The genotypic diversity. The mutational diversity
The diversity, which involves changes in genotype due to mutations or gene combinations, is called genotypic diversity. It may be of two types: mutational and combinative.
The combinative diversity. The combinative diversity is the formation of new allele combinations due to crossing over in meiosis and gene recombination. New gene combinations and interaction between them may cause new trait formation. Combinative diversity is inherited according to Mendel’s Laws. On gene expression in combinative diversity, the following factors may have some influence such as interaction of allelic and non-allelic genes: pleiotropic gene action, gene linkage, gene expressivity, penetrance, and so on. The wide traits variety is provided by combinative diversity.
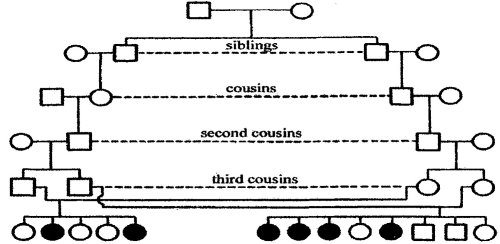
Concerning human, combinative diversity is observed in crosses that have already been made. The family crosses systems may be of two types: inbreeding and outbreeding.
The inbreeding - is crosses between relatives. The level of inbreeding depends on level of familiarity. The closest inbreeding is a marriage between sisters and brothers or between parents and kids. The less close inbreeding is between uncles and cousins. The first consequence of inbreeding is an increasing number of homozygous defect allele’s distribution. Such increases rise with every new generation.
The second consequence of inbreeding is population splitting to several independent lines. The diversity of inbreeded population will rise, but diversity of each line will decrease. The inbreeding often leads to an offspring’s degeneration. It was pointed in ancient times. All tribe taboo and inbreeding bans tell us about that. The human inbreeding in majority of cases is harmful (pic 9.2). The family relation among parents increases risk of hereditary defects in offspring.
Ріс. 9 2. The inbreeding of two related families resulted in amavrotic idioty (by T. Sjogren,1931)
The outbreeding - is crosses between unrelated individuals. The unrelated individuals are those who have no any relatives in 6 or more generation. Outbreeding is controversial crosses system. It raises heterozygote level in population, combines alleles of parents. Homozygous defect alleles are suppressed dominant alleles of other parent. All genes are combined more often so it increases combinative diversity.
The mutational diversity. The diversity with rapid, strong changes of trait is called mutational. Mutations — are occasional, stable changes of genetic cell apparatus. They may include changing allelic gene position, changing of gene structure, changing in chromosome number and state, changing of cytoplasmic DNA containing structures. First to summarize material about mutation was H. de Fris. He published “The mutational theory” in 1901. The main statements of that theory are in following:
1. Mutations appear suddenly.
2. New forms are stable.
3. Mutations are changes in quality.
4. Mutations may be harmful and usable.
5. The same mutations may appear repeatedly.
All mutations are divided on groups. The mutation classification helps to study and describe them. It is made according mutation causing factors and cells subjected to mutation.
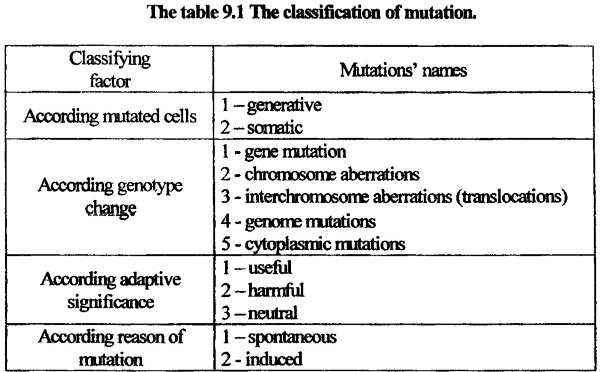
Generative mutations (mutations in sex cells), may be revealed only if affected cells take part in new organism formation. If mutation is dominant, it may be expressed in particular individual. If mutation is recessive, it may take several generations to express it in phenotype. The examples of human generative mutation are foot pemphigus, cataract, and brachiphalangia. The example of recessive human generative mutation is cases of hemophilia in some families.
Somatic mutations (mutations in somatic cells) may be transmitted to the next generation only during asexual reproduction. Somatic cell may be subject to mutation during embryogenesis. The earlier a mutation has appeared in embryogenesis, the more sever consequences of that mutation will have. The example of human somatic mutation is vitiligo (white depigmented spots on a skin with depigmented hairs). The research of somatic mutation is very important in understanding cancer causes. It was suggested that transformation normal cell phenotype to cancer one is based on somatic cell mutation.
Gene or point mutations are alteration involving only one or few nucleotides in the coding sequence. They may be as dominant as recessive one. The examples are vitamin В resistant rachitis, metabolic exchange imbalance of phenylalanine amino acid. In general all point mutation have one of following mechanisms:
1. Nucleotide pair exchange in DNA molecule
2. Deletion of nucleotide pair (or group of pairs) in DNA molecule
3. Insertion of nucleotide pair (or group of pairs) to DNA molecule
4. Translocation of nucleotide sequence inside of the gene
All these alterations lead to three classes of gene mutation: missence mutation, nonsence mutation and fiameshift mutation. The small changes in gene structure may cause reading fiameshift. They in turn cause big ultimate changes in protein structure and function.
Date added: 2023-01-09; views: 684;
