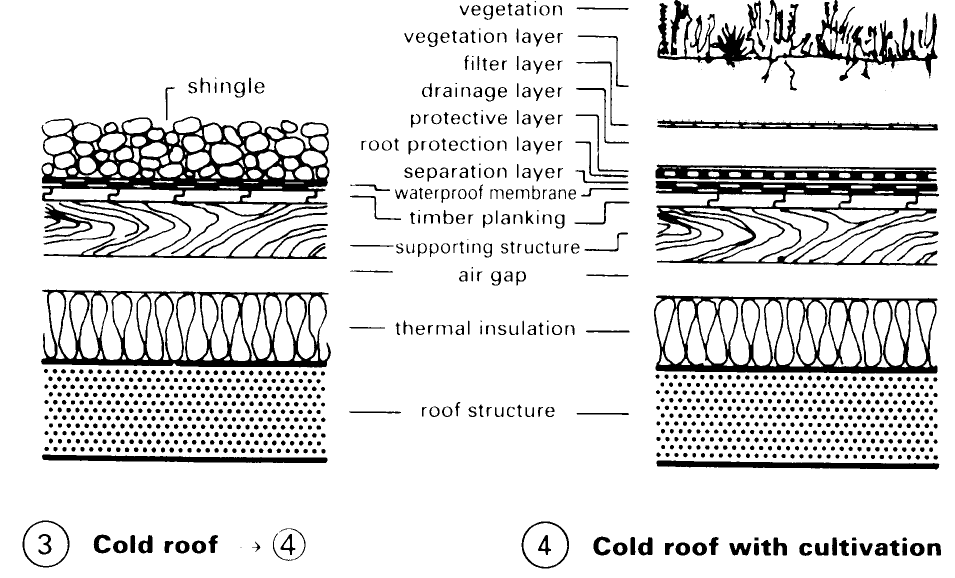
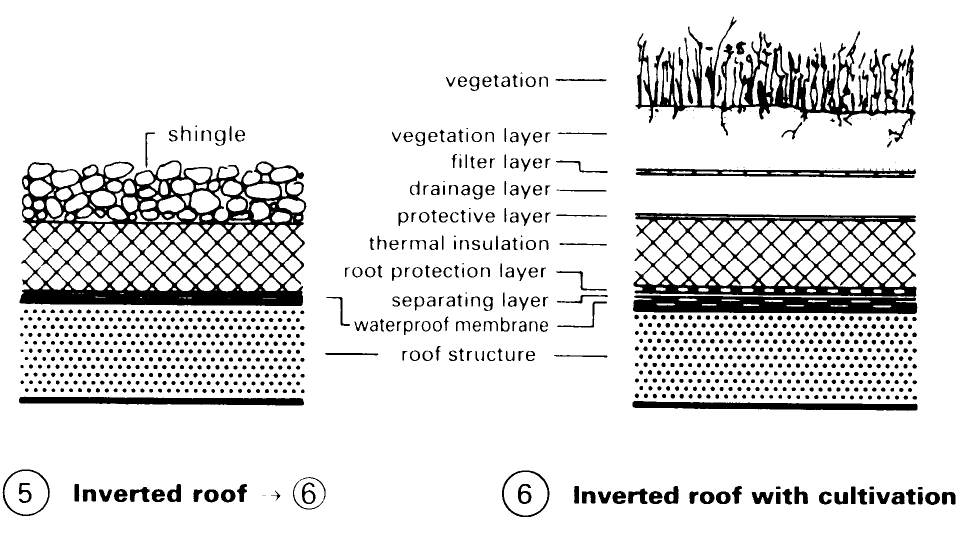
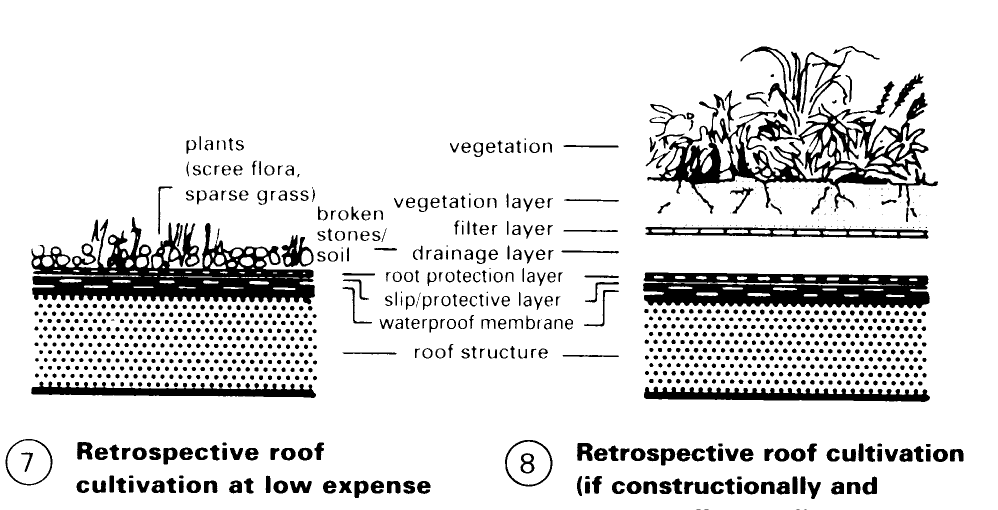
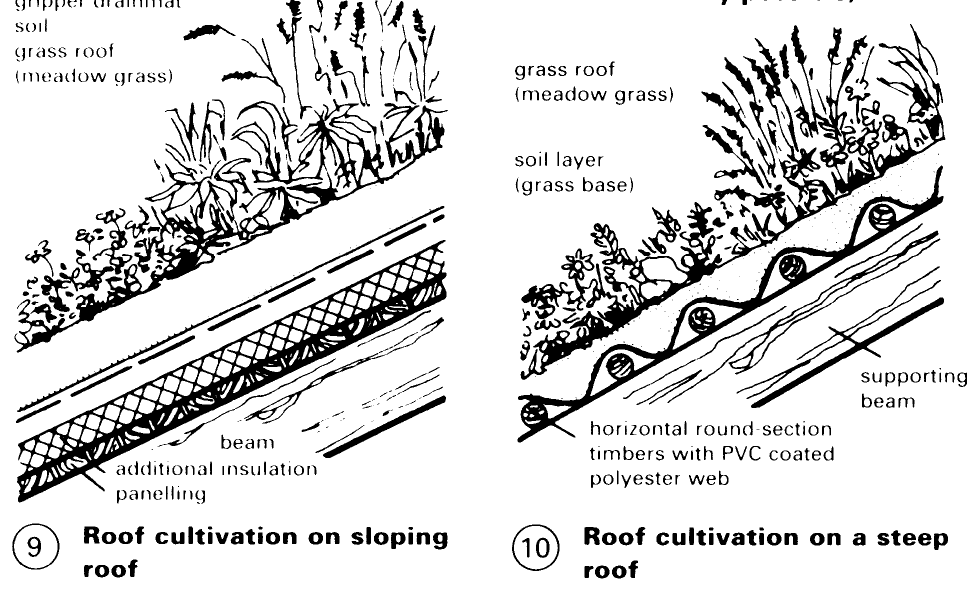
The technical condition of the roof surface must be carefully checked. Attention should be paid to: construction of the layers (condition); correct roof slope; no unevenness; no roof sagging; no waterproofing membrane faults (bubbles, cracking); expansion joints; edge attachments; penetrating elements (light shafts, roof lights, ventilating pipes); and drainage. Double pitch roofs can also be cultivated, but much preparatory construction work is needed when inclined roofs are cultivated (danger of slippage, soil drying out) (9) – (12).
Date added: 2023-01-01; views: 686;
