The methods of human genetics studying
Human genetics studies traits inheritance in human. To study such inheritance, it was discovered and was successfully applied several methods. Nevertheless, none from them is universal. Let’s look them through.
The pedigree analysis. To study how a human traits are inherited, investigators look at the results of crosses that have already been made - they studied family histories, called pedigree. This methods may be applied if it is known direct parents of individual which is studied (he is called poband) or if it is known children of such individual. To make pedigree specific signs are used (pic 10.1). They were suggested by G. Ust in 1931. We analyze pedigree to determine pattern of inheritance. There are several patterns of inheritance.
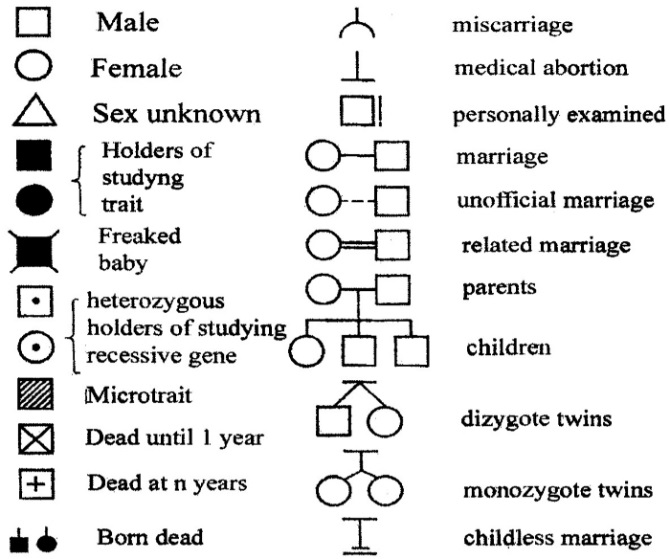
Pic 10.1. The genetic symbols for pedigree (by. G. Ust, 1931 with changes)
In the autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance, the mutated trait appears in heterozygous state in individuals of both sexes. The trait occurs in horizontal and vertical lines of pedigree as well. The child may be affected, if anyone from parents is affected too. However, it is important to remember about incomplete penetrance of dominant gene. Some diseases develop only after achieving particular age. For instance, Hantington’s chorea appears only in individual over 35 years of age. The sparkles, brachidactilia, cataract, are inherited according the autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance (pic 10.2a).
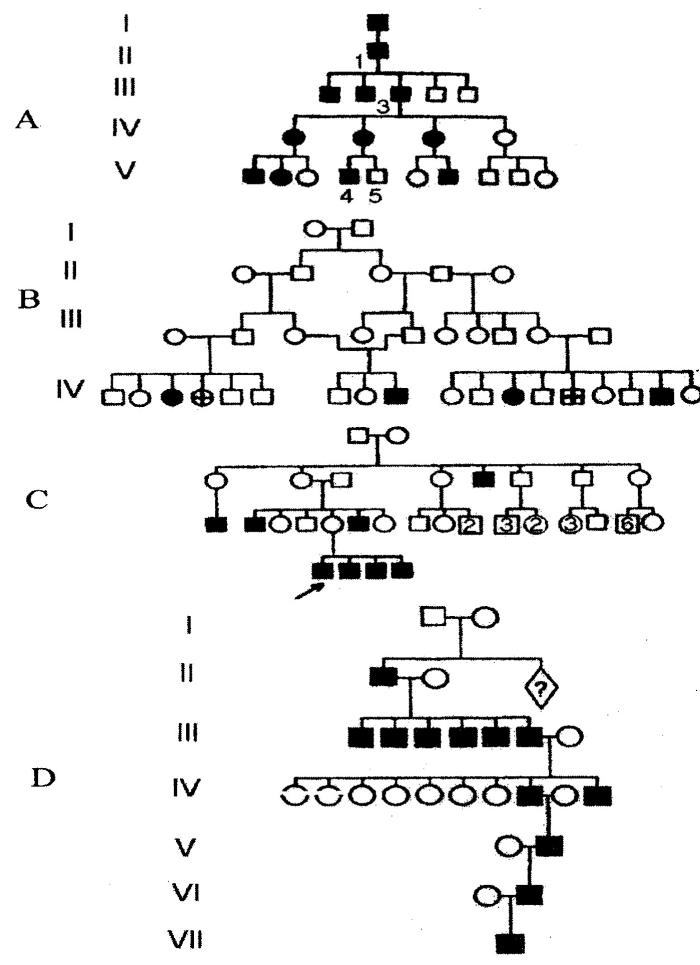
Ріс 10.2. The types of human inheriting: A - autosomal dominant (pedigree of white curl); В - autosonal recessive (pedigree of phenylketonuria); C - X-linked recessive inheriting (pedigree of Duchene’s muscle dystrophy); D - Y-linked inheriting (pedigree of “man- porcupine’’); I-VII - generations (by K. Shtem, 1965)
In the autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance, the mutated trait appears only in homozygous state in individuals of both sexes. If parents are healthy, but they are heterozygotes, you can expect that 25% of offsprings will have disease. The trait occurs in horizontal line of pedigree not in every generation. If parents are both recessive for trait, all offsprings will have such trait. The examples are albinism, phenyketonuria, diabetes mellitus, and red hair (pic 10.2b).
In the X-chromosome linked dominant pattern of inheritance, the mutated trait appears in individuals of both sexes. The trait occurs in horizontal and vertical lines of pedigree as well. Inbreeding increases probability of ill childbirth. Female express such trait more often, because they may get trait from mother and father as well. The follicular keratosis, pigment dermatosis are inherited according X-linked dominant pattern of inheritance.
In the X-chromosome linked recessive pattern of inheritance, the mutated trait appears mainly in males. In a family, there are half of males suffered from disease and half of females having gene in heterozygous state. If the male have such trait, he inherited it from mother line of pedigree. The most common diseases having such pattern of inheritance are hemophilia A, muscular Duchenne dystrophy, daltonism (pic 10.2 c).
In the Y-chromosome linked pattern of inheritance, the mutated trait appears only in males. The syndactilia, hypertrychosis of cochlea are inherited Accordinary such pattern. The ability to develop male gonads is holandric trait, located in Y- chromosome (pic 10.2d).
The pedigree analysis allows determining heterozygous state of defected gene and probability to have child with hereditary defect. The method is used for determining hereditary diseases in genetic counseling.
Date added: 2023-01-09; views: 697;
