Laboratories. Lab Workstation. Ventilation
Laboratories differ according to type of use and discipline.
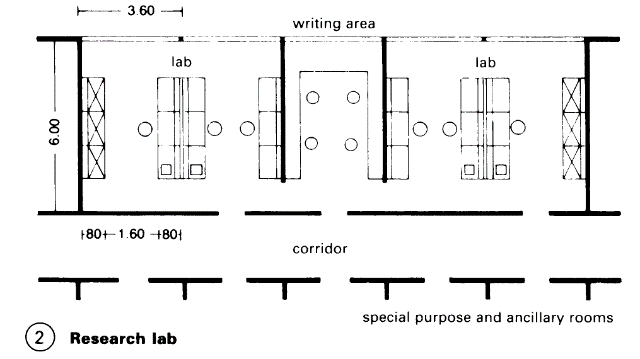
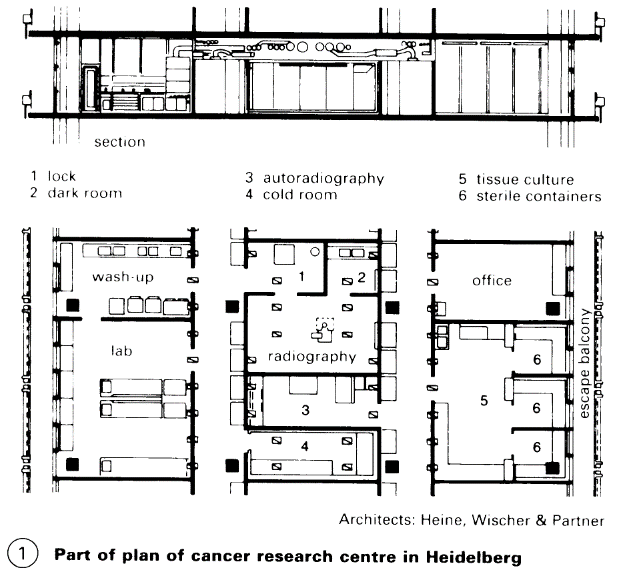
According to use: Laboratories for teaching and practical, comprising a large number of workstations, usually with simple basic equipment. (3) Research labs are usually in smaller spaces with special equipment and additional rooms for activities such as weighing and measuring, centrifuges and autoclaves, washing up, climatised and cold storage rooms with constant temperature, photographic rooms/dark rooms, etc. - (2).
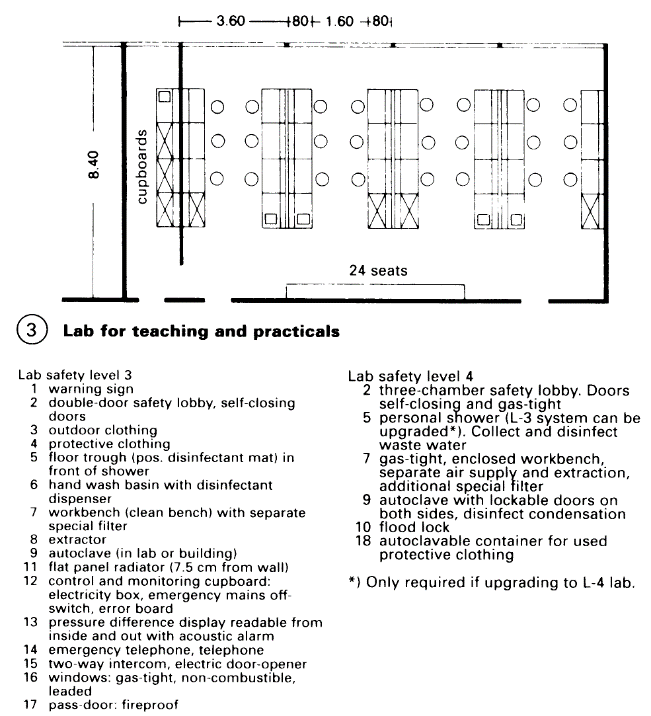
According to subject: Chemistry and biology labs with fixed benches. Rooms have frequent air exchange, often additional fume cupboards (digestors) for work which produces gas or smoke. Digestors often in separate rooms. Physics labs mainly with movable benches and a range of electrical installations in trunking in the wall or suspended from the ceiling; few air changes. Special labs for specific requirements, e.g. isotope labs for work with radioactive substance in differing safety categories.
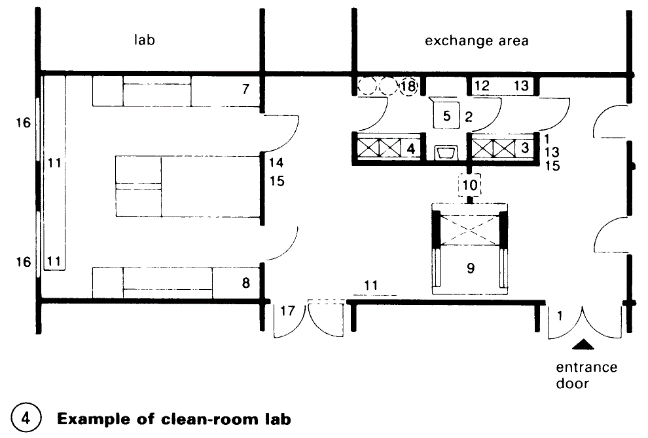
Clean-room labs - (4) for work needing dust-free filtered air, e.g. in the field of microelectronics or for particularly dangerous substances, which should be prevented from entering surrounding rooms by separate air circulation and filtering systems (microbiology, genetic engineering, safety levels L1-L4).
Unserviced work rooms are also part of the lab area: Study cells, service rooms for lab. personnel. Also central rooms such as general storerooms, chemicals stores and supplies with special protective equipment, isotope stores with cooling containers, etc. Experimental animals are kept in a special location. Particular kinds of equipment are needed, depending on the type of animal and they have differing requirements for separate air circulation.
Lab workstation. The bench, fixed or movable, is the module which determines the lab workstation; its measurements, including work space and passage space, form the so-called lab axis, the basic spatial unit. Normal measurements for standard workbench: 120cm width for practicals, several times this for a research lab, 80cm depth of work surface including energy conduit (5) - (6).
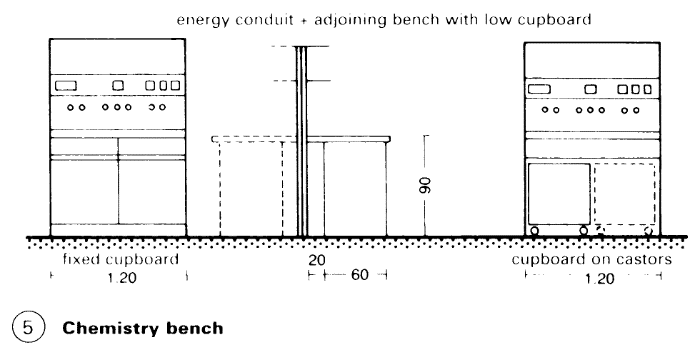
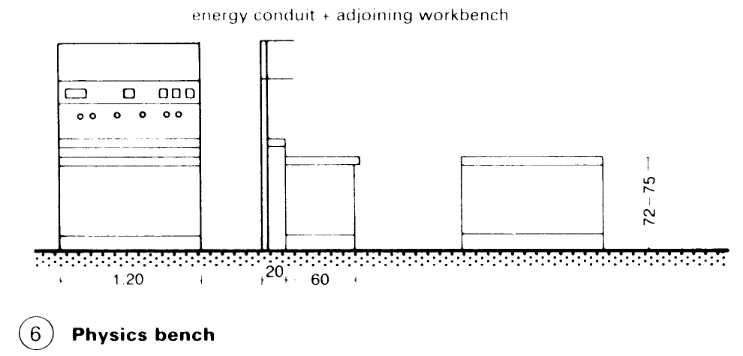
Benches and fume cupboards are usually part of a modular system, width of elements 120cm, fume cupboards 120 and 180cm (7). The conduit carries all the supply systems; benches and low cupboard are placed in front of it > (5) – (7).
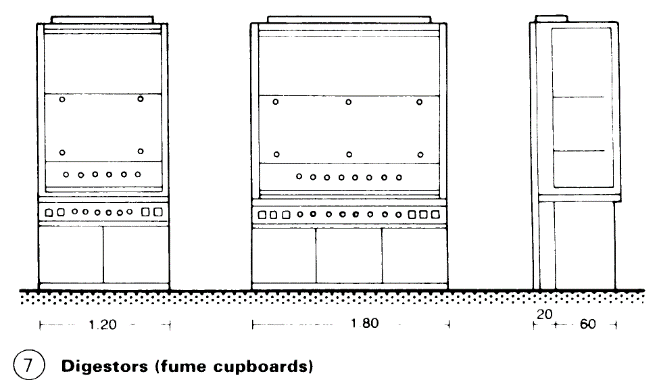
Benches are made of steel tubing, with work-surfaces of stoneware panels without joints, less frequently tiles, or chemical-resistant plastic panels. Low cupboards are of wood or chipboard with plastic laminate. Supply services are from above from the ceiling void, or from below through the floor structure.
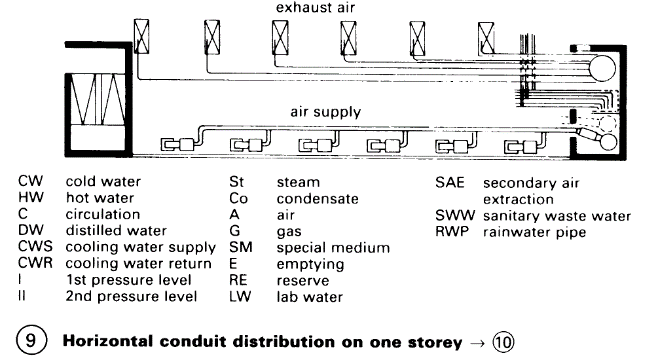
Ventilation: Low-pressure or high-pressure systems, the latter are recommended particularly in multi-storey buildings for institutes with higher air requirement in order to reduce the cross-sections of the ducts. Cooling and humidification as required. Ventilation systems have the highest space requirement of all services.
Labs where chemicals are used must have artificial air supply and extraction. Air changes per hour:
chem. labs 8
biology labs 4
physics labs 3-4 (in extraction area)
Electrical services: Where a high number of connections and special supplies of electricity are required, a separate transformer in the building is essential. Electrical plant must be in a fireproof enclosure without any other cables running through it.
There are various possible arrangements of service ducts, columns and vertical circulation cores:
1. Services concentrated in internal main shafts at each end of the building, vertical circulation core inside
2. Services concentrated in external shafts at each end of the building, vertical circulation core outside
3. Services concentrated in main shafts centrally in each part, circulation core as link element
4. Services distributed in discrete duct installations, vertical circulation core inside
5. Main services inside linked to vertical circulation core
6. Service shaft outside, vertical circulation core off-centre
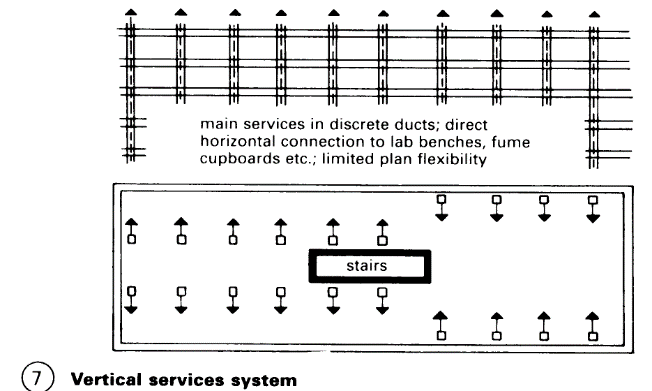
Vertical services system. There are many vertical service ducts inside the building or on the fagade, taking the services directly into the labs in separate ducts: decentrally distributed air supply and exhaust air to fume cupboards, separate ventilators on the roof.
Advantages:
Maximum supply to individual workplaces. Short, horizontal connections to the bench
Disadvantages:
Plan flexibility limited, more space needed on services plant floor – (7).
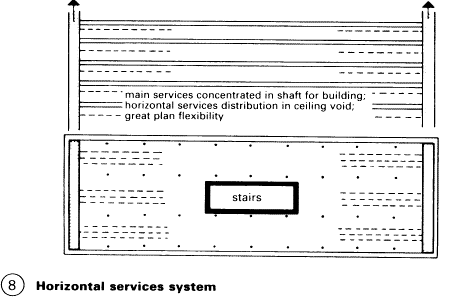
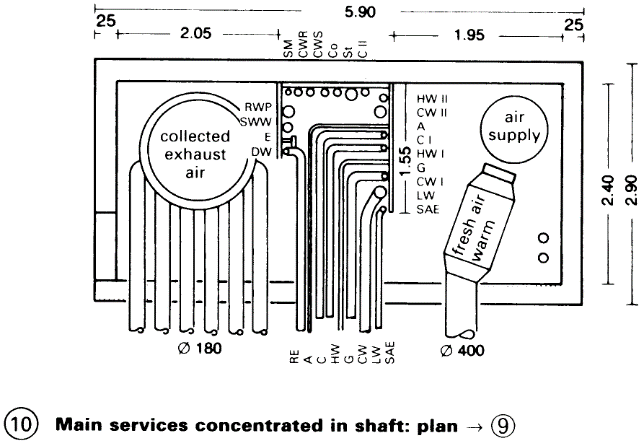
Horizontal services system. Vertical main services concentrated in shafts and distributed from there horizontally via the service plant floors to the bench by connections from above or below.
Advantages:
Fewer conduits and less space needed for the services ducts, greater flexibility of plan, easier maintenance, central ventilation plants, later installation easier - (8). High density of services requires more space. Vertical mains ducts with concentrated services are more manageable, access is easier and they can be installed later. Conduits insulated from heat, cold, condensation and noise – (9) – (10).
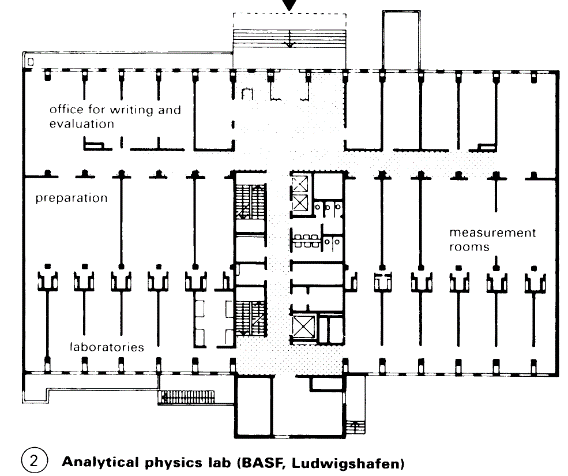
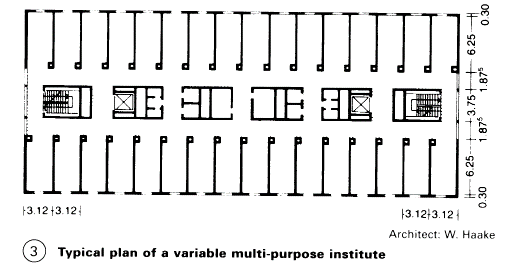
Rooms are used according to a schedule of accommodation and plan. Rooms with natural or artificial light and ventilation, with high or low servicing, allow the creation of zones of differing use and technical qualities. For this reason laboratory buildings often have large internal areas (with two corridors) (1) + (3). The building length depends on the longest reasonable horizontal run of wet services.
Services floors for plant in the basement or at roof level.
Grid for structure and fittings: For adaptability of use, a reinforced concrete frame structure, pre-cast or poured in-situ, is preferable. The main structural grid is a multiple of the typical planning grid of 120 x 120cm (decimal system). A convenient structural grid for a large proportion of rooms without columns is: 7.20 \ 7.20m, 7.20 x 8.40m, 8.40 x 8.40m. Storey height normally 4m, clear room height up to 3.0m.
Columns stands on the grid off-set from the planning grid to increase the flexibility of the servicing. Separation is by a system of partitions and suspended ceilings which enclose the rooms. Movable dividing walls should be easy to assemble and have chemical-resistant surfaces. Ceilings should be designed to be disassembled and should absorb sound. Floor coverings should be water- and chemical- resistant, without joints and be poor electrical conductors: as a rule welded plastic sheet or tiles.
Provide viewing windows into the labs from the corridor or in the doors.
Isotope labs have smooth surfaced walls and ceilings without pores, rounded corners, shielded in lead or concrete, waste water monitoring, with shower cubicles between the lab and exits. Concrete container for active waste and refuse, concrete safe with lead doors, etc.
A weighing table is part of every lab, usually in a separate balance room. Benches lie along the wall in front of vibration-free walls.
Date added: 2023-01-05; views: 756;
