Examination of Children and Adolescents Using the Panoramic Radiograph
The prevalence of dental diseases has decreased in recent years because of the effect of dental preventive measures. Bite-wing radiographs are indicated for detection of coronal caries but they are not suitable for the examination of the jaws. The method of choice today to examine the jaws for anomalies and pathologic processes is panoramic radiography, and should be performed at a minimum during the 9th, 15th and the 20th years of life.
Summarized simply, the following developmental anomalies can be expected in children and adolescents:
- Disturbance of the normal developmental morphogenic processes of the bony structures of the jaw, including the temporomandibular joints in early childhood as well as during the course of the first and second decades of life, with formation of typical tumors and tumor-like lesions
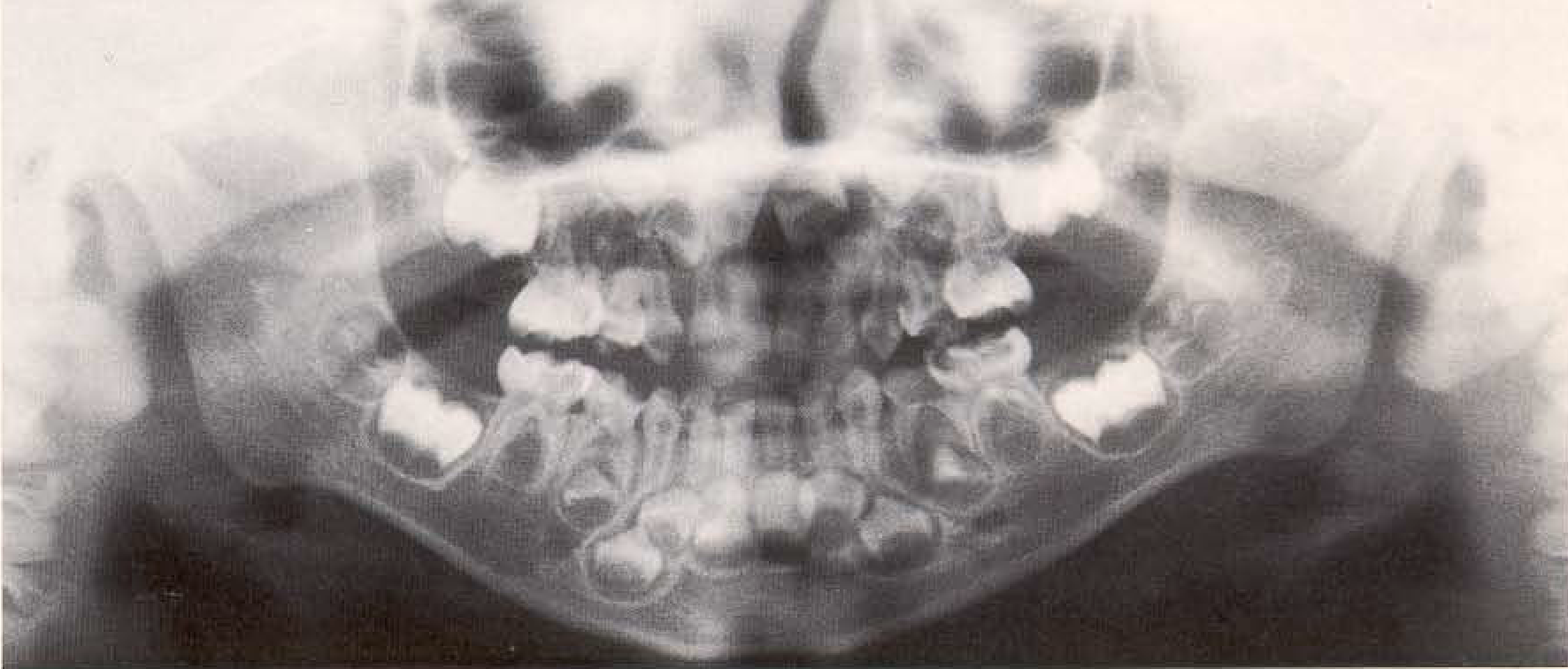
Panoramic radiograph of a 3 ½ -year-old girl with deciduous dentition. While the formation of the crowns of the first permanent molars is complete, formation of the cusps of the second molars has only begun
- Improper development of the dental structures during the growth-intensive mixed dentition stage, with congenitally missing or supernumerary teeth as well as formation of typical odontogenic cysts and tumors, especially in the second decade of life.
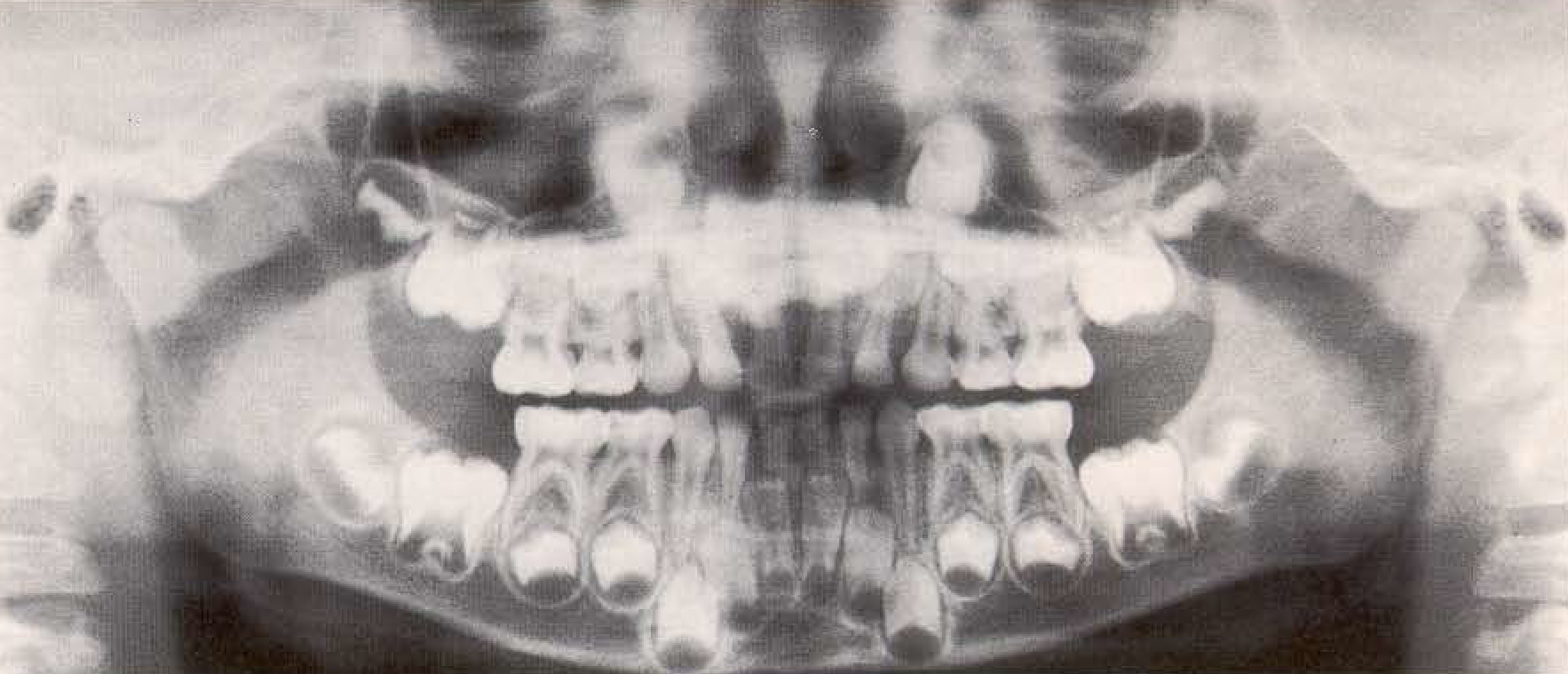
Panoramic radiograph of a 5-year-old boy with deciduous dentition. While root formation of the first permanent molars, the incisors and the canines is already in process, the formation of the crowns of the second permanent molars is not yet complete. Clearly visibleare the maxillary sinuses
- Dysgnathia
- Systemic disease
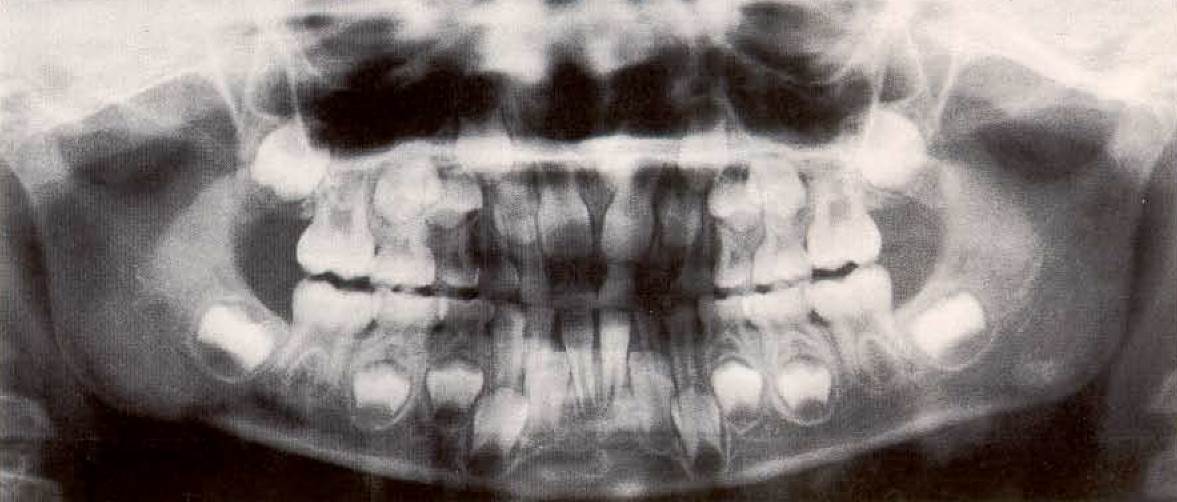
Panoramic radiograph of a 6-year-old girl in early mixed dentition stage. The first permanent molars and partially also the incisors have erupted; root formation is almost complete. The articular process has obviously begun to elongate
Specific dental diseases and inflammatory processes in the jaws may also play additional roles. The selection of panoramic radiographs presented here derived from a 3V2-year-old child to an 18-year- old adolescent. These films depict the development of the teeth and the maxillofacial structures in the facial skeleton of young persons. Of special note is the development of the maxillary sinus in the skull of early childhood, as well as the development of the ascending ramus of the mandible and the formation of the temporomandibular joints.
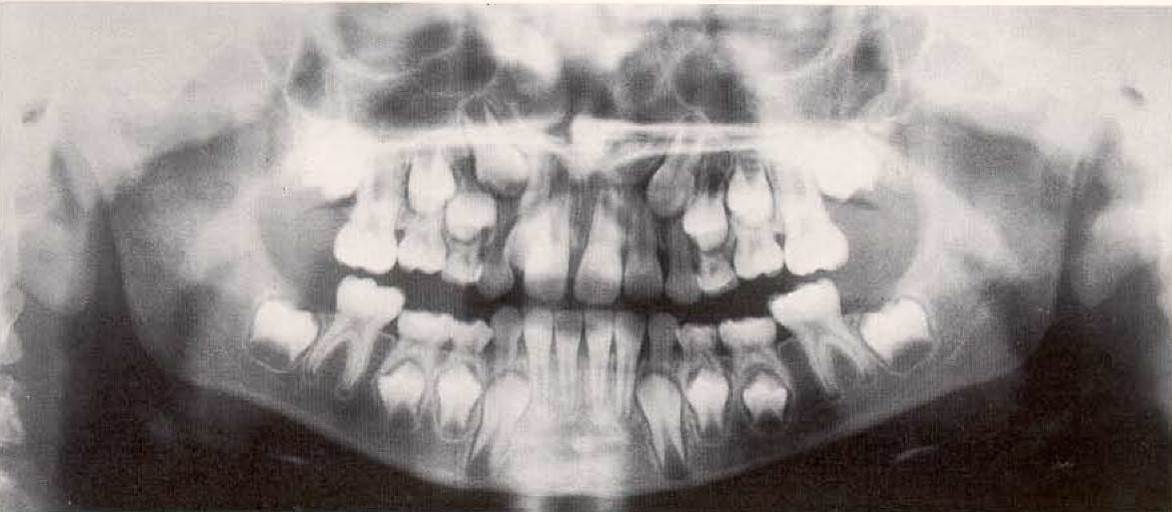
Panoramic radiograph of an 8-year-old girl in the mixed dentition stage. The apices of the roots of the first permanent molars are forming. Root formation of the other permanent teeth is progressing

Panoramic radiograph of a 10-year-old girl in the mixed dentition stage. The formation of the apical foramina of the roots of the first permanent molars is complete. The crowns of the extremely variable third molars are visible
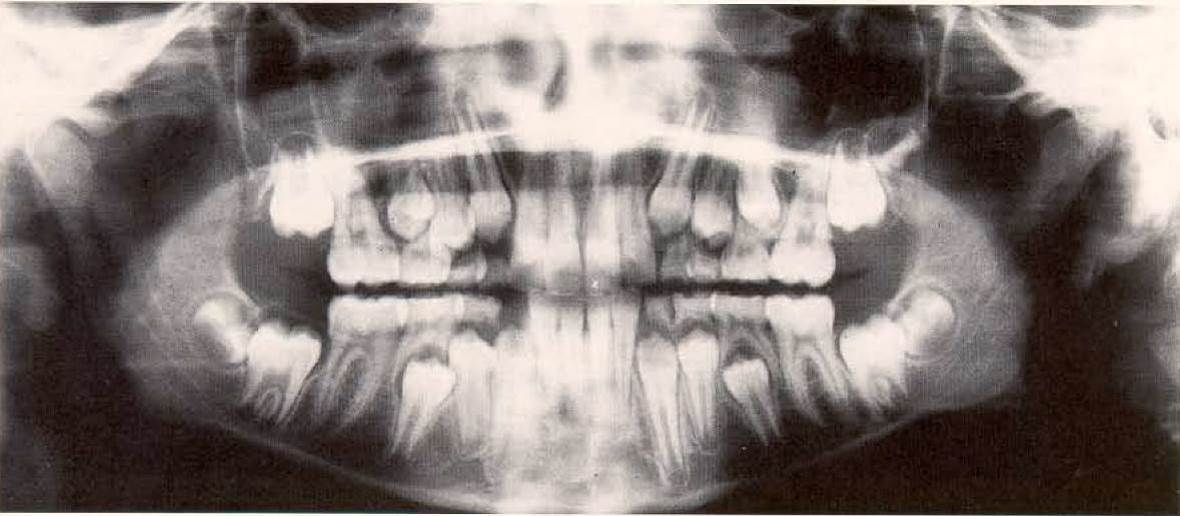
Panoramic radiograph of a 12-year-old girl in the mixed dentition stage. The deciduous canines and the deciduous molars are being resorbed by the erupting permanent teeth. The second permanent molars are erupting. The condyles no longer exhibit the round shape characteristic of children

Panoramic radiograph of a 14-year-old male with permanent dentition. The roots of the permanent teeth and most of the apical foramina have formed
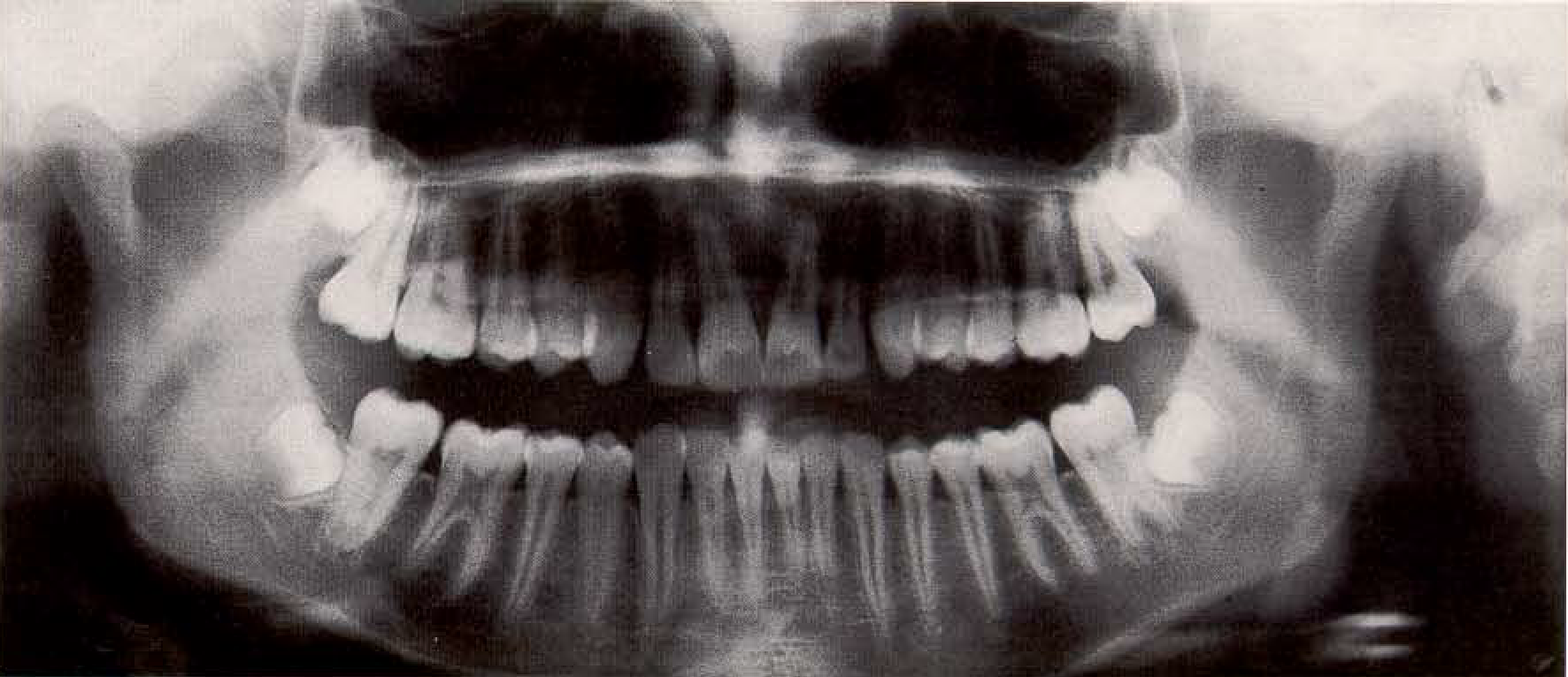
Panoramic radiograph of a 16-year-old female with permanent dentition. The root canals of the most recently erupted teeth are becoming narrower. The extremely variable third molars appear in various stages of development

Panoramic radiograph of an 18-year-old male with fully developed permanent dentition
Diagram of Formation and Eruption of the Deciduous Teeth. The eruption of the deciduous teeth occurs according to the following time sequence:

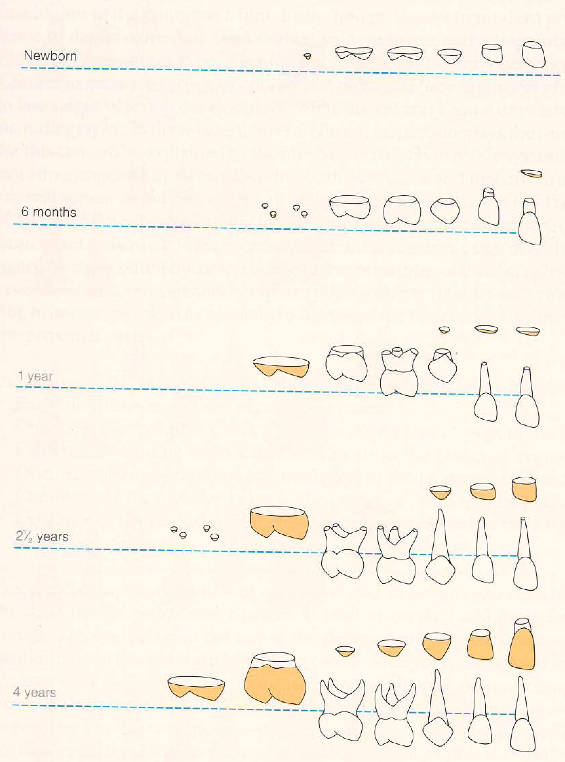
Formation and eruption of the deciduous teeth of the maxilla. The eruption times of the deciduous teeth in the mandible are very close to their maxillary analogues
Diagram of the Formation and Eruption of the Permanent Teeth. The eruption of the permanent teeth usually occurs according to the following time sequence:


Formation and eruption of the permanent teeth of the maxilla. The eruption times of the mandibular permanent teeth are similar to their maxillary analogues.
Date added: 2022-12-17; views: 694;
