Libraries. Floor Area Calculation for Double-sided Shelving
Facilities inside the controlled area should include reading room information, bibliographies, on-line catalogue terminals, the issue and return of books which can only be used in the reading room, copying equipment (in separate rooms), open- access book shelves, work spaces and, if necessary, the open- access book stacks.
Facilities outside the controlled area should include cloakrooms or briefcase and coat lockers, toilets, a cafeteria, a newspaper reading area, an exhibition room, lecture and conference rooms (possibly for use outside library opening hours), an information desk (central enquiries), card and microfiche indexes, on-line catalogue terminals, book return and a collection area for ordered/reserved books.
The provision of work spaces in college libraries depends on the number of students and the distribution of individual subject groups. Special work places are required for people with disabilities (wheelchair users and the visually impaired) and for special operations (microform reading and enlarging equipment, PCs, terminals, use of CD-ROMs etc; take note of the relevant guidelines), as well as for individual study (cubicles, carrels, individual work rooms). Work spaces should preferably be in daylight areas. The area required for a simple reading/work place is 2.5m2; for a PC or individual work place, > 4.0m2 is needed.
Security is vitally important in user areas. Fire precautions must comply with national and local building regulations and procedures. The installation of a book security system will prevent theft, and the optimal security of unsupervised escape exits is achieved with automatic electronic lock-up when an alarm is triggered. Securing emergency doors mechanically with acoustic and/or visual alarms is less effective.
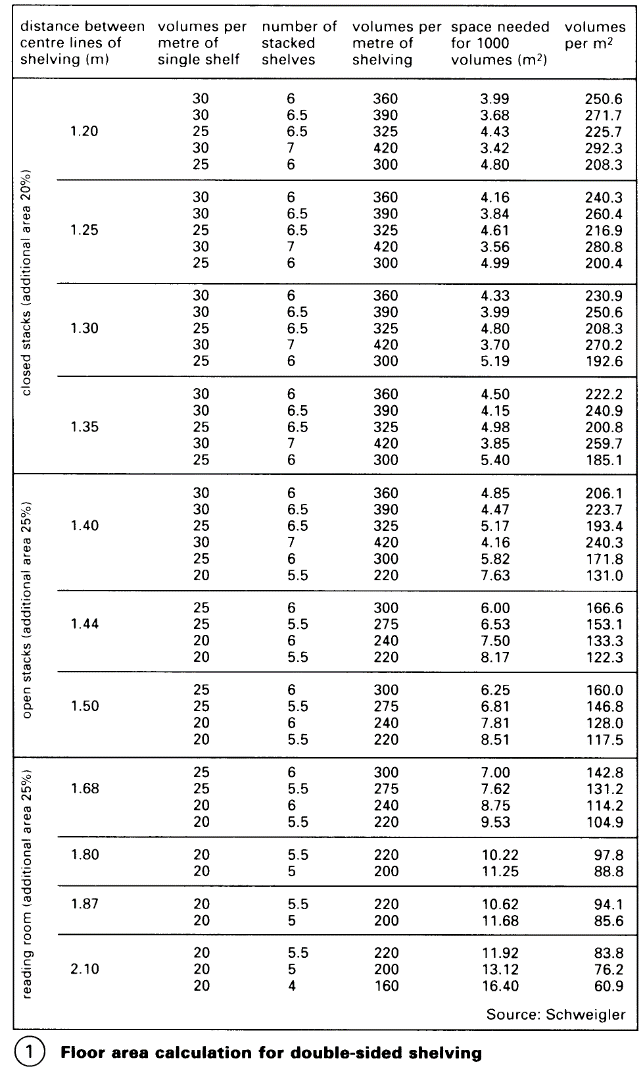
The archive store is best situated in the basement because of the high floor loads and the more even climate. 'Book towers' are not convenient because of the increased need for climate control, transport and staff, as well as limited flexibility. The most efficient method is to have linked areas which are as large as possible without changes in level. The divisions between fixed stacks and those of mobile (compact) systems are dependent on the structural grid of the columns. Capacity can be increased by approx. 100% by using mobile stacks. The floor loading with fixed stacks is at least 7.5kN/m2; with mobile stacks it is at least 12.5kN/m2 .
The internal climate in user areas should be 20° ±2°C, with approx. 50 ±5% relative air humidity and air changes (fresh replacement air) of 20m3 per hour per person. These values can be increased or reduced depending on the weather conditions. Avoid direct sunlight, since UV and heat radiation destroy paper and bindings. Because of the high energy consumption, and therefore high running costs, air conditioning should be introduced only where absolutely necessary. Natural ventilation is possible with narrow buildings.
The internal climate in archive stores should be 18° ±2°C, with 50 ±5% relative air humidity and air changes (fresh replacement air) of >3m3hr1nrr1. Air filtration is necessary to eliminate any harmful substances in the atmosphere (e.g. dust, S02, NOx etc.). By using wall materials with good moisture- and heat-retaining properties, it is possible to reduce the necessity for air conditioning. Slight air circulation is necessary to prevent the growth of mould, particularly with mobile stacks (use open ends). Special collections and materials (e.g. photographic slides, film, and sound and data media, as well as cards, plans and graphics) require a special internal climate. The internal environment should be appropriate to each area of the library, rather than being uniform throughout, and no open-plan offices should be sited in administrative areas. However, full environmental control is needed in stacks, because the building structure alone cannot provide suitable condition.
Floor loading in administration and book-processing areas should be >5.0kN/m2. In technical areas (workshops), individual structural requirements will depend on the types of machinery and equipment. Reinforced concrete and steel-frame buildings with a structural grid of >7.20m x 7.20m have been found to be suitable owing to the flexibility they allow in fitting out. Room heights should be >3.00m.
Transport books horizontally in book trolleys (avoid thresholds; changes of level should have ramps <6% or platform lifts) and/or on conveyer belts. Transport books vertically in lifts, on conveyer belts (the route must be planned very carefully, with sloping inclines; very low maintenance costs), by a container transport system (mechanically programmable, a combination of horizontal stretches and paternoster lifts) or by an automatic container transport system (routes can be horizontal and/or vertical as desired, fully automatic, generally computer-controlled; high investment cost, rather high running costs).
Date added: 2023-01-05; views: 794;
