Securing Embankments. Garden Enclosures
Long rounded banks with their faces planted as lawns or with shrubs and trees are aesthetically desirable but all steeply sloping surfaces must be secured. For a bank which is steeper than the natural angle of repose, turf, wattle, cobbles or retaining walls can be used for this purpose.
If the slope is more than 1:2 use grass turf fixed with wooden pegs or stepped turf for securing steeper slopes of 1:1.5 to 1:0.5 -» p. 230. Wattle is suitable for fixing steep slopes on which it is difficult to establish plant growth p. 230. It is necessary to distinguish between dead and live wattle: in the case of live wattle (willow cuttings) subsequent permanent planting with deciduous shrubs is called for because willow is only a pioneer plant.
Vegetation is not suitable for securing large bank cuttings, such as in road building or on sloping plots, so more expensive artificial forms of retention are necessary – (1) – (6).
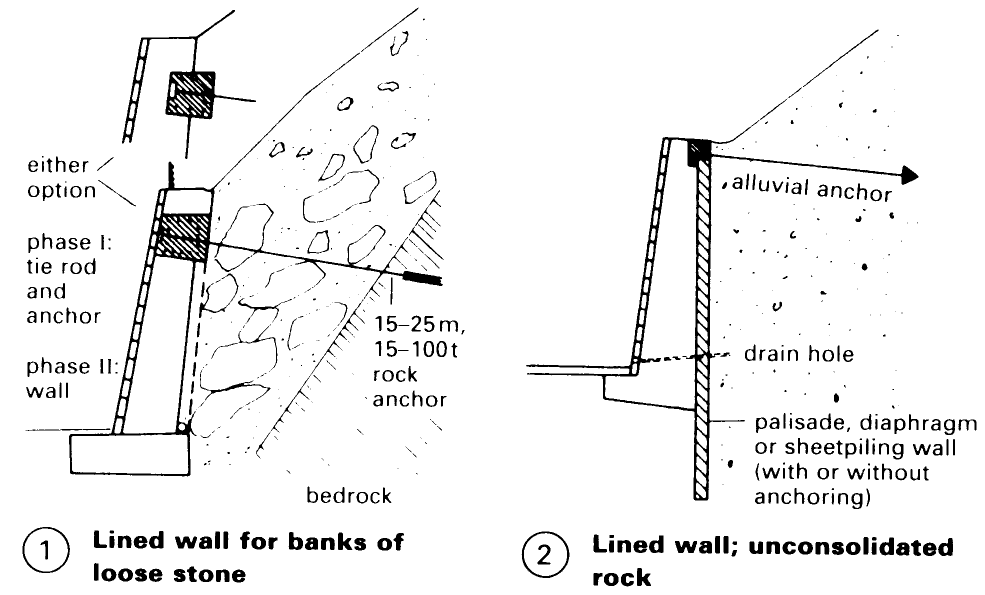
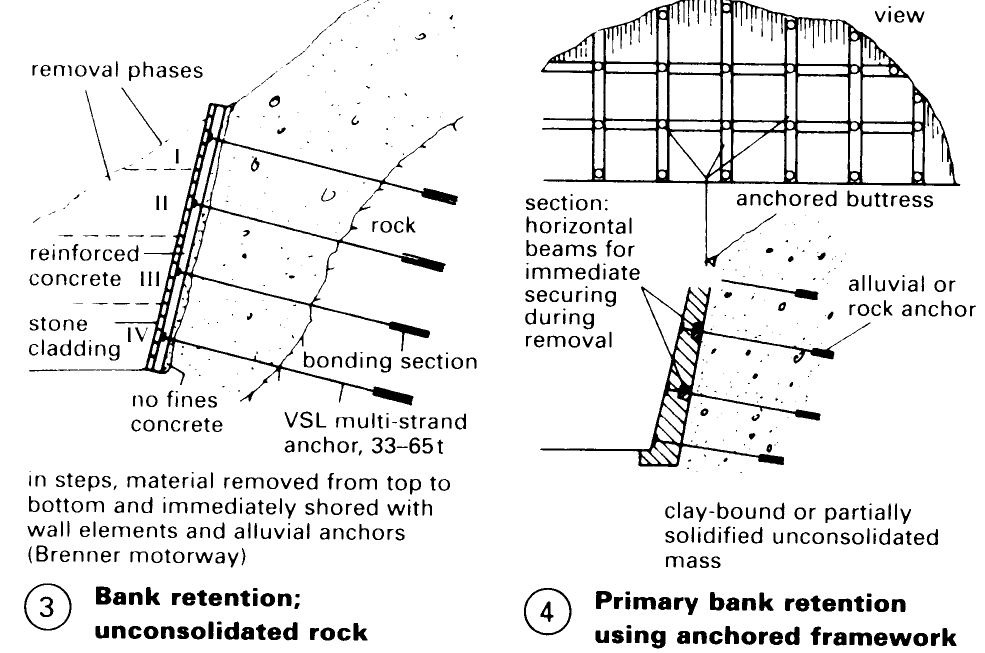
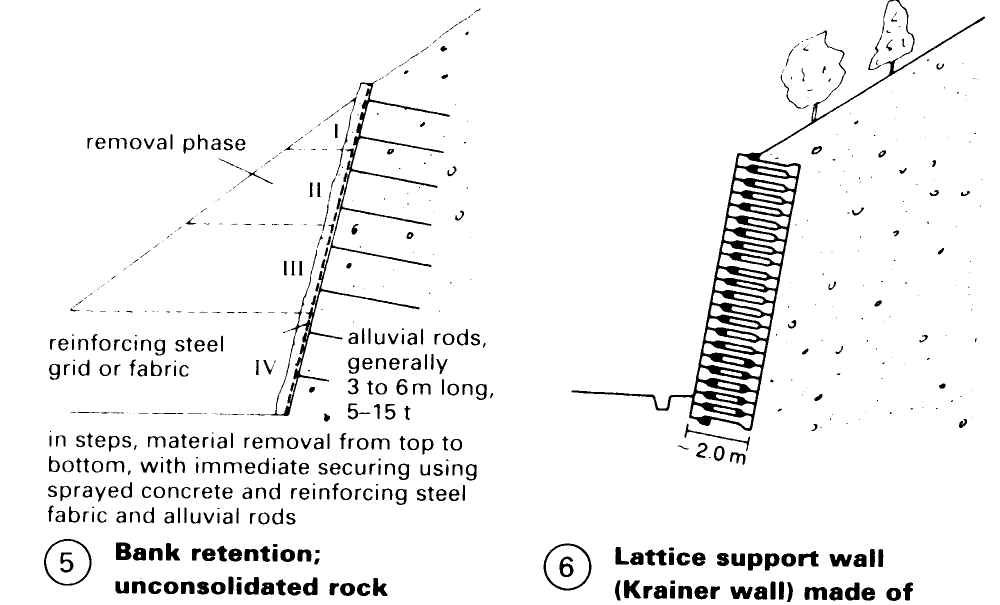
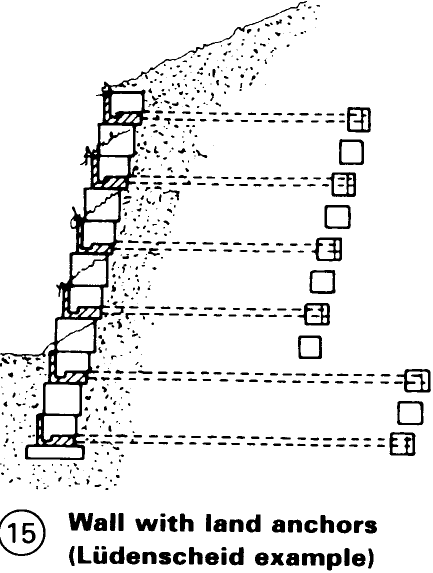
There are several types of anchored frameworks that can be used to create retaining walls. The simplest consists of horizontal, preanchored beams and vertical posts, with intermediate areas covered with reinforced sprayed concrete (4). With planted supporting walls considerable height differences can be overcome to create ample space for roads or building plots in uneven terrain – (6) + (7). High walls can also be built with earth anchors, depending upon the system and the slope – (15).
Garden Enclosures. In most countries, neighbours have legal rights in relation to fencing. Within an area built as an integrated development, the owner of a building used for domestic or business purposes is obliged at the request of the owner of the neighbouring plot to enclose his plot along the common boundary. Local (or national) regulations may, if both plots are built on or used commercially, require both owners to erect a boundary fence/wall jointly and share the cost. Under English law, ownership of, and responsibility for, fences etc. is spelt out in the property owner's deeds.
A 'common fence' is located in the centre of the boundary whereas with an 'own fence' the foundation wall should be flush with the boundary.
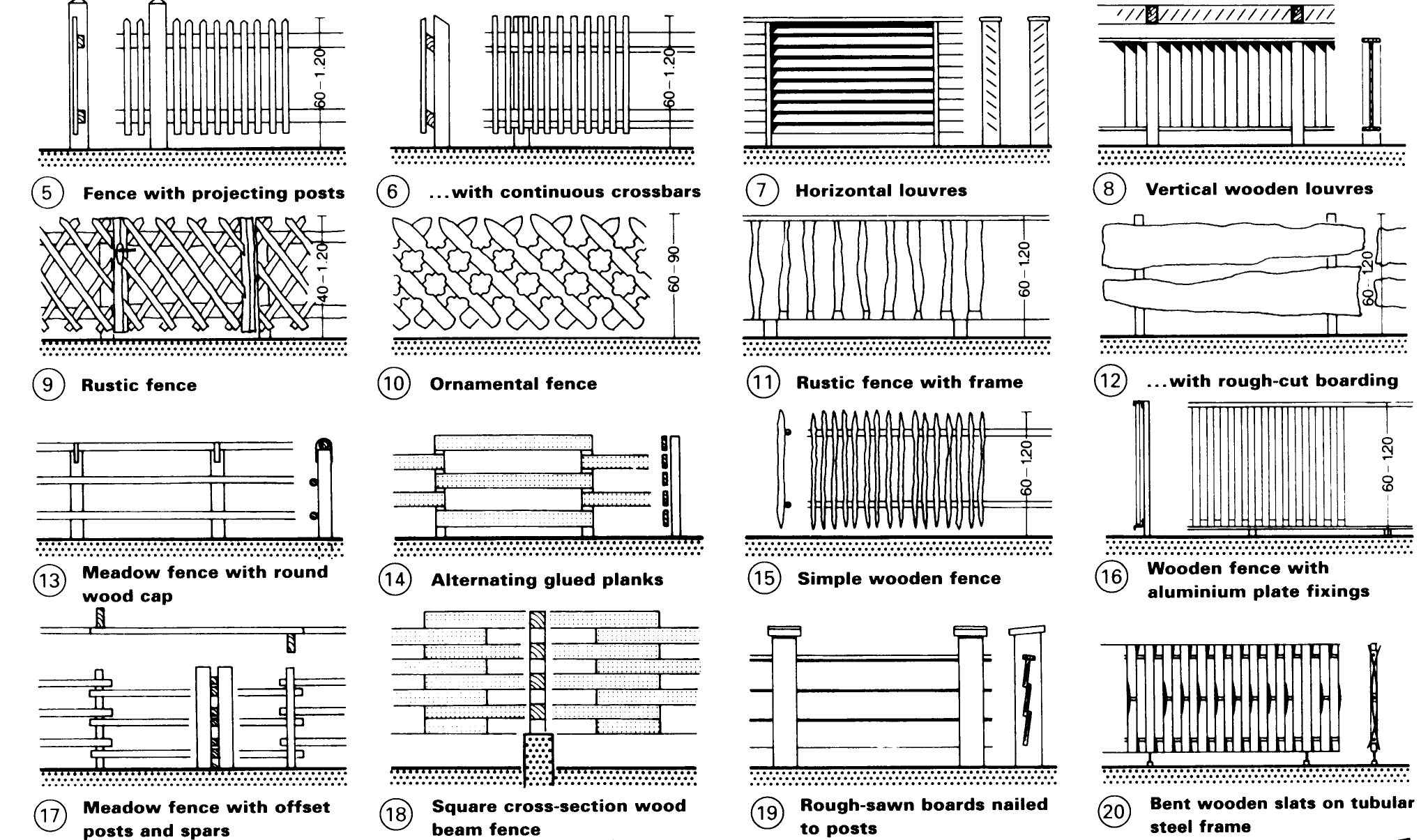
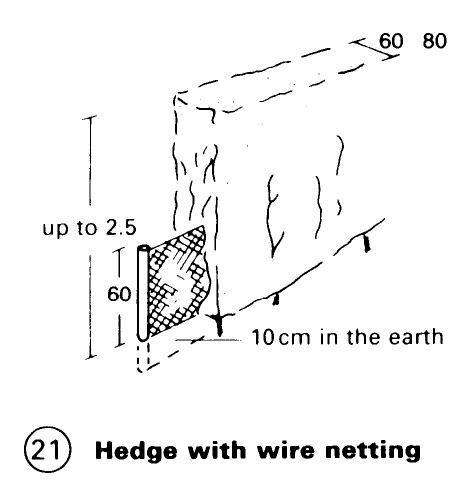
The style of fence chosen should always suit the locality as far as possible – (5) – (20). Fencing that is intended to protect against wild animals should be sunk 10-20cm into the ground, particularly between hedges – (21).
Wooden fencing, posts, frames and palisades can last more than 30 years if they are first chemically impregnated in a tank.
Wooden louvre fences are best for privacy - (7) + (8) and can also provide some measure of sound insulation. Scissor or rustic fencing is also popular for plot enclosure – (9).
The owner of a plot usually erects fencing only on one long side since the neighbour on the other side puts up the fence on that long boundary.
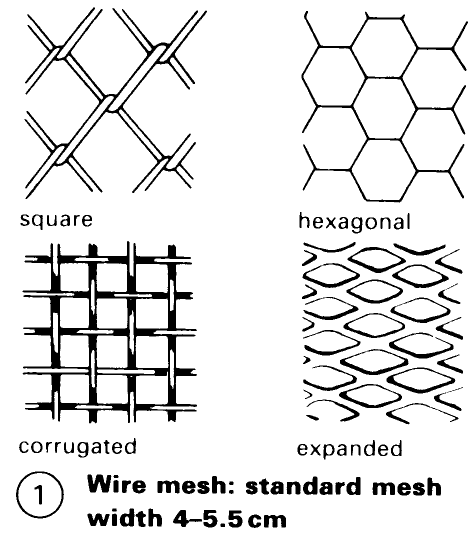
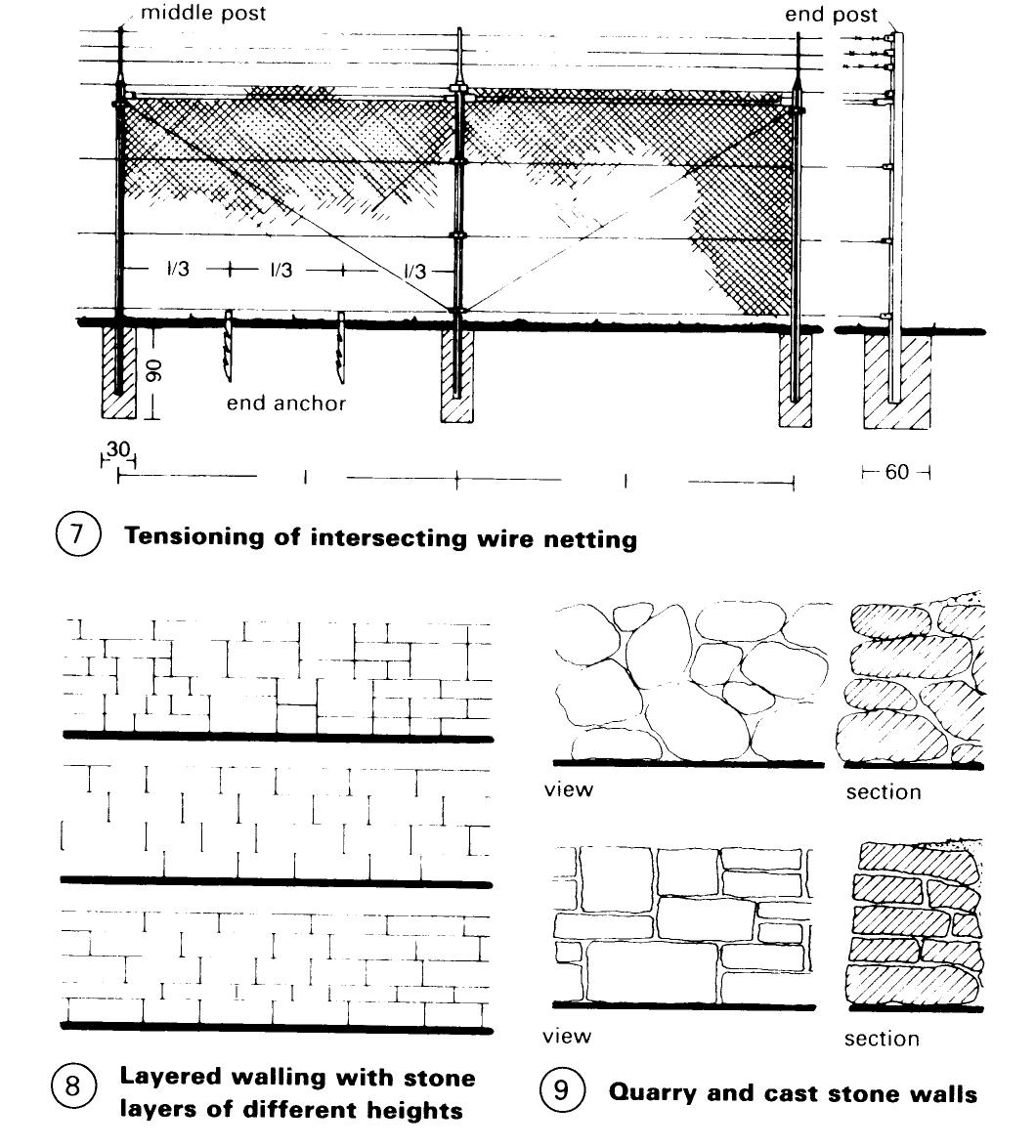
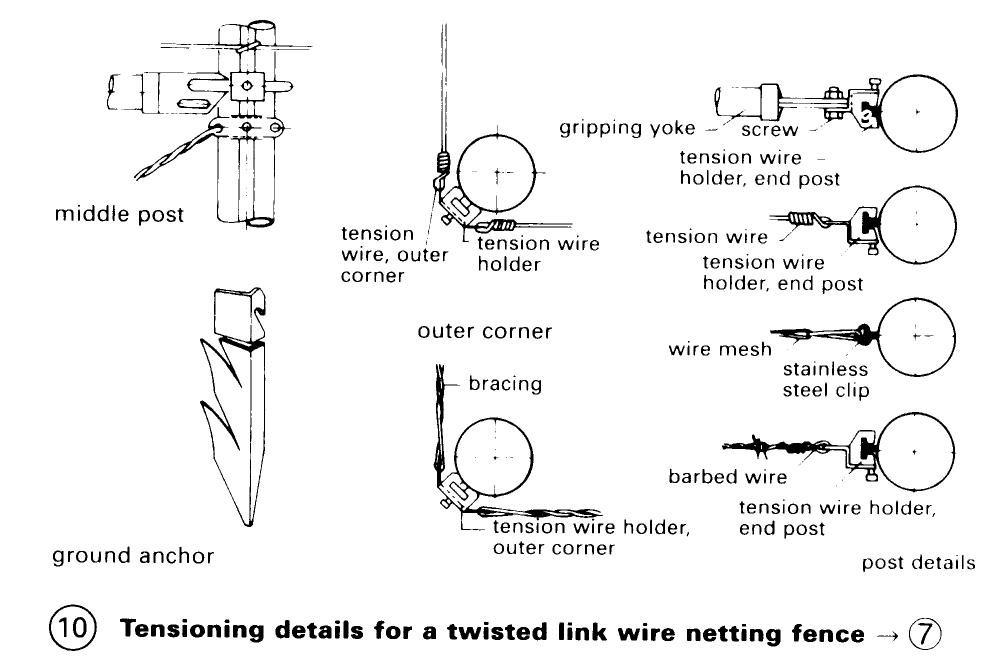
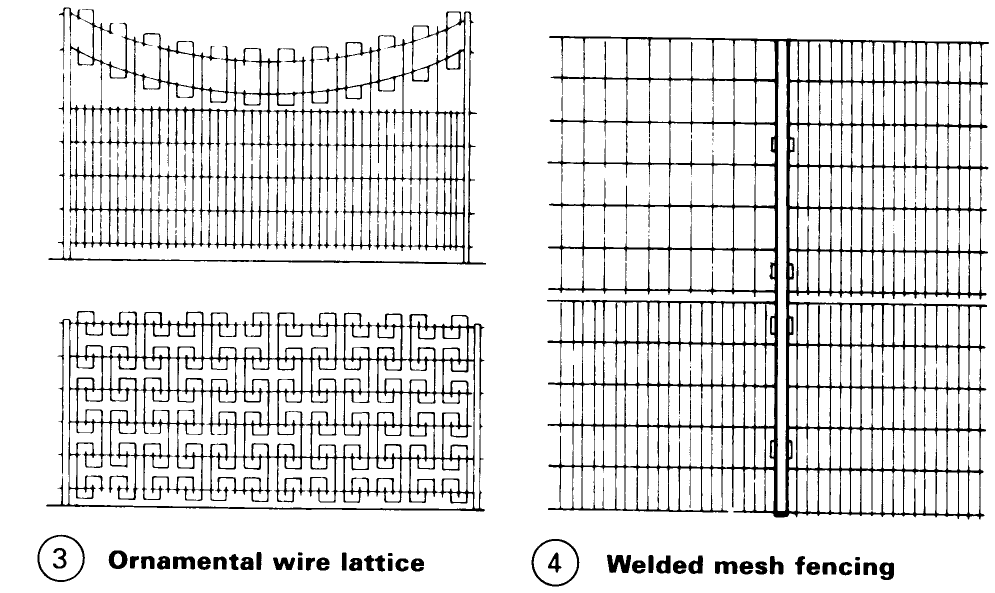
Wire mesh fencing – (1) can be obtained in many mesh sizes to cover a wide range of usage conditions and if the mesh is plastic coated and supported by galvanised posts the fence will require close to no maintenance. Mesh fences can be braced with wooden, concrete or steel posts which are anchored in the ground – (7) + (10). Ornamental wire or lattice fencing is usually spot-welded and galvanized – (3) – (4).
Wrought-iron fencing can be elaborate or simple in design and almost any shape is possible - (6).
Natural stone such as granite or quartz quarry stone can be used without any processing - (9) or cut to shape by a stonemason – (8). If possible, only one sort of stone should be used.
Date added: 2023-01-05; views: 638;
