Fire-resistant Glass. Skylights and Dome Rooflights
Normal glass is of only limited use for fire protection. In cases of fire, float glass cracks in a very short time due to the one-sided heating, and large pieces of glass fall out enabling the fire to spread. The increasing use of glass in multistorey buildings for fagades, parapets and partitions has led to increased danger in the event of fire. In order to comply with building regulations, the fire resistance of potentially threatened glazing must be adequate.
The level of fire resistance of a glass structure is classified by its resistance time: i.e. 30, 60, 90, 120 or 180min. The fire resistance time is the number of minutes that the structure prevents the fire and combustion gasses from passing through. The construction must be officially tested, approved and certificated – (1).
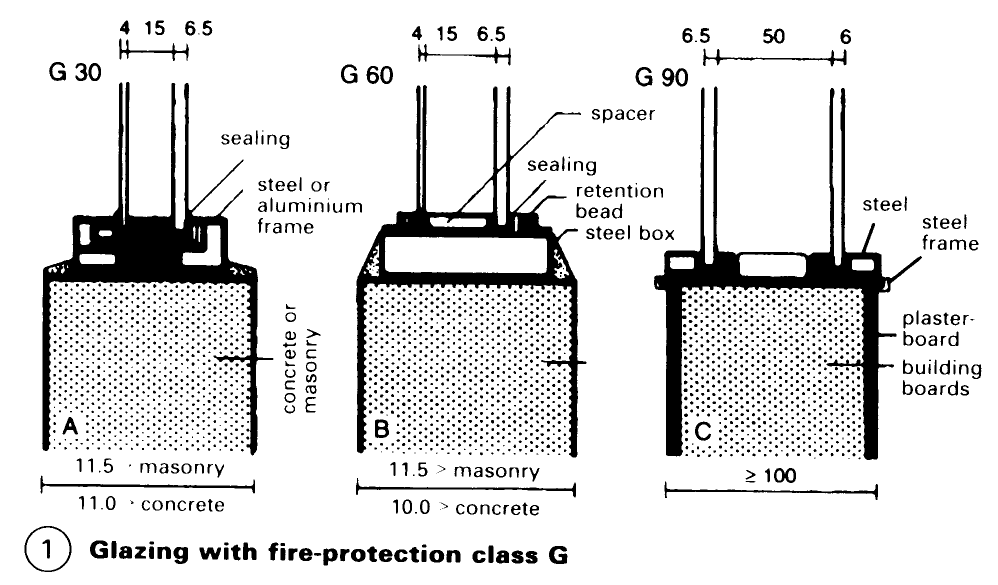
Fire-resistant glass comes in four forms: wired glass with point-welded mesh, maximum resistance 60-90 min; special armoured glass in a laminated combination with double-glazing units; pre-stressed borosilicate glass, e.g. Pyran; multi-laminated panes of float glass with clear intumescent interlayers which turn opaque on exposure to fire, e.g.
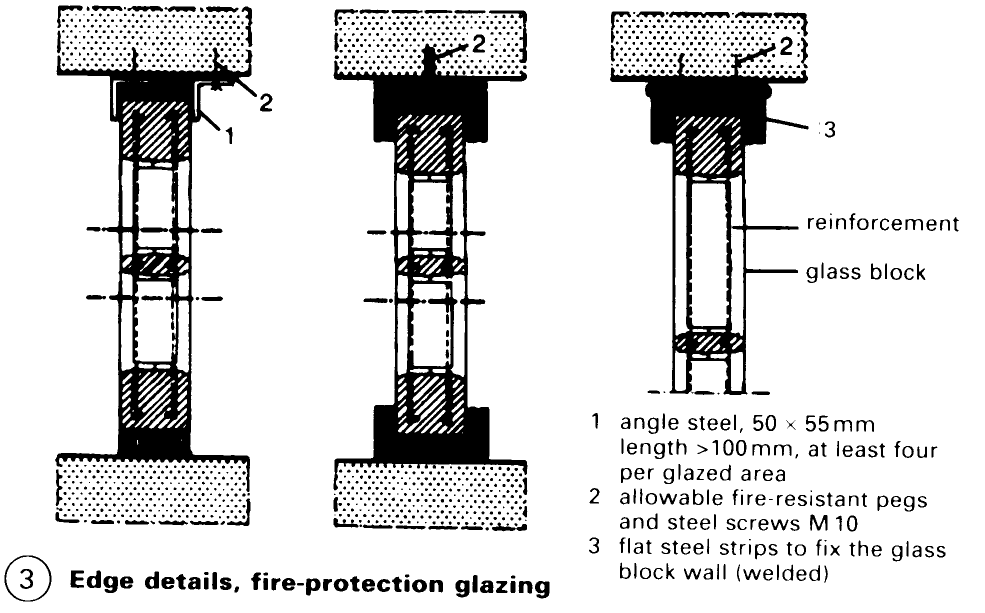
Glass blocks with steel reinforcement. Fire-resistant, steel-reinforced glass blocks can, as with all other glass block walls, be fixed to the surrounds with or without U sections. All other types of fixing methods are also applicable. Because of the strongly linear spread of fire and the production of combustion gases, fire-resistant glass block walls should be lined all round with mineral fibre slabs (stonewool) (3).
Sound reduction. Because of its weight, a glass block wall has particularly good sound insulation properties:
1.00kN/m2 with 80mm glass blocks;
1.25kN/m2 with 100mm glass blocks;
1.42 kN/m2 with special BSH glass blocks.
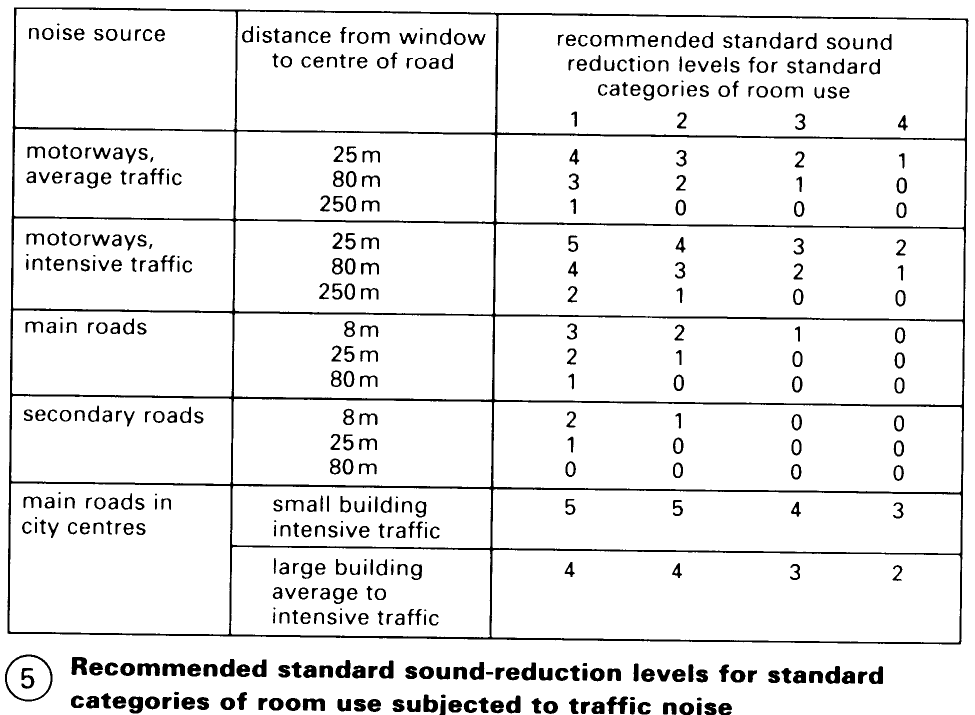
To be effective, the surrounding building elements must have at least the same sound reduction characteristics. Glass block construction is the ideal solution in all cases where good sound insulation is required. In areas where a high level of sound reduction is necessary, economical solutions can be achieved by using glass block walls to provide the daylight while keeping ventilation openings and windows. These can serve as secondary escape routes if they conform to the minimum allowable size.
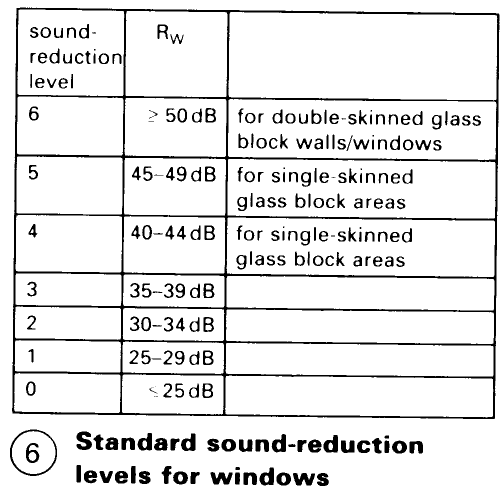
Follow the relevant regulations with regard to sound reduction where the standards required for particular areas can be found. The sound reduction rating (R'w) can be calculated from the formula R'w = LSM + 52dB (where LSM is the reduction value of airborne sound) – (5). Single-skin glass block walls can meet the requirements of sound reduction level 5 – (6).
Skylights and Dome Rooflights. Domes, skylights, coffers, smoke vents and louvres, as fixed or moving units, can be used for lighting and ventilation, and for clearing smoke from rooms, halls, stair wells etc. All these can be supplied in heat-reflecting Plexiglas if required.
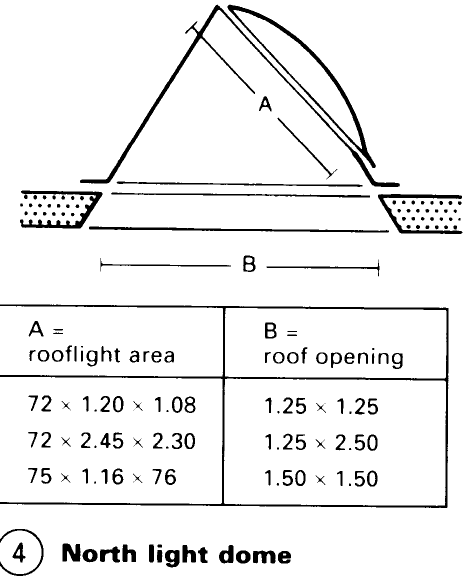
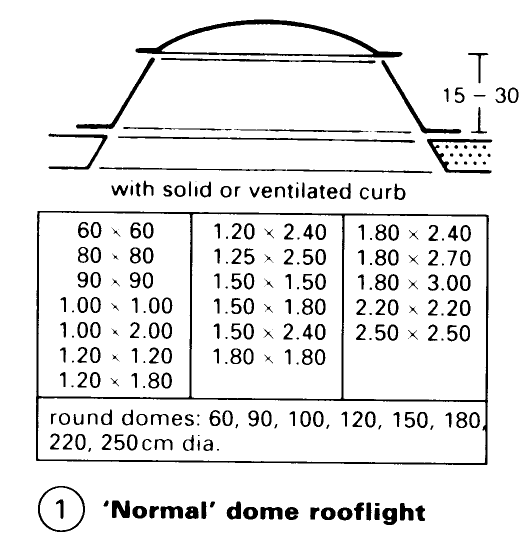
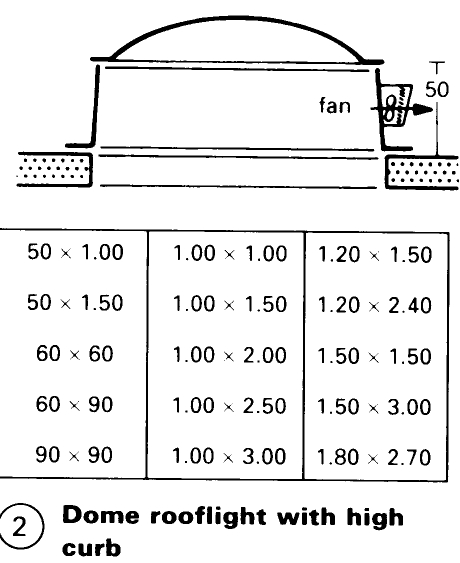
By directing the dome towards the north (in the northern hemisphere), sunshine and glare are avoided – (4). The use of high curb skylights (1) will reduce glare because of the sharp angles of incidence of the sunlight. Dome rooflights used for ventilation should face into the prevailing wind in order to utilise the extraction capacity of the wind. The inlet aperture should be 20% smaller than the outlet aperture. Forced ventilation, with an air flow of 150-1000m3/h, can be achieved by fitting a fan into the curb of a skylight - (2). Dome rooflights can also be used for access to the roof.
Attention should be given to the aerodynamic extraction surfaces of smoke exhaust systems. Orientating each extraction unit at an angle of 90° from the adjacent one will allow for wind coming from all directions. Position to leeward/windward if pairs of extraction fans are to be mounted in line with or against the direction of the prevailing wind.
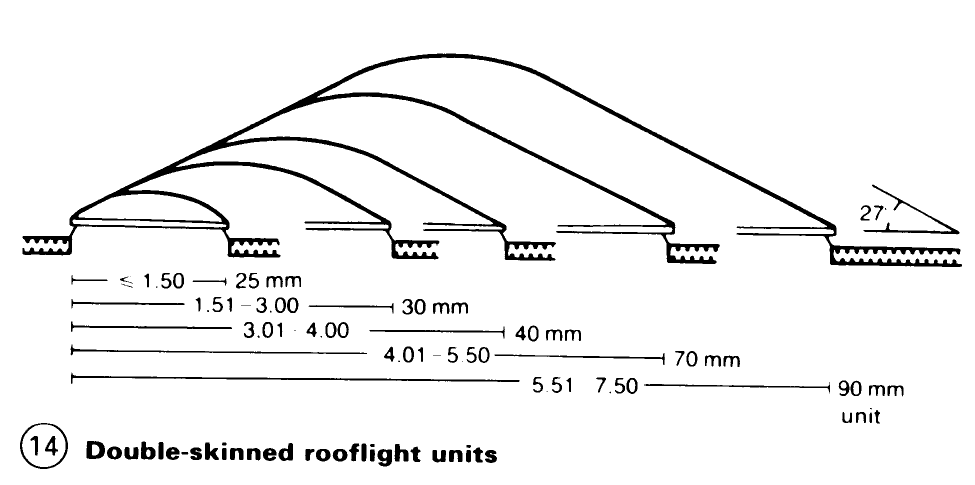
Smoke extraction vents are required for stair wells more than four complete storeys high. Variable skylight aperture widths up to 5.50m are available, as is a special version up to 7.50m wide which does not need extra support.
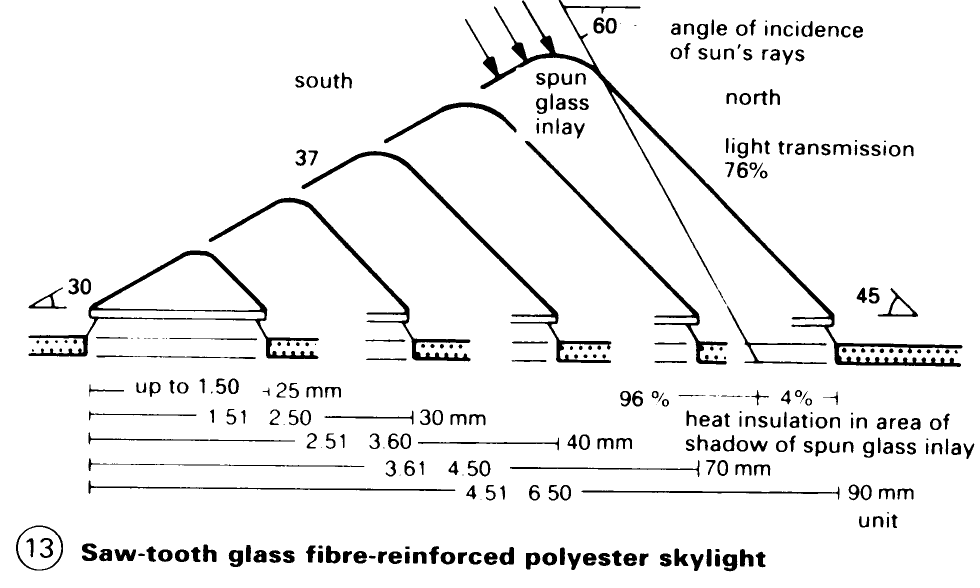
Skylight systems offer diffuse room lighting which is free from glare – (14). North-facing skylights with spun glass fibre inlays guarantee all the technically important advantages of a workshop illuminated by a north light – (13). Traditional flat roofs can be modified to admit a north light by inserting skylights with curbs.
Date added: 2023-01-01; views: 603;
