Loft Windows. Windows: Construction. Windows: Cleaning
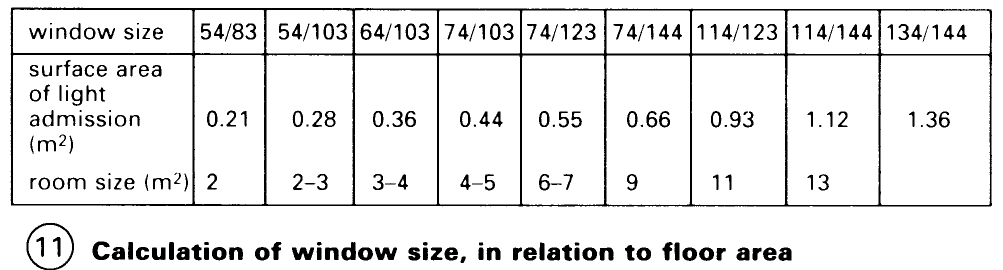
In planning the size of windows, the optimum daylight level relative to the purpose of the room must be the deciding factor. For instance, building regulations require a minimum window area of 1/8 of the floor surface area for living rooms – (11).
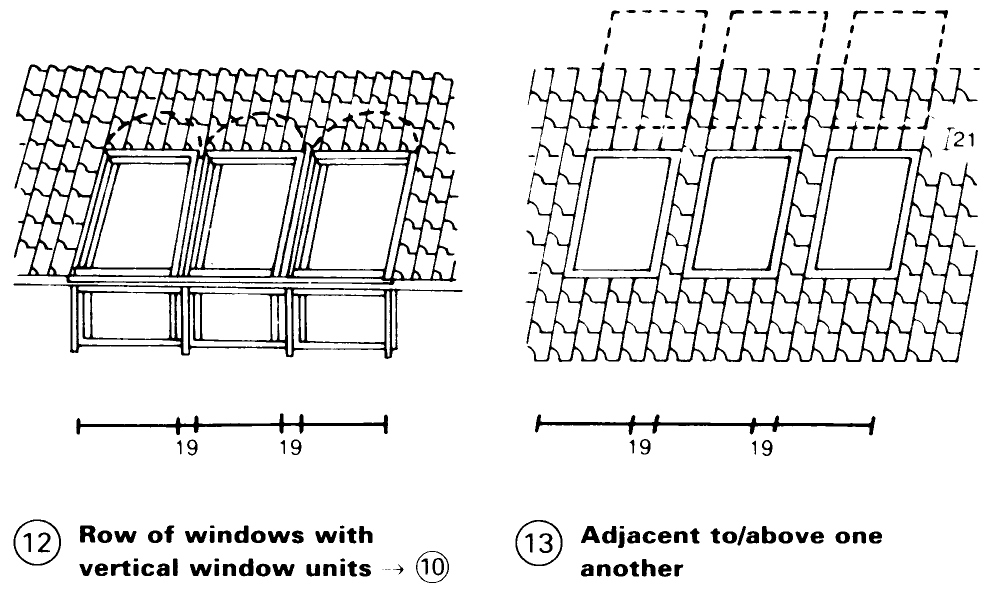
Large windows make living rooms more comfortable. The window width in secondary rooms can be chosen according to the distance between the rafters. Generously wide windows in living rooms can be achieved by the inclusion of rafter trimmers. Steeper roofs need shorter windows, while flatter roofs require longer windows. Roof windows can be joined using purpose-made prefabricated flashing, and can be arranged in rows or in combinations next to or above one another (12) + (13).
Windows: Construction. Wooden sections for turning, turn and tilt, and tilting windows have been standardised. Windows are classified according to the type of casement (a) – (d) or the type of frame – (e) – (h). The many demands made on windows (e.g. protection against heat and noise) have resulted in a vast range of window shapes and designs (1) - (5). Externally mounted windows and French windows must at the very least be fitted with insulation or double glazing. The coefficient of heat transfer of a window must not exceed 3.1 W/m2K.
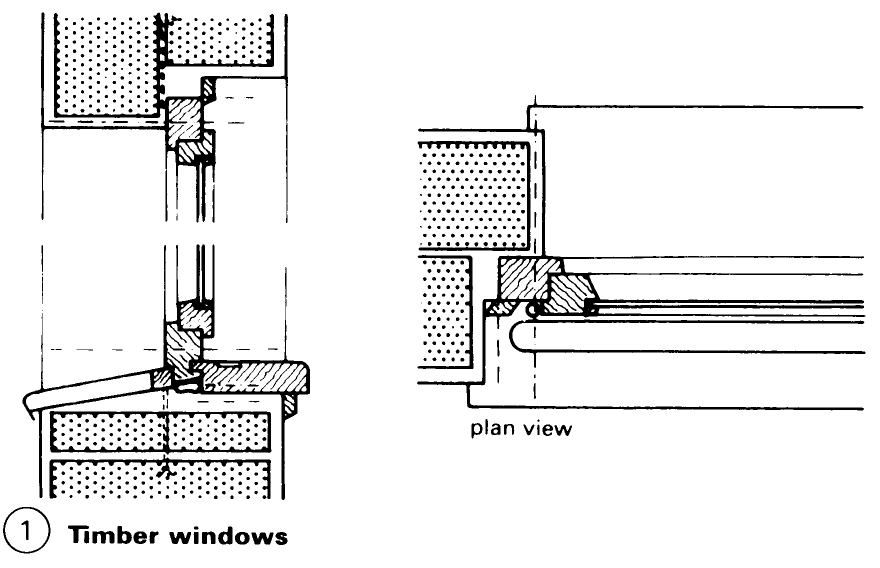
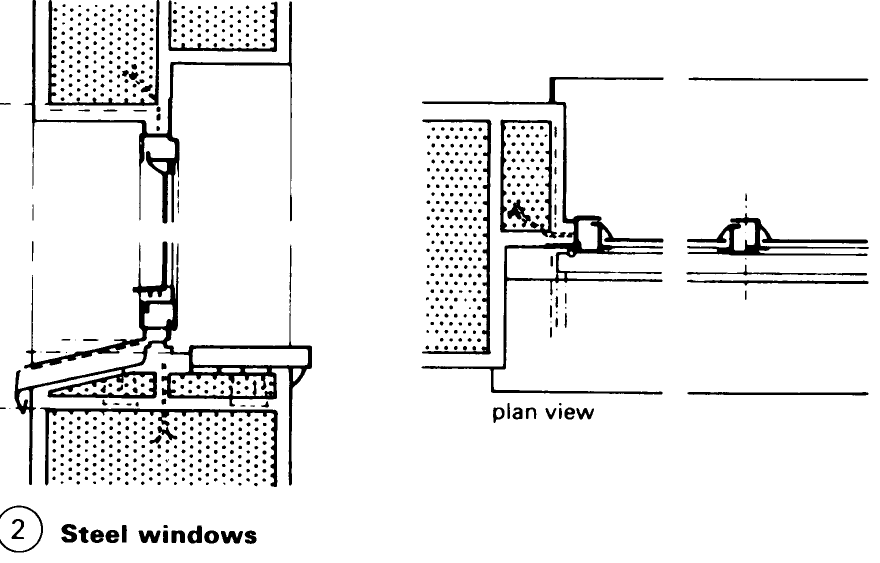
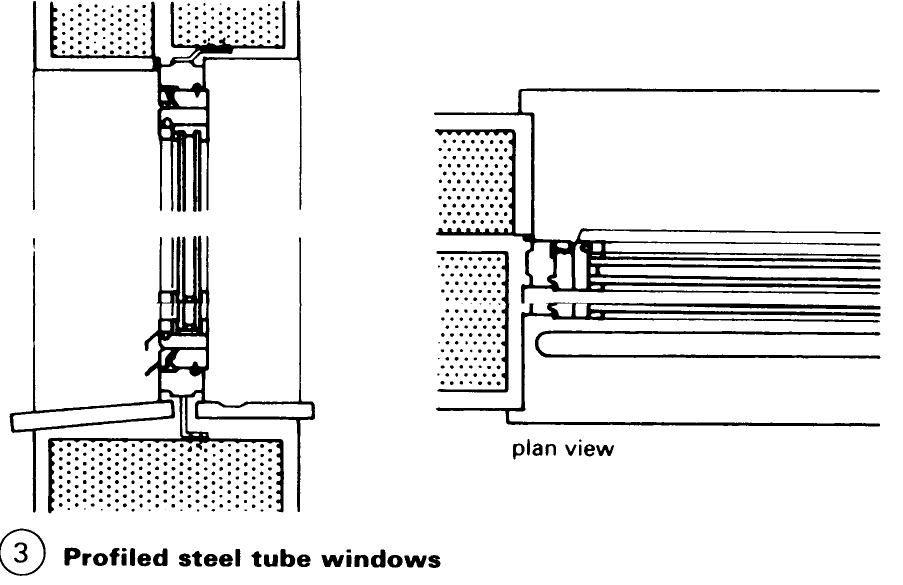
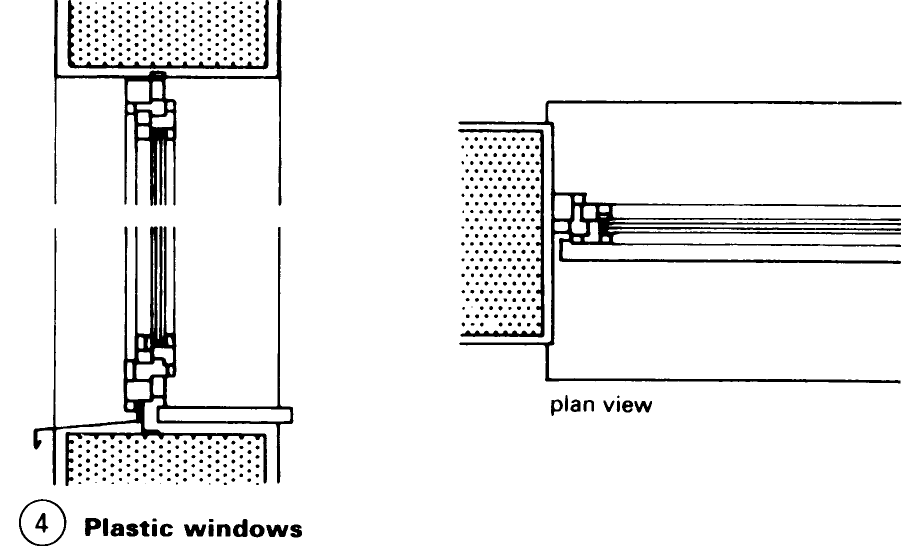
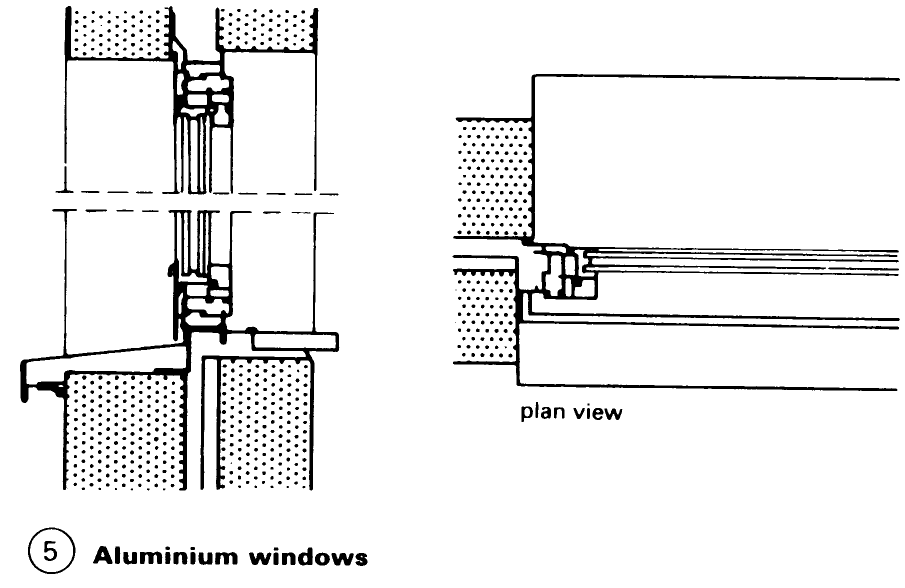
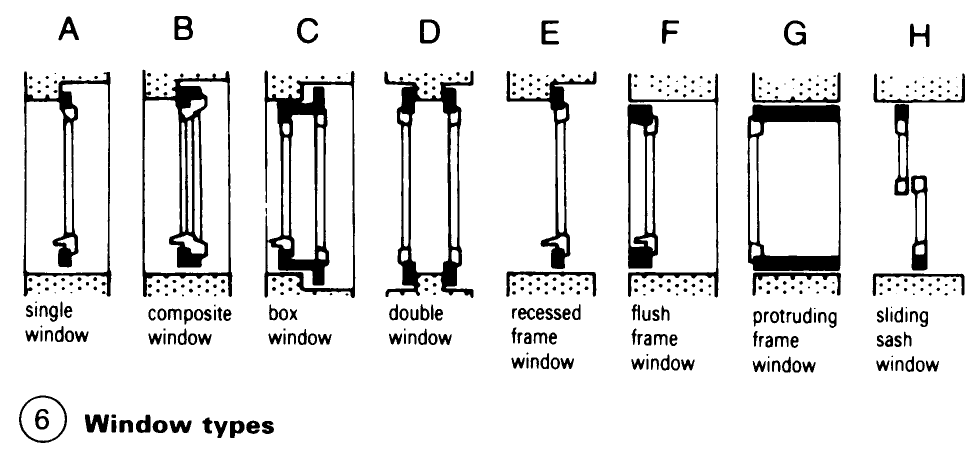
Any window design must satisfy the technical requirements of the relevant parts of the building. The main considerations are the size, format, divisions, way of opening, frame material and surface treatment. Ventilation, thermal and sound insulation, fire resistance and general safety issues, including the use of security glazing, must also be taken into account.
The design of the sections and the location and type of sealing are of great importance in guaranteeing a long-lasting water- and draught-proof seal. Built-in components such as roller shutter boxes, window sills and vents must match the noise insulation of the windows – (10) – (12) as well as other technical specifications.
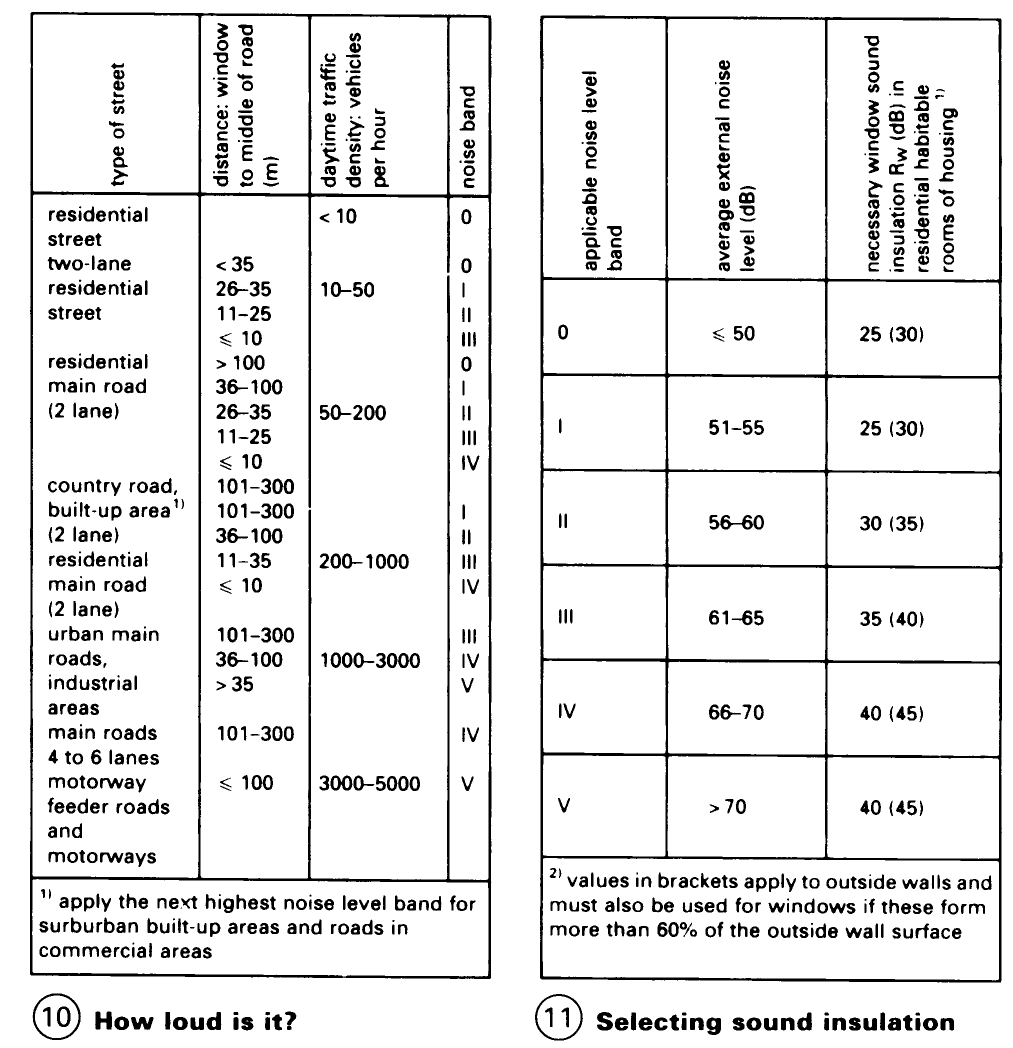
Windows: Cleaning. Safety belts with straps, safety cables or safety apparatus for working at heights should be used as a protection against falls – (1).
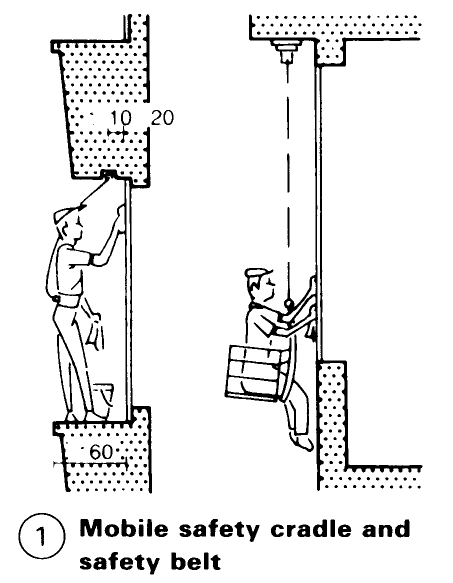
Fagade hoists and mobile equipment (allowing access to fixed glazing) for cleaning windows and fagades - (8) – (11) are available to carry out maintenance and repair work (thus saving the cost of scaffolding). If fitted at the right time, they can be used to carry out minor building work (such as fixing blinds, installing windows etc.). With slight modifications, fagade hoists and access equipment can be used as rescue apparatus in the event of a fire. The options available include mobile suspended ladders mounted on rails, trackless roof gantry equipment with a cradle, and a rail-mounted roof gantry with a cradle and attached to the roof deck or the balustrade.
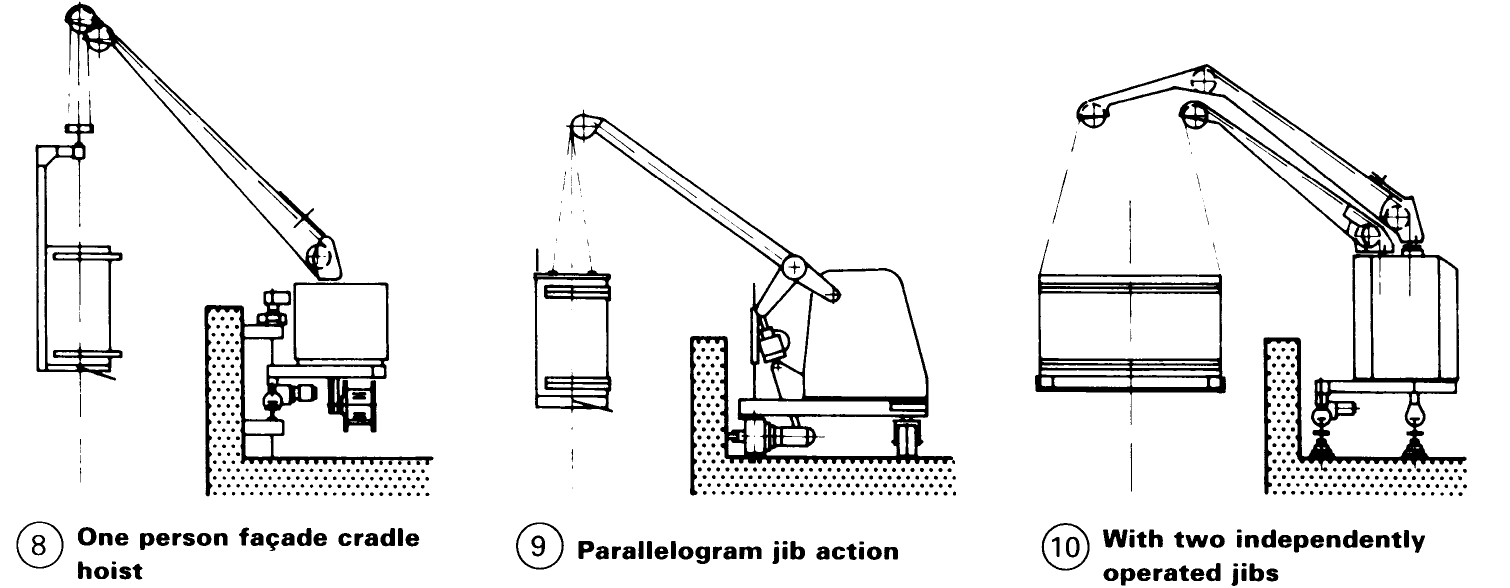
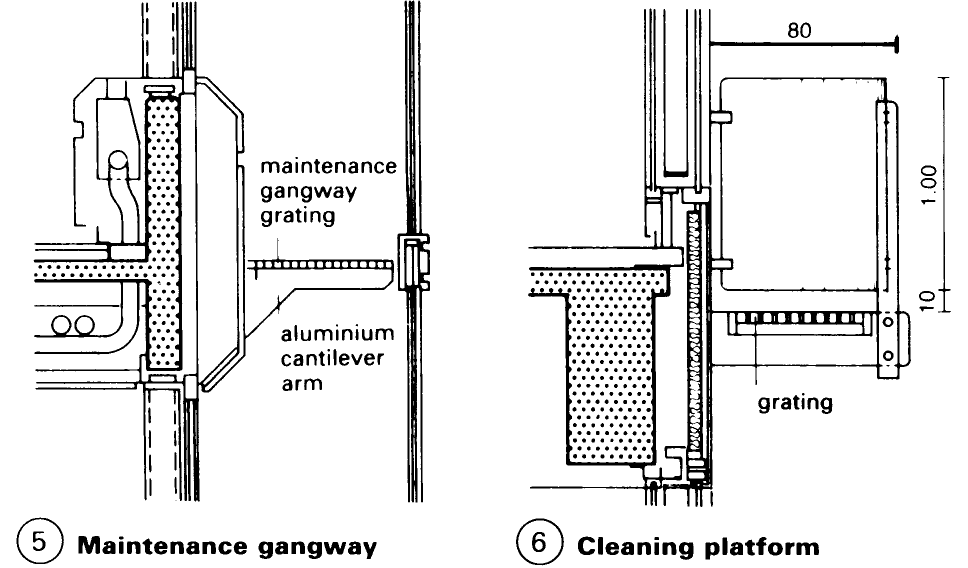
Suspended aluminium ladder equipment (for fagade access) - (2) consists of a suspended mobile ladder on rails. The width of the ladder is 724mm or 840mm, and the total overall length is 25m maximum, depending on the shape of the building. The maximum safe working load (S.W.L.) is 200kg (i.e. two men and the apparatus itself). Alternatives are available, such as maintenance gangways (5) and cleaning balconies – (6).
Date added: 2023-01-01; views: 682;
