Water, Oil and Natural Gas Wells
Well is a hole in the earth from which a fluid is with-drawn. Water wells are the most common type. Oil and natural gas wells are also common. Mining companies also pump steam and hot water down wells to remove salt and sulfur from deep in the ground.
Scientists and engineers use seismographs and other equipment to locate underground deposits of oil or water (see Seismograph). They then determine at what rate they can take these materials out of the ground. They also decide how much they can remove without damaging the natural resources.
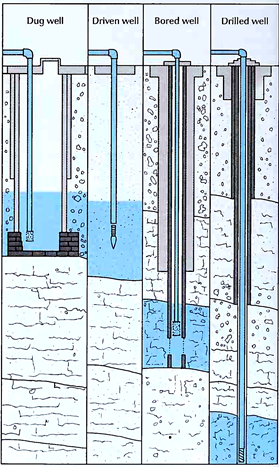
Kinds of water wells. Water wells may be dug, driven, bored, or drilled. Dug wells can be constructed with hand tools or power tools. They measure up to 50 feet (15 meters) deep and have the greatest diameter of any water well. Driven wells consist of a series of pipes with a point at one end. The point is driven into the ground to a depth of up to 50 feet (15 meters). Bored wells, which are constructed with tools called augers, may be up to 100 feet (30 meters) deep. Drilled wells are constructed with special well-drilling equipment. They measure up to 1 ,000 feet (300 meters) deep
Water wells. The underground water that flows into wells is called ground water (see Ground water). Most of this water comes from rain that soaks into the ground and slowly moves down to the ground water reservoir, an area of soil and rock saturated with water. The top of this zone is the water table, the level at which water stands in a well that is not being pumped.
In damp places, the water table may lie just below the surface. It is easily reached by digging. A dug well is usually lined with bricks, stone, or porous concrete to keep the sides from caving in. In drier places, the water table may be hundreds of feet or meters down. It may be necessary to drill the well and sink pipes. Power-driven pumps usually draw the water out of deep wells.
In some areas, underground water moving down from the slopes of hills and mountains becomes trapped under watertight layers of clay or shale. Wells drilled through these layers in valleys and plains run into water under pressure. Such wells are called flowing artesian wells. See Artesian well.
Many people depend on wells for their water supply, especially in rural areas. Underground water is usually pure, because soil makes a good filter. This water generally contains dissolved minerals. A well that taps water with a high mineral content is called a mineral well.
Water wells should be located so that they do not collect poisons or disease germs. A well should be at least 100 feet (30 meters) from a cesspool and should never be located so that sewage drains toward it. Water from a well sunk through limestone may be dangerous because water runs through crevices and caves in limestone without being filtered. It is also important that surface water does not drain into a well.
Oil and natural gas wells. Oil and natural gas are lighter than water. Because of this, they would normally float upward and escape from the ground. But oil and gas become trapped beneath thick beds of rock in areas called reservoirs. Wells penetrate deep into the earth to reach these reservoirs and bring the oil and gas to the surface. Wildcat wells a.re drilled in search of reservoirs. A production well is drilled into a proven field.
Date added: 2023-05-02; views: 706;
