Office Building. Principles. Office Work
The way in which office work is organised and roles are defined (office structure, customer management, office technology) affects the requirements for office space.
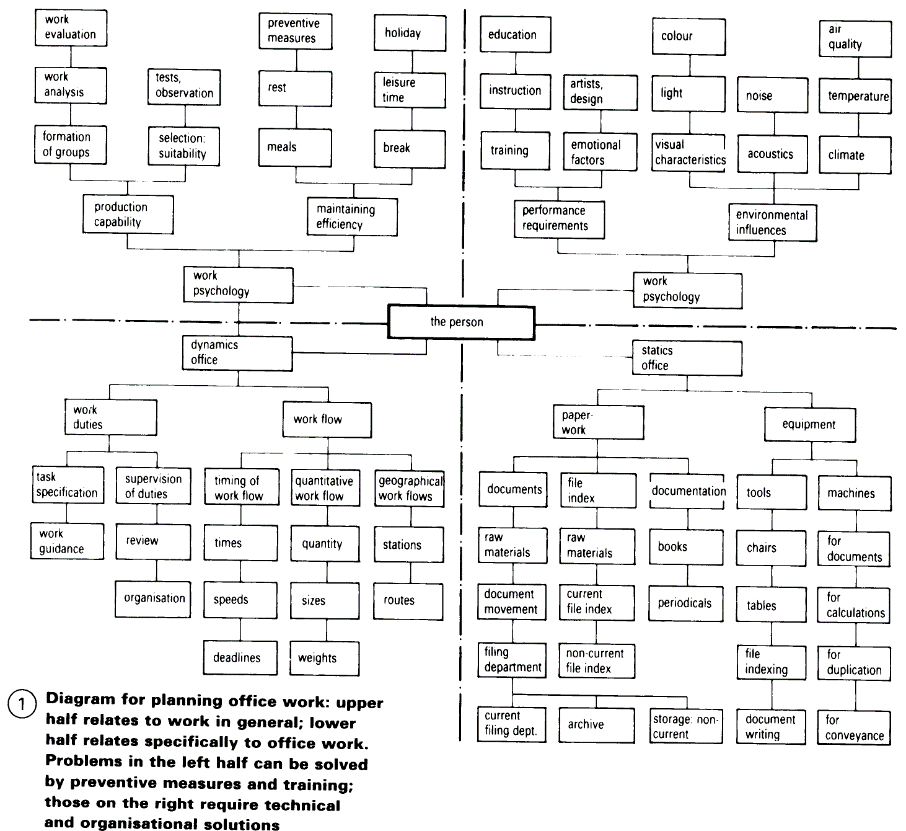
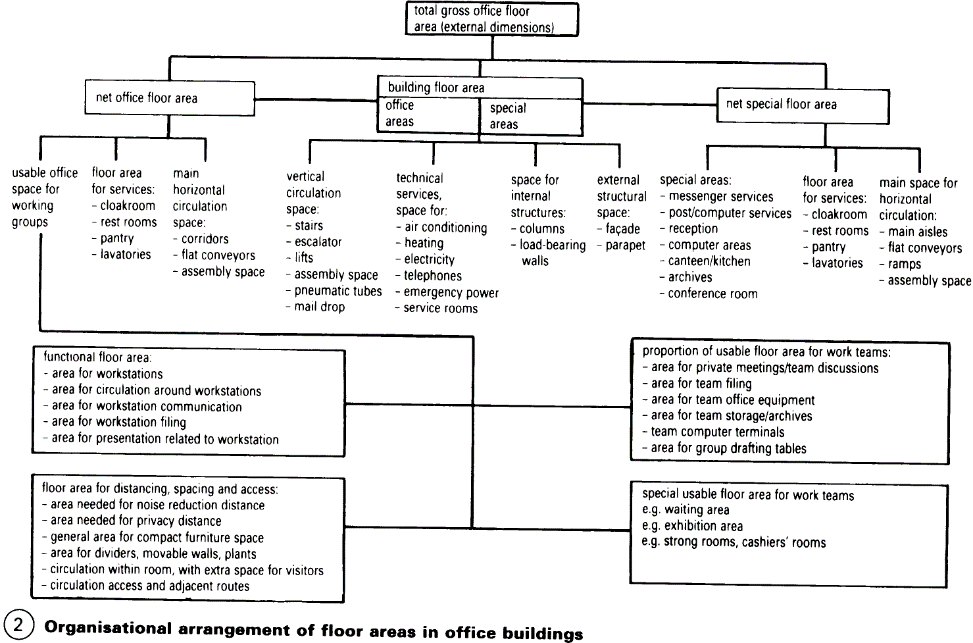
Building types develop and change over time. In addition to innovative prototypes, there are types of buildings which are representative of the forces and influences around when they were built - (3). The organisation of office work increasingly focuses on human relationships and communications – (1). As office work continues to change (from the introduction of new technologies), a clear understanding of the task required becomes a significant motivating force. Designers can influence all aspects of the working environment. Good design is extremely important, and has a strong influence on job satisfaction.
The space allocated to a person to execute a task is referred to as a workstation. This can be a private office with full-height partitions and a door, an open-plan 'cubicle' configured from systems furniture or low-height partitions, or an individual desk in an undivided space.
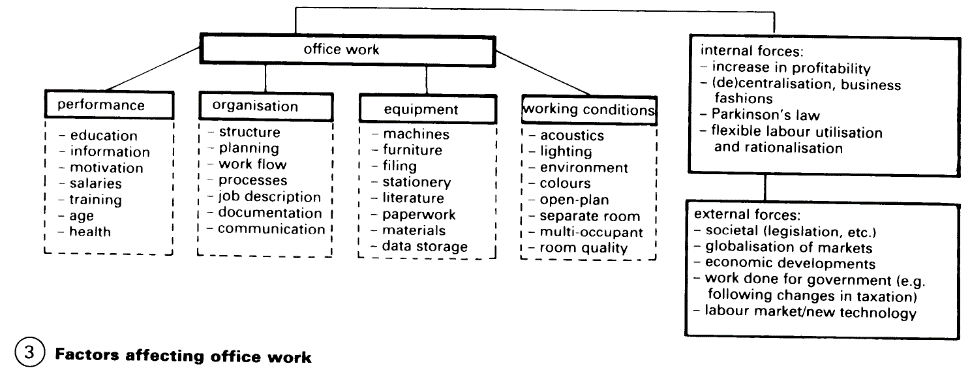
A large office building will consist of several different types of space - (2). (1) Office areas will have separate offices for one to three people with workstations for trainees, group offices for up to 20 people, also with workstations for trainees, and open-plan offices for up to 200 people on a single level. Some offices may combine individual workstations with areas used by groups. In an open-plan office, all spaces are multipurpose for individual or team work, except for a separate secretarial depart ment. (2) Records areas are for the storage of files, drawings, microfilm and electronic media, filing and recording equipment, document reproduction, play back and shredding.
(3) Central clerical services areas contain dictating, duplicating, printing and photocopying equipment, and personal computers. (4) The post room handles all incoming and outgoing post. (5) Corporate display areas contain board rooms with moveable walls, exhibition areas, conference rooms and meeting rooms. (6) Social facilities should include cloakrooms, a kitchen for each floor or area, toilets, a rest area for employees, refreshment rooms, sports facilities and a dining room with a kitchen. (7) Additional spaces and extensions may be needed for training on audio-visual equipment.
(8) It may also be necessary to have an entrance drive, parking spaces (possibly underground) and delivery bays. (9) Circulation spaces include corridors, stairways, lifts, and internal and external emergency exits. (10) Central services are responsible for technical equipment, air conditioning, ventilation, heating, electric power, the water supply, data processing, the computer centre, telecommunications, and cleaning and maintenance.
A detailed description of the company and its organisational structure, including company- specific functions and relationships, will help produce a suitable analysis of its requirements.
Date added: 2023-01-05; views: 785;
