Brain. The structure of the human brain. Interesting facts about the brain
Brain is the master control center of the body. The brain constantly receives information from the senses about conditions both inside the body and outside it. The brain rapidly analyzes this information and then sends out messages that control body functions and actions. The brain also stores information from past experience, which makes learning and remembering possible. In addition, the brain is the source of thoughts, moods, and emotions.
In such simple animals as worms and insects, the brain consists of small groups of nerve cells. All animals with a backbone have a complicated brain made up of many parts. Animals that have an exceptionally well developed brain include apes, dolphins, and whales. Human beings have the most highly developed brain of all. It consists of billions of interconnected cells and enables people to use language, solve difficult problems, and create works of art.
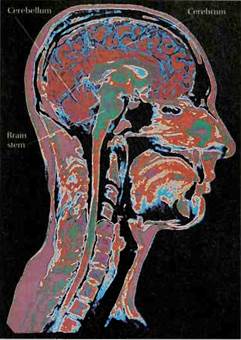
The structure of the human brain is revealed in remarkable detail by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This Image through the center of the head shows the brain's three main regions—the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brain stem.
The human brain is a grayish-pink, jellylike bail with many ridges and grooves on its surface. A newborn baby's brain weighs less than 1 pound (0.5 kilogram). By the time a person is 6 years old, the brain has reached its full weight of about 3 pounds (1.4 kilograms).
Most of the brain's nerve cells are present at birth. The increase in weight comes mostly from the growth of nerve cells, development and growth of supporting cells, and development of connections among cells. During this six-year period, a person learns and acquires new behavior patterns at the fastest rate in life.
A network of blood vessels supplies the brain with the vast quantities of oxygen and food that it requires. The human brain makes up only about 2 percent of the total body weight, but it uses about 20 percent of the oxygen used by the entire body when at rest. The brain can go without oxygen for only three to five minutes before serious damage results.
The brain is at the upper end of the spinal cord. The spinal cord is a cable of nerve cells that extends from the neck about two-thirds of the way down the backbone. The spinal cord carries messages between the brain and other parts of the body. In addition, 12 pairs of nerves connect the brain directly with certain parts of the body. For more information about the nervous system and the brain's place in it, see Nervous system.
The brain works in some ways like both a computer and a chemical factory. Brain cells produce electrical signals and send them from cell to cell along pathways called circuits. As in a computer, these circuits receive, process, store, and retrieve information. Unlike a computer, however, the brain creates its electrical signals by chemical means. The proper functioning of the brain depends on many complicated chemical substances produced by brain cells.
Scientists in various fields work together to study the structure, function, and chemical composition of the brain. This field of study, called neuroscience or neurobiology, is rapidly increasing our understanding of the brain. But much remains to be learned. Scientists do not yet know how physical and chemical processes in the brain produce much of the brain's activity.
This article deals chiefly with the human brain. The last section of the article briefly discusses the brain in various kinds of animals.
Interesting facts about the brain:
- During the embryonic period of human development, the brain is formed and develops much more quickly than other internal organs or limbs.
- Your brain had reached its full weight of about 3 pounds (1.4 kilograms) by the time you were 6 years old.
- The left side of your brain controls movements on the right side of your body, and the right side of your brain controls movements on the left side of your body.
- Chimpanzees have the largest brains, In relation to their body weight, of any animals except for human beings.
- The brain does not feel pain directly because it has no pain receptors. As a result, doctors can perform some types of brain surgery on patients who are conscious.
- Brain cells begin to die if they are deprived of oxygen for three to five minutes.
- A study of German-born physicist Albert Einstein's brain revealed that while the overall size was average, a portion of his brain related to mathematical ability was about 15 percent larger than average. Scientists think this key difference may explain the great physicist's genius.
- Scientists do not completely understand why people dream. They think dreaming may help the brain restore its ability to focus attention, to remember, and to learn.
- The brain requires about 20 percent of the body’s oxygen supply though it makes up only about 2 percent of a person's total body weight.
- Your brain is as individual as your face. Everyone's brain has the same physical features, but no brain looks exactly like any other brain.
Date added: 2023-08-28; views: 701;
