Stairs. Wet Rooms and Bathrooms. Guidelines for Road Noise Shielding
In early times the sizing of load-bearing floor beams in old buildings was calculated empirically by the carpenter. The loads are normally carried by cross-beams which are supported by one or more longitudinal joists.
An old building manual from 1900 gives a ratio of 5:7 for the height and the width of a beam as a starting point for the determination of the required beam strength. Another rule of thumb held that the beam height in cm should be approximately half the size of the room depth in decimetres. Because of these methods, old wooden beam floors often display significant sagging. However, this does not endanger the structural stability as long as the permitted tensions are not exceeded.
There are several options when carrying out renovation work: for example, joists can be strengthened by adding a second wooden beam and an improvement in load distribution can be achieved with the installation of additional floor beams or steel girders – (1) – (4).
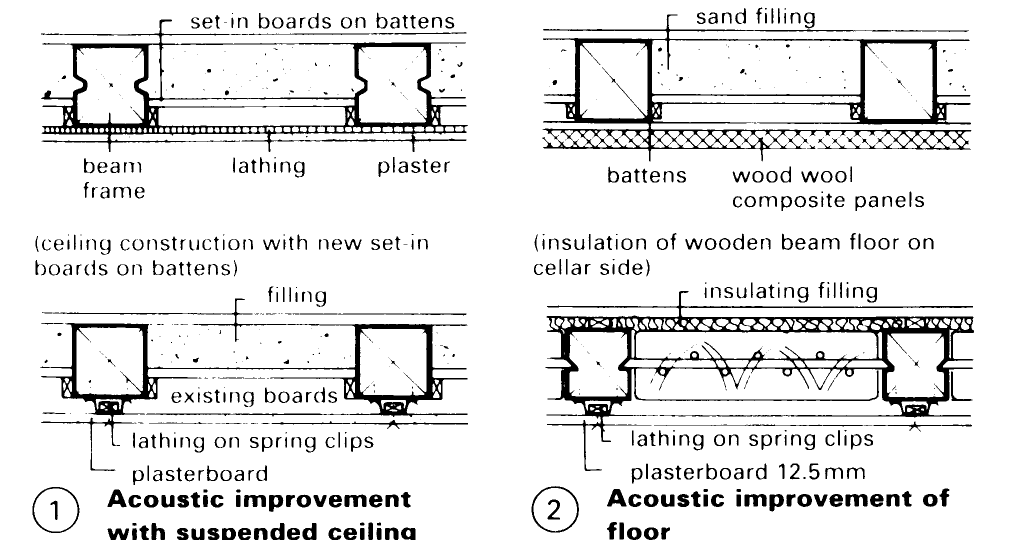
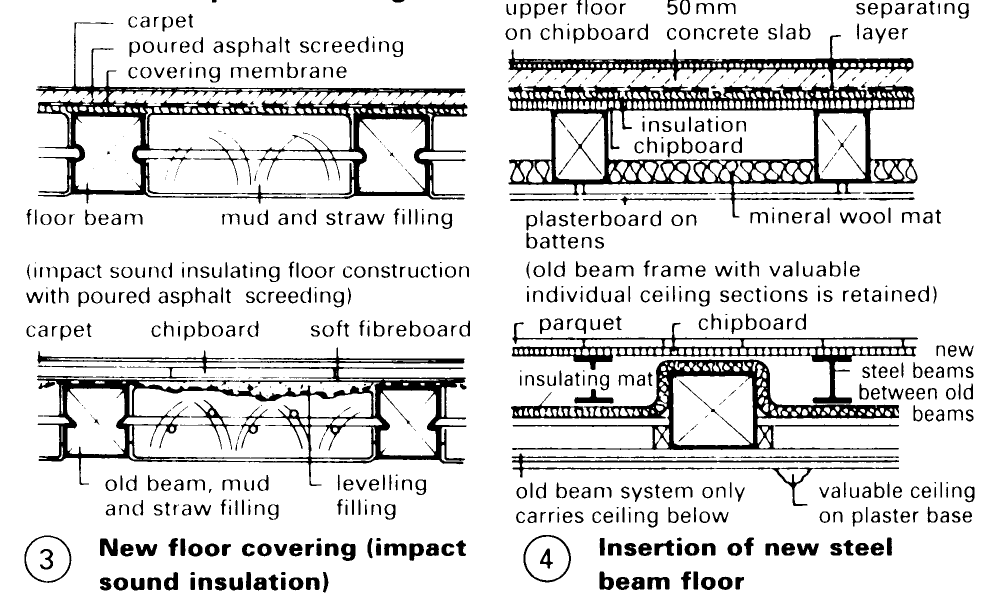
In addition, the span can be shortened by installing one or more additional joists or a supporting cross-wall. However, structural changes of the framework must be preceded by an accurate analysis of all load-carrying and stiffening functions and the integrity of all connections must be checked thoroughly.
Stairs. External and internal stairs are significant structural features in old buildings. If the stairs are in poor condition remember the most important rule for repairs is: repair only what can be repaired (1) - (4).
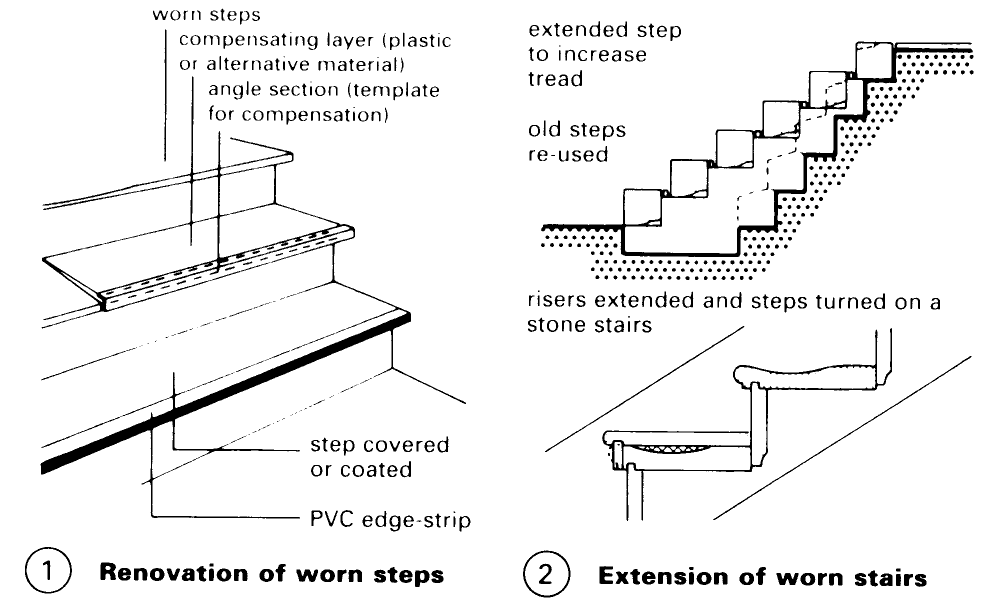
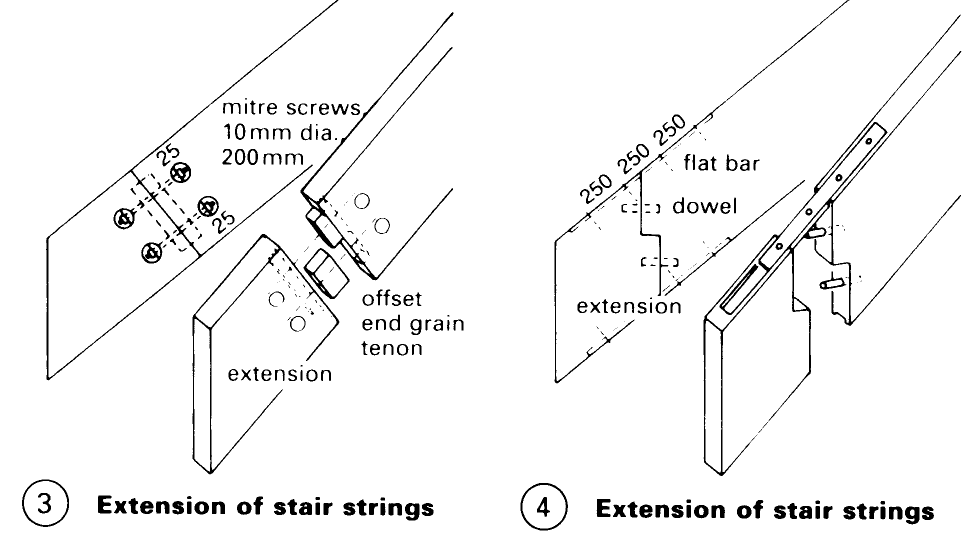
External stairs are mostly made of natural stone and normally serve to reach floor levels on plinths - (2). Worn-down stone steps can sometimes be restored if they are reversed and dressed underneath.
There are many types of design and materials used for internal stairs although the most common material used is wood.
Wet Rooms and Bathrooms. Improvement in sanitary facilities is one of the most important modernisation tasks. Planning of the new solutions should be highly sympathetic to the existing layout and then coordinated with the technical necessities – (5) – (9).
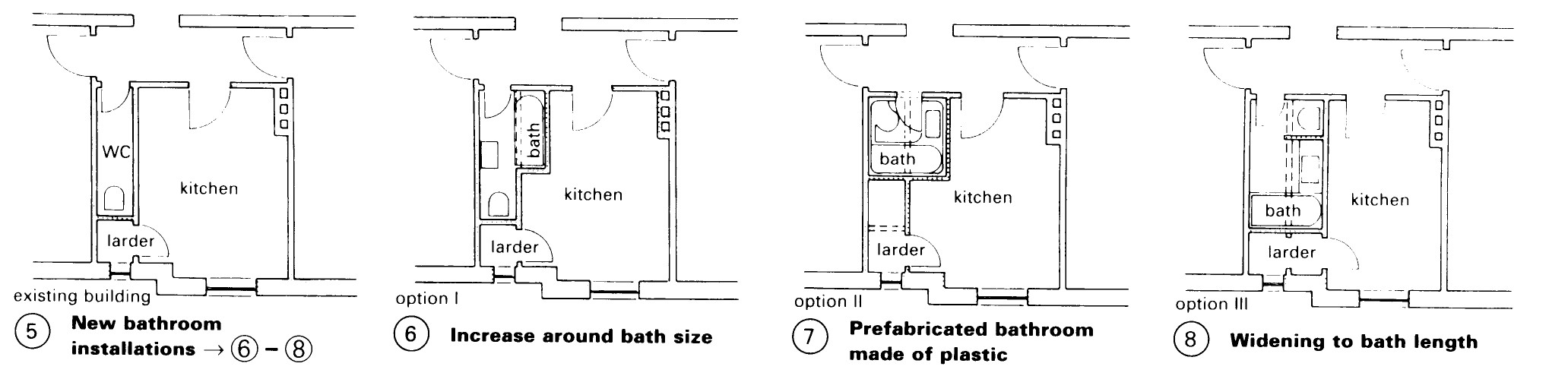
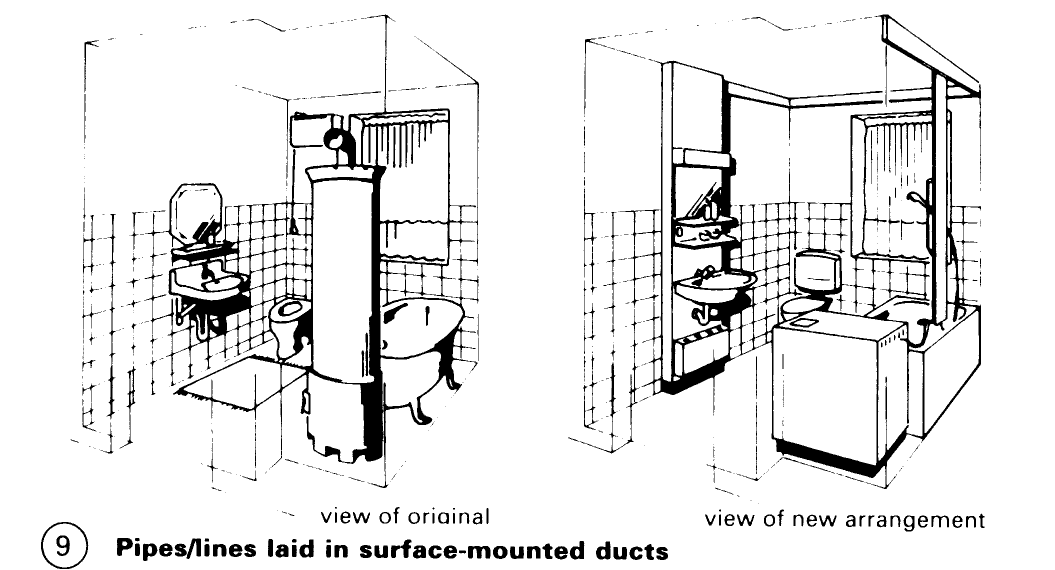
Walls and floors must be planned and installed with care. The most serious damage to be avoided is that associated with leaks around showers and baths – (12) – (14).
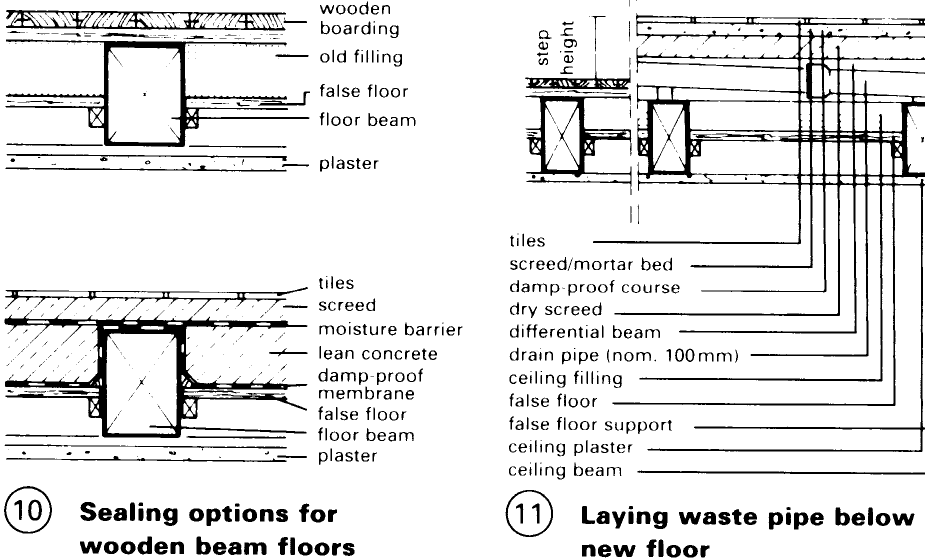
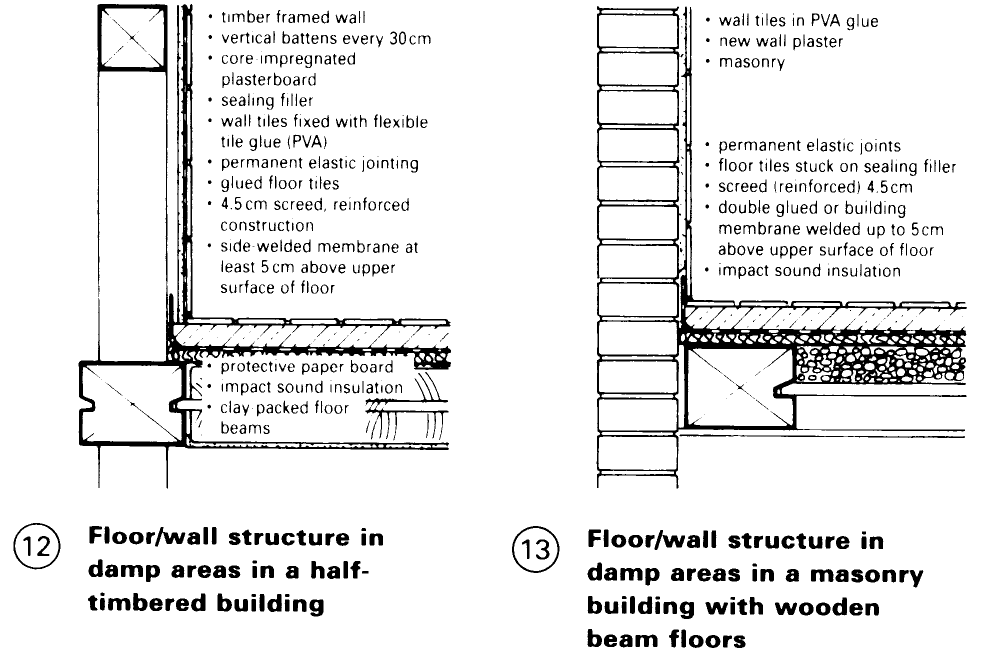
Faulty or missing vapour barriers mainly on outer walls with internal insulation can also lead to condensation forming in the structure. This is a major cause of rot and the incidence of mould.
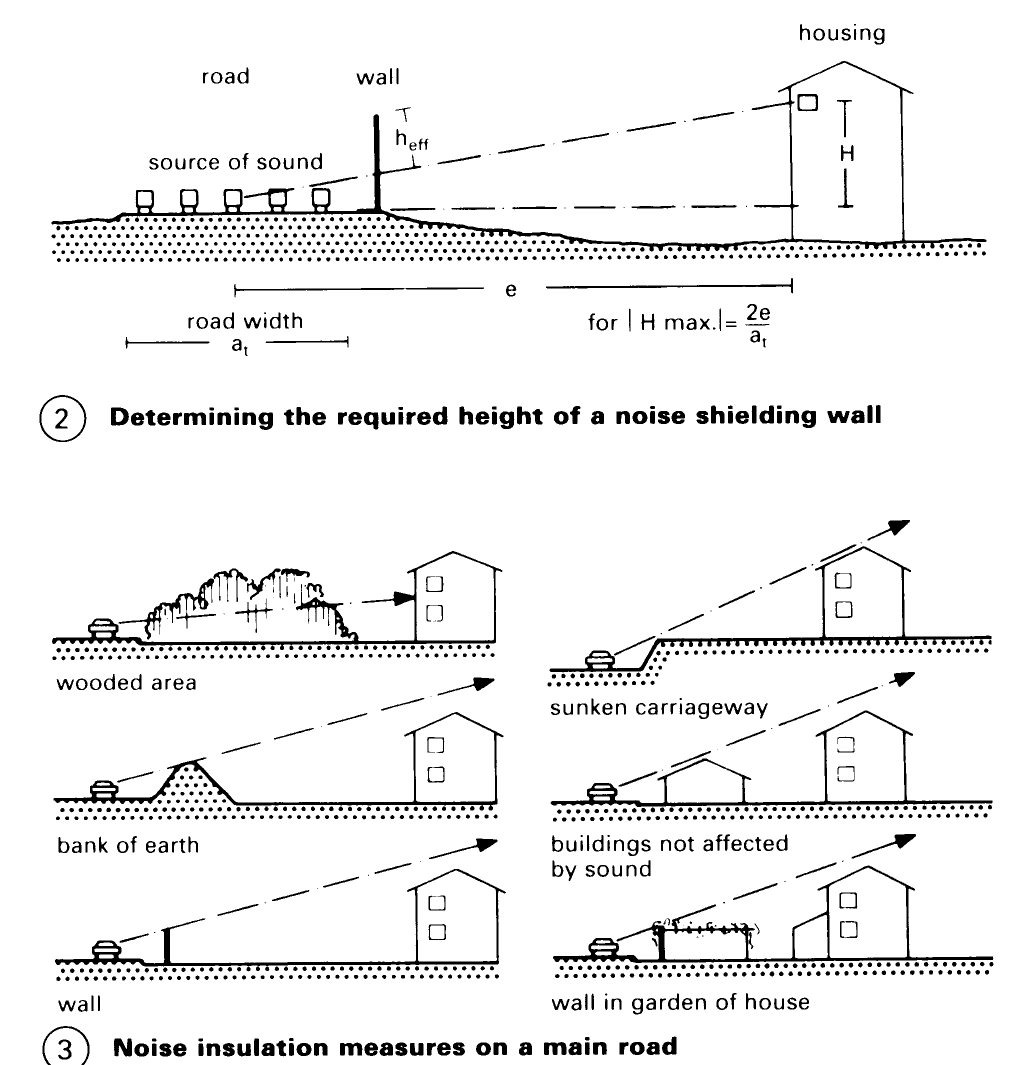
Guidelines for Road Noise Shielding. Increased environmental concerns have made reduction of traffic noise a top priority. Effective measures include earth mounds and noise shielding walls and pyramids — (1) - (7).
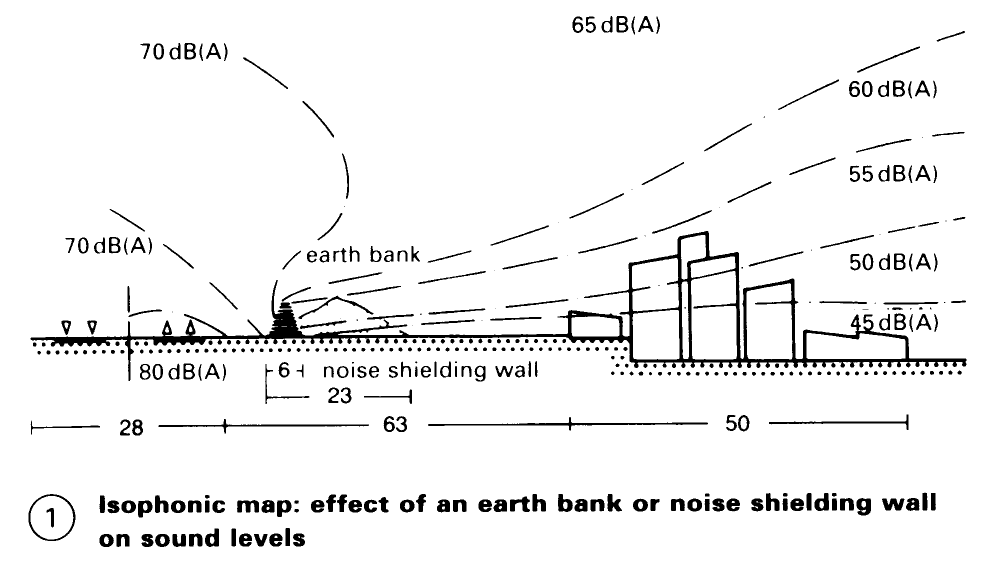
There are many suitable pre-cast concrete products on the market today as well as sound insulating walls made from glass, wood and steel.
The sound level of road traffic can be reduced by >25 dB(A) after passing through a noise shielding wall. (With a reduction of 10 dB(A), the sound seems half as loud.)
The shielding effect is dependent on the wall material but far more so on its height. This is because refraction bends the path of the sound waves so a small part of the sound energy arrives in the shadow area. The higher the wall the lower the amount of sound penetration, and the longer the detour for the refracted sound.
Date added: 2023-01-05; views: 604;
