The twins’ method. The dermatogliphic method
The method’s idea was suggested by F. Galten in 1876, and was developed by G. Simens in 1924. The method is based on studying of traits of twins having same sex, which are changed by environmental condition. Twins are two or more delivered at the same time individuals in animals usually having only one (cow, horse, and human). Twins, who develop from one fertilized ovum, are called monozygote twins (pic 4.1). Twins, who develop from two different fertilized by different sperms ova, are called heterozygote twins (pic 10.4).

Pic. 10.4. The dizygote non-identical twins (brother is albino, whereas sister is pigmented) (by S. Sinnot, L. Dunn, Th. Dobzhansky, 1958)
Heterozygote twins may have different sex. The most common situation is having two twins, but it is possible but rare to have three, four, five and even more twins. Twins rate in population is around 1%. One fourth of them are monozygote. But monozygote rate in different population is different. For instance, in mongoloid race it is 60%, in other races it is around 30%.
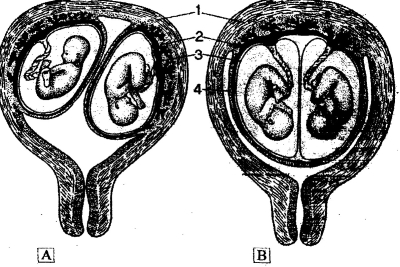
Ріс. 10.5. The twins: A - dizygote twins with independent coats; В - monozygote twins with common placenta; 1 - uterus wall; 2 - chorion vilia; 3 - amnion; 4 - smooth chorion (by E.L.Potter, 1948)
Both types of twins are used for genetic research. By this way, we can understand both influences of different environmental conditions on same genotypes and influences of same environmental conditions on different genotypes. If studied trait is expressed in both twins, it is called concordance. If studied trait is expressed only in one twin, it is called discordance. Comparing level of traits concordance in different twins’ groups, we can determine the impact of genotype and environment to phenotype formation. Such method is not presented in routine doctor’s job, but it is important to remember about twins’ concordance in disease development.
Twins’ method is based on comparing level of traits concordance. It allow listing hereditary diseases, determining role of environment in disease development. For these purposes, the coefficients of herediting (H) and environment impact (E) are used. They are calculated by Holtzinger’s formula.
![]()
Where Cmz is percentage of concordated pairs of monozygote twins, Cdz is percentage of concordated pairs of dizygote twins.
With help of twins’ method, we can study the following:
- The role of environment in disease development.
- The definite factors enhancing environment impact.
- The correlation between traits and functions.
The dermatogliphic method. The dermatogliphic is a branch of genetics studying hereditary patterns of fingerprints, handprints and footprints of human. The first to suggest such studying was F. Galton in 1892 (pic 10.6). The fingerprints are individual. The process of papillary picture formation occurs in 3-6 month of embryo development. It is based on epidermal and dermal differentiation and on growth and movement of cell complexes.
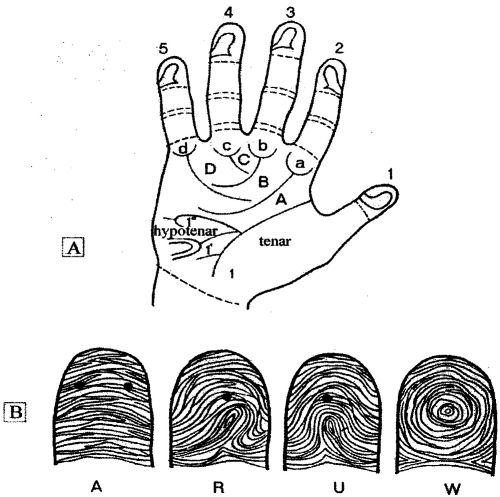
Pic. 10.6. The human skin hand folds (A) and papillary pictures (B): A - arches, R - radial loop, U - ulnar loop, W - helix (by G. D. Berdyshev, I. F. Kriviruchko, 1979)
Genes responsible for fingerprints type formation participate in derma saturation by water. So, gene A determine arch appearance on water saturated finger; gene W determine appearance of helix on significantly saturated finger pillow; gene L determine appearance of arch on fingers with directed water distribution. It was stated that ulnar loops are more common in first and fourth finger, where radial loops are more common in third finger.
In fourth and fifth fingers normally there are no radial loops. Helixes are more common in first and fourth fingers; arches in second and third. Arches are expressed very rare. On a left hand usually ulnar loops and arches are. On a right hand usually radial helixes and loops are. In a literature, it is stated that females have higher arches rate and loops rate and lower helixes rate in compare with males. The frequency rate for radial loops is 0.2-10%, for ulnar loops is 25-75%.
The dermatoglifics is widely used in hereditary disease diagnostics. Some inherited diseases have specific dermatoglific features (such as trisomy in 13th,
18th, 21st chromosome pair). The analysis of fingerprints may be used for diagnostics. The changes in flexor hand lines occur in individuals with Schereshevsky-Terner syndrome. It was described the specific features in fingerprints for myasthenia gravis, schizophrenia and others diseases. The fingerprints’ studying has a wide distribution in forensic surveys.
Date added: 2023-01-09; views: 919;
