Primary Schools. Open-plan. Further Education Colleges
Classrooms: one classroom per class, square if possible, in exceptional cases rectangular, max. 32 pupils, min. of 65-70m2 (approx. 2.00m2 x 2.20m2 per pupil) if possible daylit on two sides – (3) + (6). Furniture either in rows or informally arranged.
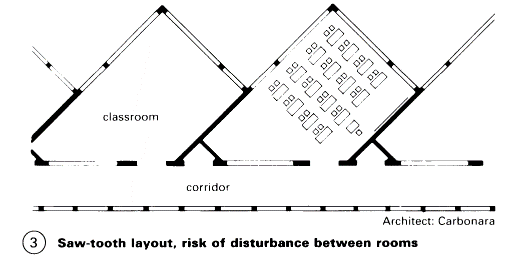
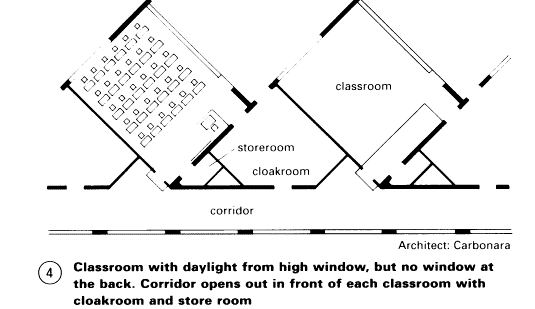
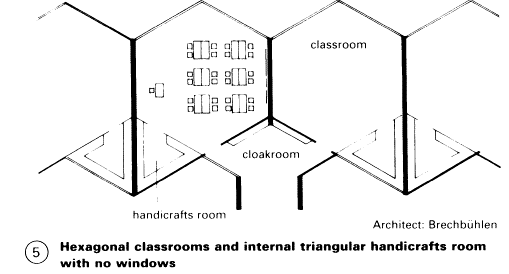
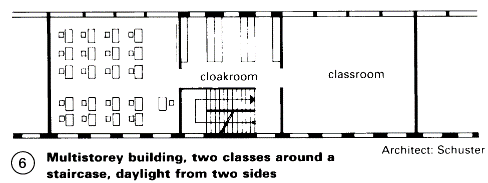
Front of class: chalkboard with sliding panels, projection space, socket for TV, radio, tape recorder, etc., wash-basin near entrance. Provision for hanging maps. Facility to black out windows. Group rooms divided into separate workspaces to accommodate mixed ability classes only in special cases.
Alternatives to individual classes and group rooms: 2-3 classrooms joined together to make teaching spaces for discussions between pupils and teachers, or lessons in larger groups; can also be divided by partitions. Draught- excluding lobbies and entrance areas also connect to horizontal and vertical circulation (corridors, stairs, ramps) and can be used during breaks (0.50m2/pupil). Multi-use area for parties, play or exhibitions.
Room for teaching materials 12-15m2: centrally positioned, part of the staff area or in a multi-purpose room.
Open-plan. Nowadays, it is often considered normal for offices to be open plan. This sometimes influences school architecture. The two have similar requirements regarding size of room, lighting, ventilation, acoustics, floor and ceiling finishes, furniture, and colour.
Main advantage: flexibility – (1) + (2). Team teaching in groups of up to 100 pupils. Space per pupil (not incl. core) 3.4m2-4m2.
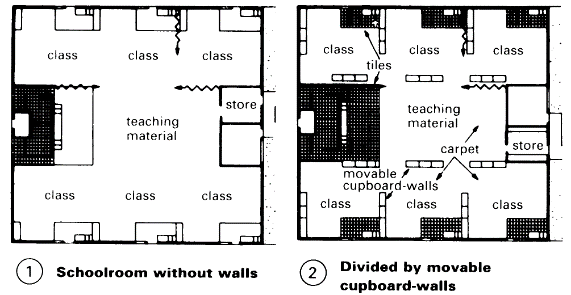
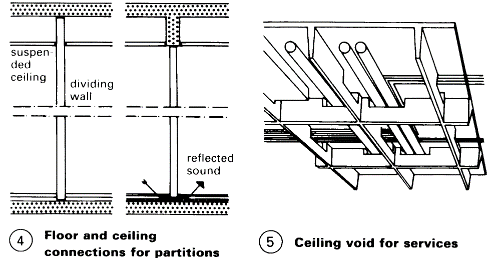
The later addition of partitions should be possible - (4). There are many US examples. German model example: Tannenberg School, Seeheim - (3). However, vertical drainpipes and service ducts, etc. are a problem because of the need to fix sound-insulating partitions - (4). Ceiling panels should be removable so that services in the ceiling void are accessible - (5).
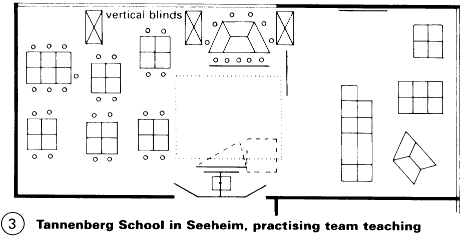
Large groups of 40-50 pupils, divided into medium-sized groups of 25-26 pupils, small groups of 10 pupils - (3).
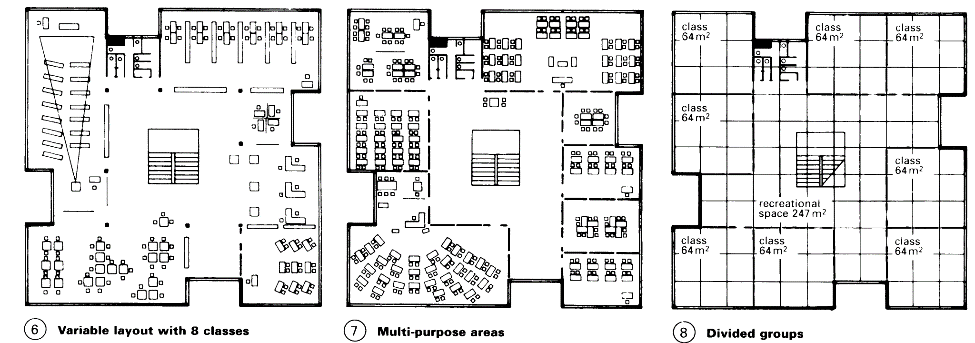
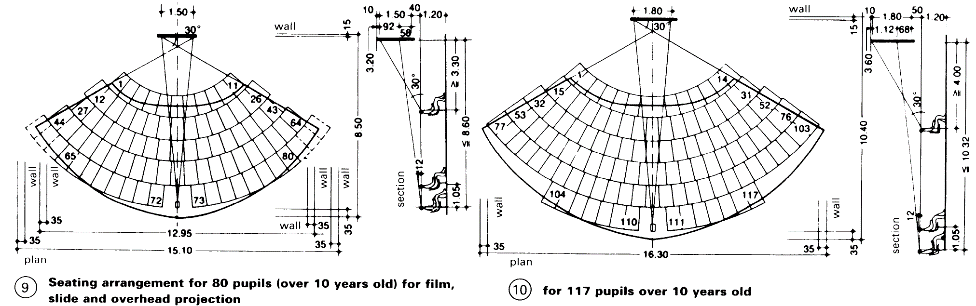
Planning grid 1.20 x 1.20m throughout; clear room height 3 m. Movable partitions which can be taken down provide a solution for the transition from old fixed classrooms to open plan – (4). Also, building forms which create small spaces – (1) + (2) and - (6) – (8). Examples of seating arrangement for watching films, slides etc - (9) – (10).
Educational experts maintain that, during conscious learning, people best retain information that they have obtained themselves, more precisely:
- 10% of what they read;
- 20% of what they hear;
- 30% of what they see;
- 50% of what they hear and see;
- 70% of what they say themselves; and
- 90% of what they do themselves involving their own actions.
Further Education Colleges. Technical colleges and colleges of further education. The type of college depends on regional and local factors, so that it is not really possible to give absolute sizes for systems. The figures cover both part-time and full-time students; as an approximate guidelines, and depending on the area served, there are 2000-6000 pupils per 60000-150000 inhabitants. Owing to the large catchment areas, the schools should be well served by public transport. Site: at least 10m2 per part-time student and at least 25m2 per full-time student of college site area, as far as possible free of pollution from noise, smoke, odour and dust. Ensure a good-shaped site and the possibility for extension.
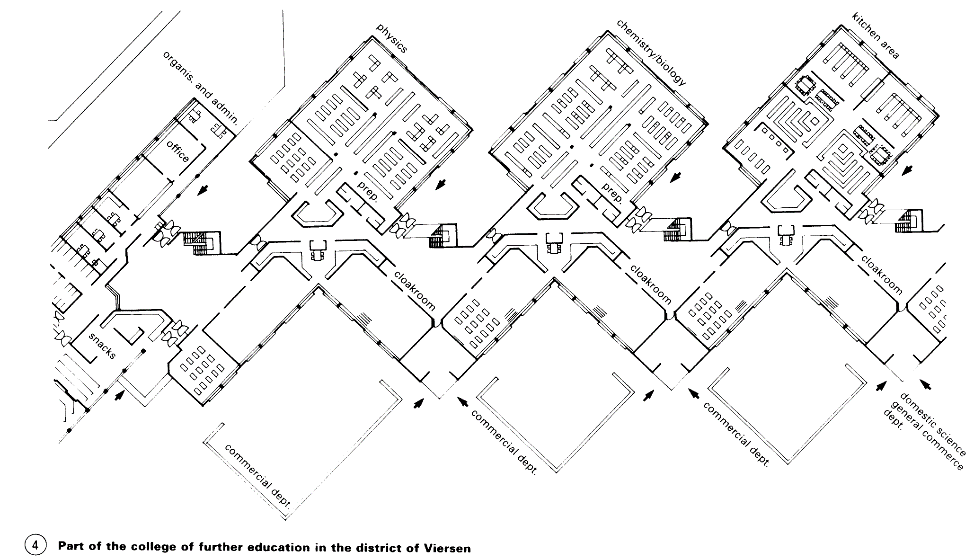
Arrangement on the site, type of construction and building design depend on the sizes of the spaces that can be accommodated on several levels (classrooms for general subjects, specialist subjects, administration) and those which cannot - areas for non-academic work, e.g. workshops or sports areas. College buildings are, as a rule, 2-3 storeys, higher only in exceptional cases. Workshop buildings with heavy machines or frequent deliveries are single storey only.
Access: entrance area and foyer with central facilities used as circulation space connecting horizontal and vertical movement as in general school centres or comprehensive schools. Teaching areas divided according to type of teaching and their space requirements. General-purpose teaching areas occupy 10-20% of the space. General classrooms as normal with 50-60m2, small classrooms 45-50m2, oversize classrooms 85m2, possibly open-plan classrooms doubling as a film or lecture hall of 100-200m2
Building requirements, furnishings and fittings basically the same as for general school centres and comprehensive schools. An assembly room of 20m2 per 5 normal classes.
Date added: 2023-01-05; views: 617;
