The cytogenetic and statistic method
It is usually called cytological analysis of human karyotype in normal and pathological conditions. The term “cytogenetic” can be used, only if cytological analysis is combined with pedigree analysis and it is possible to link cytological pictures with phenotype effect. It is based on chromosome microscoping. Chromosomes are studied in metaphase of mitosis in fibroblasts and lymphocytes, which are cultivated in artificial conditions. The luminescent microscoping also may be used. In this case, we need to stain chromosomes by fluorochrom. Chromosomes are classified according Denver classification. This method allows determining diseases related with changes in chromosome set and shape. It is also used for chromosome mapping.
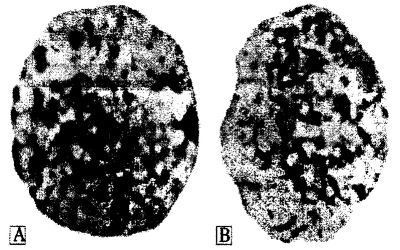
Pic. 10.3. The female chromatin-positive (A) and male chromatin-negative (B) nucleuses (by E. F. Davidenkova, 1965)
The method is kind of complicated. The lymphocytes grow in a culture. They are stimulated to division by phytohemaglutinin. In metaphase, spindle proteins are destroyed by colhicin. After that, chromosomes are available for observation for long time. Using this method J. Tiyo and A. Levann in 1956 stated that human karyotype has 46 chromosomes.
In 1969 T. Casperson discovered the method of chromosome staining. It made possible to distinguish chromosomes accordinary their segments staining. The aneuploidity, chromosome aberrations, translocations, polyploidity may be revealed with help of this method. Among aneuploidities we can determine excessive X- and Y-chromosome, trisomy in 13th, 18th, 21th chromosome. We may determine deletion of 5th chromosome (“cats scream” syndrom), of 18th (mental retardation, deformation of skeleton) and of X-chromosome. The deletion of short arm of X- chromosome is referred as partial monosomy in X-chromosome. The most common translocation is translocation of 21st chromosome on 15th, 13th, 14th chromosome in females and on 22nd chromosome in males.
If there are defects in sex chromosome set, we can determine them easily. For such purpose evaluation of sex chromatin in somatic cells are used. The most common material for that is buccal epithelium (pic 10.3). Sex chromatin (Barr’s body) - is condensated second X-chromosome in female cells. It is inactivated on 16 day of embryogenesis. It looks like heterochromatin body nearby nucleus membrane. It is revealed on preparations stained by aceto-orsein.
Normally, Barr’s bodies are determined in 20-40% of female cells and in 1-3% of male cells. Number of X-chromosomes is calculated according such formula: Barr’s bodies number plus one. For example, if woman has one Barr’s body that means she has two X- chromosomes (1+1); if there is no Barr body in female cell that means she has one X-chromosome (0+1); if man hasn’t Barr’s body that means he has sex chromosomes set like that - XY (0+1).
In somatic cells, in particular in buccal epithelium, it is possible to determine Y-chromatin. Slides need to be stained by akrychin followed by ultraviolet microscoping. Y-chromatin is intensively stained body in a nucleus, usually near nucleolus. Normally, Y-chromatin is determined in 20-40% of male cells.
The express-methods for sex chromatin determining are used for hereditary, related with changing in sex chromosome set, diseases diagnostic, sex determining in hermaphrodites, transsexuals, and in forensic medicine.
The statistic method. The method is based on demographic statistics data and mathematic analysis of them. Using Hardy-Weinberg principle, we can calculate rate of defect gene staying in heterozygous state in human populations (see chapter 17.1).
The population statistic method is widely used for health care management. It allows calculating necessary amount of drugs, medical devices etc. for supplying population.
Such method also is useful in understanding dynamic genetic assortment in populations. Different populations have a different genetic structure. For example, let’s look through gene assortment for genes of ABO blood group system. Thus, in India and China the concentration of allele lb is highest. This concentration falls down to east and to west from those countries. Among Native Americans and Australians there isn’t lb allele. At the same time, Native Americans and Australians have highest concentration of Io allele. The allele la is expressed very rare in Native Americans, Indians, Arabs, and Western Europeans. It was suggested that such distribution was made because of epidemics of plague and smallpox.
The smallpox primary affects people with blood group A. That lead to higher mortality among them and elimination la allele from population. The places where smallpox was wide spread (India, America, Arabic countries) have a low la allele rate among population. In the pointed above regions allele lb became most frequent.
The data acquired with help of population statistics are used for planning health care funds, required drugs and required specialists number.
Date added: 2023-01-09; views: 626;
