Image Enhancement and Restoration
In image enhancement, the purpose is to process an acquired image to improve the contrast and visibility of the features of interest. The contrast and visibility of images actually depend on the imaging modality and on the nature of the anatomical regions. Therefore, the type of image enhancement to be applied has to be suitably chosen.
Image restoration also leads to image enhancement, and generally, it involves mean-squared error operations and other methods that are based on an understanding of the type of degradation inherent in the image. However, procedures that reduce noise tend to reduce the details, whereas those that enhance details also increase the noise. Image enhancement methods can be broadly classified into two categories: spatial-domain methods(H) and frequency-domain methods.
Spatial-domain methods involve manipulation on a pixel-to-pixel basis and include histogram-based methods, spatial filtering, and so on. The histogram provides information about the distribution of pixel intensities in an image and is normally expressed as a 2-D graph that provides information of the occurrence of specific gray-level pixel values in the image.
Histogram equalization is a commonly used technique that involves ‘‘spreading out’’ or “stretching” the gray levels to ensure that the gray levels are redistributed as evenly as possible. Minor variations in structures or features are better visualized within regions that originally looked uniform by this operation. Figure 6 shows the result of applying histogram equalization to a CT image.
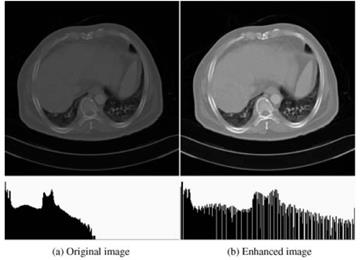
Figure 6. CT images of the liver and the associated histograms: (a) original image and (b) enhanced image
In some instances, however, global equalization across all possible pixel values could result in loss of important details and/or high-frequency information. For such situations, local histogram modifications, including localized or regional histogram equalization, can be applied to obtain good results.
In spatial-domain methods, pixel values in an image are replaced with some function of the pixel and its neighbors. Image averaging is a form of spatial filtering where each pixel value is replaced by the mean of its neighboring pixels and the pixel itself. Edges in an image can be enhanced easily by subtracting the pixel value with the mean of its neighborhood. However, this approach usually increases the noise in the image. Figure 7 shows the results of applying local spatial-domain methods.
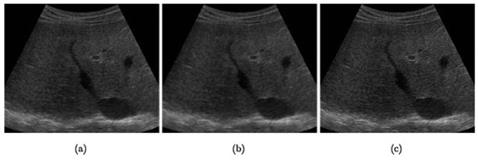
Figure 7. Ultrasound images of liver. (a) Original image. (b) The result of image averaging where the image becomes smoother. (c) The image of edge enhancement where the image becomes sharper but with increased noise levels
Frequency-domain methods are usually faster and simpler to implement than spatial domain methods. The processing is carried out in the Fourier domain for removing or reducing image noise, enhancing edge details, and improving contrast. A low-pass filter can be used to suppress noise by removing high frequencies in the image, whereas a high-pass filter can be used to enhance the high frequencies resulting in an increase of detail and noise. Different filters can be designed to selectively enhance or suppress features or details of interest.
Date added: 2024-03-07; views: 570;
