The immunological, biochemical and ontogenetic method
Such methods are based on studying antigens of human cells and fluids (blood, saliva, stomach juice). Most common are erythrocyte antigens, leukocyte antigens, blood proteins. Different erythrocyte antigens form different blood group: ABO, Rh, MN, Luis, Lutheran, Daffi.
Blood group determining is important for blood transfusion. Also it was stated a correlation between having a blood group and having a disease: stomach cancer more frequent among people with blood group A, whereas peptic ulcer is more frequent among people with blood group O.
It was shown by K. Landsteiner and I. Levin that human erythrocytes have antigen similar to rhesus monkey. It resulted in discovering new blood group - Rh-group. The Rhesus factor is inherited dominantly in homozygote and heterozygote state as well. Only 15% of Europeans have Rhesus negative blood group. If Rhesus negative mother has Rhesus positive embryo, it may lead to a potentially fatal condition called erythroblastosis fetalis. If mother is homozygous in recessive allele and father is homozygous in dominant allele, the child inherits fathers Rh- factor (pic 10.7). 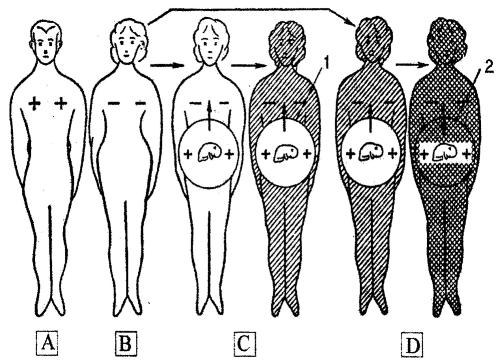
Ріс. 10.7. The Rh-factor inheriting in human and erythroblastosis fetalis: A - father is Rhesus positive (Rh+); В - mother is Rhesus negative (Rh-); C - first pregnancy, Rh+ antigene cause antibodies formation, baby can be normal (oblique crossing - 1); D - second pregnancy, erythroblastosis fetalis, bady dies (2) (by N. P. Dubinm, 1976)
During first pregnancy, Rh-positive erythrocytes of embryo stimulate antibodies formation in mother’s organism. However, child is not affected by them because of low concentration of them. However, during second pregnancy, the antibodies concentration becomes critical and erythroblastosis fetalis is developed. Next pregnancies will have more and more severe erythroblastosis.
The biochemical methods. Contemporary families have a few children. Its make using of pedigree analysis very complicate. Therefore, biochemical methods of evaluation of different enzymes activity and interesting chemical substances are widely used. Thus, we can check different stages of metabolic pathways and reveal crucial defected points in them.
The biochemical methods are applied for diagnostics hereditary metabolic exchange diseases. They are determined on a three levels: molecular (protein structure and quantity assessment), cellular (evaluation of defect enzymes), and organism (searching for intermediate metabolites).
The following diseases can be determined by biochemical methods: hemoglobinopathy, failure in amino acid exchange (phenylketonuria, alkaptonuria), in carbohydrate exchange (diabetes mellitus, galactosemia, fructoseuria), in lipids exchange (hypercholesterinemia, amavrotic idioty), in minerals exchange (Konovalov-Wilson desease, hemochromatosis) and so on. Taking into account polymorphism of hereditary exchange diseases, biochemical method is crucial in its diagnostics.
The ontogenetic method. The ontogenetic method is the studying gene expression during development. There are two periods of human development: antenatal (before birth) and postnatal. Postnatal is divided to morphogenetic and postmorphogenetic. In morphogenetic period, there are last stages of brain cortex and different organ’s systems formation. Gradually, the immune system is formed. In morphogenetic period, gene activity can be of two types: switching on and switching off, activation and suppression of gene action. In postmorphogenetic period, there is formation of secondary sex signs. Only several genes are activated (which responsible for secondary sex signs) during this period.
The gene repression is presented wider. The genes, which are responsible for г-globulin synthesis, melanin synthesis, connective tissue matrix synthesis, are repressed. Such repression occurs on a level of transcription and translation. But main is gene activity activation and suppression. The heterozygote state gene expression may be changed, thus, phenylketonuria gene may affect a human mind in heterozygote state. Men while aging express changing in voice, body’s shape, in mind (become more impressive, crying). Women acquire harder voice, new character and, unfortunately, changing in body’s shape.
It is known that some hereditary diseases may be expressed not only in homozygous state, but also in heterozygous state as implicit forms. Therefore, developing of new methods of diagnostics such disease expression are in great importance today. So, the individual having heterozygous phenylketonuria allele can be determined by intravenous phenylalanine injection following by evaluating of its level in blood. Normally the phenylalanine level stays the same, but in individual having heterozygous phenylketonuria allele the phenylalanine level increases.
Very often heterozygotes have intermediate enzymes activity. Now it was developed the methods to determine heterozygous allele state for more than 40 hereditary diseases. Such diagnostics is important for in time treating and for assessment the risk of having child with such defect. Such diagnostics performed for cripple child parents and siblings is necessary for prognosis his offspring genotype. Recognizing of individuals having heterozygous defect allele can be performed by different ways. First one is thoroughly examination of patient looking for microsymptons. Thus, heterozygotes for anoftalmia have decreased eye size; heterozygotes for Duchenne muscular dystrophy have increased level of creatinphosphokinase in blood. Second one is load tests.
We have described it for phenylketonuria above. The same tests can be performed for assessment essencial hyperlipidemia and disaccharidase insufficiency. Third one is cells and tissue microscoping. So, the “foam” lipid loaded cells are founded in lipidosis’s heterozygotes, cells reached in glycogen are founded in glycogenolisis’s heterozygotes. Fourth one is direct evaluation of enzyme activity, suffered from mutation. It is possible in hemophilia, galactosemia, glucose-6-phosphatase insufficiency.
In addition, ontogenetic method is used to determine mechanism of disease development on different ontogenetic stages, which is important for further treatment and preventive measures. Method includes biochemical, immunological and cytogenetic methods. In particular, we may determine on early stage of development a phenylketonuria, galactosemia, vitamin-D-resistant rachitis and so on; and on later stages of development - alkaptonuria, diabetes mellitus etc.
Date added: 2023-01-09; views: 716;
